Mnemonics: Pastoralists in the Modern World | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
1. Characteristics of Nomads
Mnemonic: “Moving Herds Feed, Barter Smartly”
- Moving → Mobile lifestyle (Nomads move for livelihood, not randomly, with territorial awareness)
- Herds → Animal rearing (Depend on goats, sheep, camels, buffaloes)
- Feed → Food from grains (Consume wheat, rice, bajra, maize, some self-grown)
- Barter → Barter economy (Exchange animals for food/grains, some use money)
- Smartly → Selective animals (Choose animals based on prestige, climate, vegetation, e.g., camels in deserts)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase paints a picture of nomads moving with herds, feeding on grains, bartering smartly, and selecting animals wisely. It covers the key characteristics: mobility, animal rearing, grain-based diet, barter system, and selective animal choice, making them memorable through a vivid narrative.
How to Use: Visualize nomads moving herds, eating grains, and bartering smartly with chosen animals. Link each word to its characteristic (e.g., “Moving” = Mobile lifestyle). Test by recalling: mobile lifestyle, animal rearing (goats, camels), grain diet (wheat, rice), barter economy, selective animals (camels, sheep).
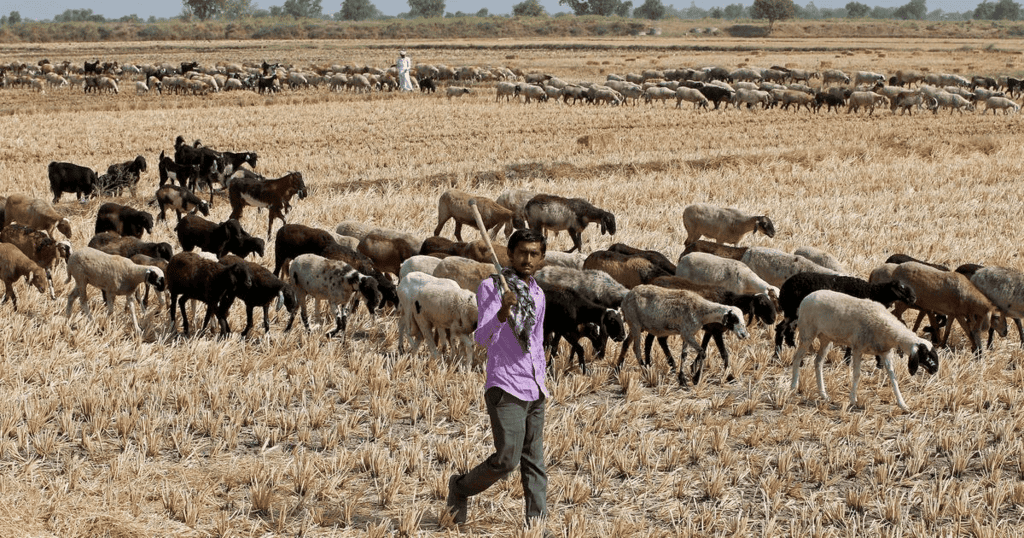

2. Pastoral Nomad Groups in India
Mnemonic: “Gujjars Graze, Gaddis Climb, Dhangars Roam, Gollas Weave, Banjaras Trade, Raikas Herd”
- Gujjars → Gujjar Bakarwals (J&K, winter in Siwalik, summer in Kashmir pastures)
- Graze → (Reinforces Gujjars’ goat/sheep grazing)
- Gaddis → Gaddi shepherds (Himachal, winter in Siwalik, summer in Lahul/Spiti, harvest crops)
- Climb → (Reinforces Gaddis’ mountain movement)
- Dhangars → Dhangars (Maharashtra, monsoon in plateau, migrate to Konkan, manure fields)
- Roam → (Reinforces Dhangars’ migration)
- Gollas → Gollas/Kurumas/Kurubas (Karnataka/Andhra, cattle/sheep herders, weave blankets, move to coast)
- Weave → (Reinforces Kurumas/Kurubas’ blanket weaving)
- Banjaras → Banjaras (UP, Punjab, Rajasthan, MP, Maharashtra, trade cattle/goods)
- Trade → (Reinforces Banjaras’ trading)
- Raikas → Raikas (Rajasthan, Maru Raikas herd camels, others sheep/goats, migrate post-monsoon)
- Herd → (Reinforces Raikas’ herding)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase creates a vivid sequence of Indian pastoral groups grazing, climbing, roaming, weaving, trading, and herding. Each group (Gujjars, Gaddis, Dhangars, Gollas/Kurumas/Kurubas, Banjaras, Raikas) is paired with an action reflecting their lifestyle, making their regional and seasonal patterns memorable.
How to Use: Picture Gujjars grazing, Gaddis climbing mountains, Dhangars roaming, Gollas weaving, Banjaras trading, and Raikas herding. Link each word to its group (e.g., “Gujjars Graze” = Gujjar Bakarwals). Test by recalling: Gujjars (J&K, Siwalik-Kashmir), Gaddis (Himachal, Siwalik-Lahul), Dhangars (Maharashtra, Konkan), Gollas/Kurumas/Kurubas (Karnataka, coastal migration), Banjaras (trade), Raikas (Rajasthan, camel/sheep).
3. Colonial Impacts on Pastoralists in India
Mnemonic: “Wasted Forests Taxed, Criminalized Settlements”
- Wasted → Waste Land Rules (Converted grazing lands to farms, shrank pastures)
- Forests → Forest Acts (Reserved/protected forests, restricted grazing access)
- Taxed → Grazing Tax (Taxed per animal, auctioned to contractors, later direct collection with passes)
- Criminalized → Criminal Tribes Act (1871) (Classified nomads as criminals, restricted movement)
- Settlements → Settlement Policies (Promoted settled life, distrusted nomads)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase depicts colonial policies wasting grazing lands, restricting forests, taxing herds, criminalizing nomads, and forcing settlements. It covers the major impacts: Waste Land Rules, Forest Acts, Grazing Tax, Criminal Tribes Act, and settlement policies, with vivid imagery for recall.
How to Use: Visualize colonial officials wasting pastures, blocking forests, taxing herds, criminalizing nomads, and pushing settlements. Link each word to its policy (e.g., “Wasted” = Waste Land Rules). Test by recalling: Waste Land Rules (farms), Forest Acts (restricted forests), Grazing Tax (per animal), Criminal Tribes Act (criminalized), Settlement Policies (settled life).
4. Pastoralists’ Coping Strategies
Mnemonic: “Shrink Herds, Seek Pastures, Settle, Borrow, Diversify”
- Shrink → Reduce herd size (Fewer animals due to limited pastures)
- Herds → (Reinforces focus on livestock)
- Seek → Explore new pastures (Find alternative grazing areas, e.g., Raikas post-1947)
- Pastures → (Reinforces new grazing grounds)
- Settle → Shift to sedentary life (Wealthier pastoralists bought land, became peasants/traders)
- Borrow → Financial adaptations (Poor pastoralists borrowed from moneylenders)
- Diversify → Adaptation and diversification (Combined pastoralism with other income sources)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase shows pastoralists shrinking herds, seeking pastures, settling, borrowing, and diversifying to cope with challenges. It covers the five coping strategies, with a clear narrative of adaptation, making it more engaging than a list.
How to Use: Picture pastoralists shrinking herds, seeking new pastures, settling down, borrowing money, and diversifying work. Link each word to its strategy (e.g., “Shrink” = Reduce herd size). Test by recalling: reduce herds, new pastures, sedentary life, borrowing, diversification.
5. Pastoralism in Africa (Maasai Focus)
Mnemonic: “Maasai Lose Grazing, Borders Trap, Droughts Starve”
- Maasai → Maasai pastoralists (Lost 60% of lands, confined to arid reserves)
- Lose → Land loss (Colonial partition, white settlements, game reserves like Serengeti)
- Grazing → Grazing lands gone (Converted to farms, reserves, caused overgrazing)
- Borders → Closed borders (Confined to reserves, needed permits, restricted trade)
- Trap → (Reinforces confinement’s impact)
- Droughts → Drought effects (Cattle starved, worsened by limited grazing lands)
- Starve → (Reinforces livestock losses, e.g., 1933–34 Maasai cattle deaths)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase depicts the Maasai losing grazing lands, trapped by borders, and facing droughts that starve cattle. It covers key African pastoralism challenges: land loss, colonial restrictions, reserve confinement, trade bans, and drought impacts, with a vivid narrative for recall.
How to Use: Visualize Maasai losing lands, trapped by borders, and cattle starving in droughts. Link each word to its concept (e.g., “Lose” = Land loss). Test by recalling: Maasai (land loss), grazing lands gone (farms/reserves), closed borders (reserves, permits), droughts (cattle losses).
|
63 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Pastoralists in the Modern World - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What are the main characteristics of nomads? |  |
| 2. Which pastoral nomad groups can be found in India? |  |
| 3. How did colonial rule impact pastoralists in India? |  |
| 4. What coping strategies do pastoralists employ to adapt to challenges? |  |
| 5. How does pastoralism manifest in Africa, specifically regarding the Maasai? |  |
















