Mnemonics: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
1. Sorrieu’s Vision (Democratic and Social Republics)
Mnemonic: "SORRIEU"
Interpretations:
S: Social and democratic republics envisioned
O: Overthrow of absolutist institutions
R: Representation of nations through flags
R: Revolutionaries marching in procession
I: Illustration of liberty as a female figure
E: Enlightenment torch symbolizes freedom
U: United aspirations for democracy
Explanation:
Social and democratic republics were imagined by Sorrieu. The Overthrow of absolutist institutions was shown through shattered symbols. Representation of different nations was depicted via flags, while Revolutionaries marched in a grand procession. Liberty was Illustrated as a female figure holding the Enlightenment torch, symbolizing freedom. The United aspirations of various nations reflected the growing demand for democracy.
 The Pact Between Nations, a print prepared by Frederic Sorrieu, 1848
The Pact Between Nations, a print prepared by Frederic Sorrieu, 1848
2. French Revolution & Nationalism
Mnemonic: "FRENCH"
Interpretations:
F: Fatherland (La Patrie) and citizen (Le Citoyen)
R: Rights of man and national identity formation
E: Estates General became National Assembly
N: National symbols like tricolor flag emerged
C: Centralized administration with common laws
H: Hymns, oaths, and commemorations promoted unity
Explanation:
The French Revolution introduced the concept of the Fatherland (La Patrie) and Citizen (Le Citoyen), fostering a collective identity. The Rights of man were emphasized, and the Estates General was transformed into the National Assembly. National symbols like the tricolor flag were adopted. A Centralized administration with uniform laws strengthened governance, while Hymns and national celebrations reinforced unity.
3. Making of Nationalism in Europe
Mnemonic: "NATION"
Interpretations:
N: No single nation-state existed initially
A: Austria-Hungary and other empires ruled over diverse groups
T: Territories lacked common identity and political unity
I: Increasing nationalist movements aimed for self-rule
O: Overlapping cultures made unity challenging
N: New nation-states emerged after struggles
Explanation:
Before nationalism, No single nation-state existed in Europe. Austria-Hungary and other large empires controlled various ethnic groups. Territories lacked common identity, making political unity difficult. Increasing nationalist movements sought self-rule. Overlapping cultures complicated unification, but after years of struggle, New nation-states eventually emerged.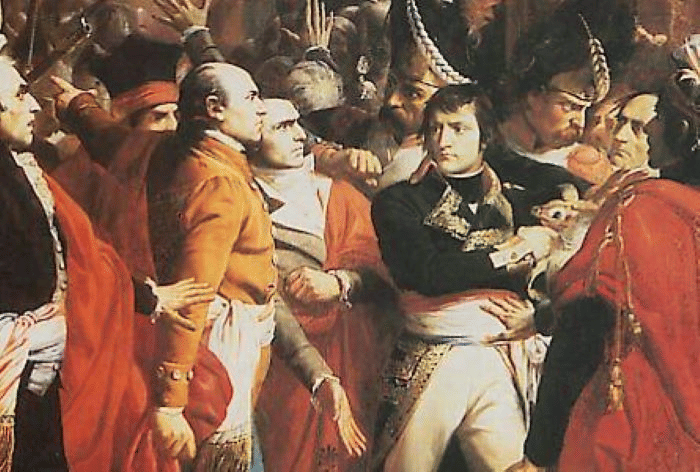 Effects of French Revolution
Effects of French Revolution
4. Unification of Germany & Italy
Mnemonic: "BISMARCK" (Germany) & "GARIBALDI" (Italy)
Germany - "BISMARCK"
B: Bismarck led the unification process
I: Industrial growth fueled national strength
S: Strong Prussian army fought unification wars
M: Monarch-led empire established in 1871
A: Austria defeated to unify German states
R: Rival France was defeated in the final war
C: Centralized administration was introduced
K: Kaiser William I was crowned emperor
Explanation:
Bismarck led the German unification using Industrial strength and a Strong Prussian army. A Monarch-led empire was declared in 1871 after Austria and Rival France were defeated. A Centralized administration ensured national unity, with Kaiser William I becoming the first German emperor.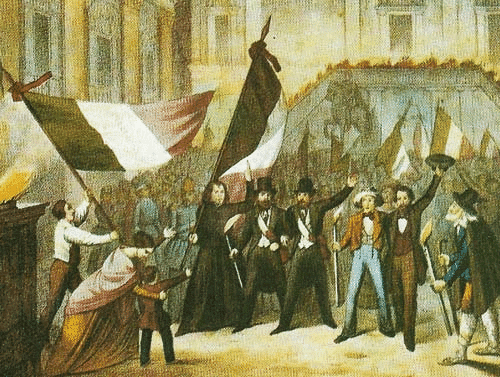 Unification
Unification
Italy - "GARIBALDI"
G: Garibaldi led the Red Shirts army
A: Austria controlled northern Italian states
R: Republic was Mazzini’s vision
I: Italy was divided into seven states
B: Bourbon kings ruled the south
A: Alliance with France helped Sardinia defeat Austria
L: Leadership of Cavour guided unification
D: Declaration of Italian kingdom in 1861
I: Illiteracy kept many unaware of nationalism
Explanation:
Garibaldi and his Red Shirts played a major role in unifying Italy. Austria controlled northern regions, and the Bourbon monarchy ruled the south. Republican ideas were promoted by Mazzini, but under the Leadership of Cavour, Sardinia allied with France to defeat Austria. The Declaration of the Italian kingdom was made in 1861, but high Illiteracy meant many Italians were unaware of the nationalist movement.
5. Nationalism and Imperialism
Mnemonic: "BALKANS"
Interpretations:
B: Balkan states sought independence from the Ottoman Empire
A: Alliances among European powers fueled conflicts
L: Land disputes and ethnic rivalries increased tensions
K: Kingdoms fought for territorial control
A: Austria-Hungary and Russia competed for influence
N: Nationalist uprisings intensified in the late 19th century
S: Struggle led to World War I
Explanation:
The Balkan states fought for independence from the Ottoman Empire. European Alliances fueled conflicts, while Land disputes and ethnic tensions grew. Kingdoms competed for territorial control, and Austria-Hungary and Russia vied for regional influence. Nationalist uprisings and Struggles eventually contributed to the outbreak of World War I.
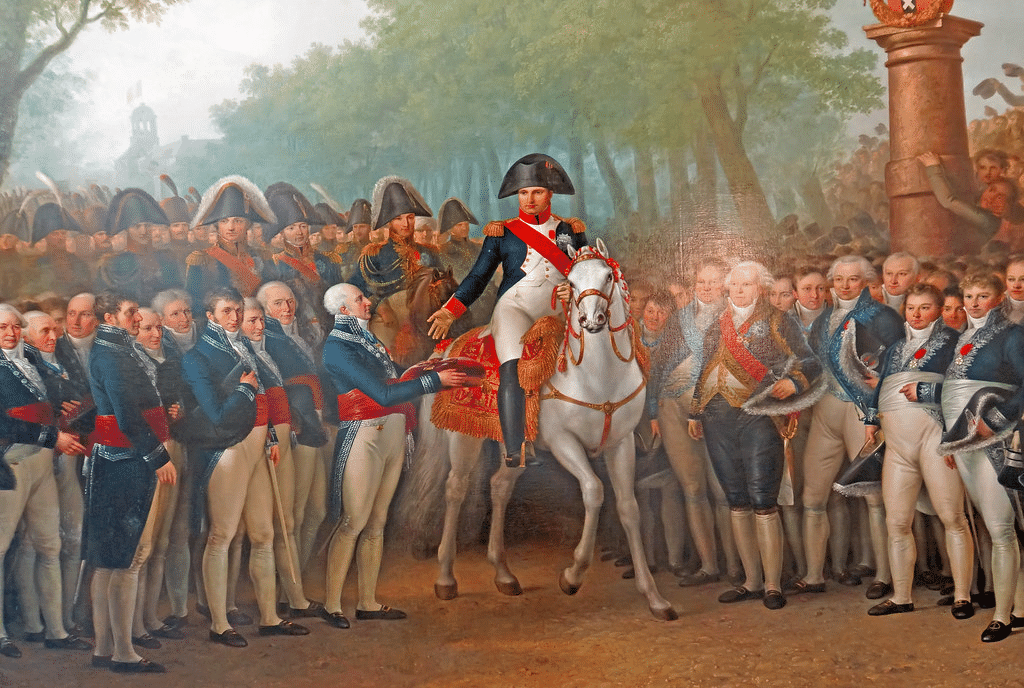 Nationalism and Imperialism
Nationalism and Imperialism
These mnemonics serve as a quick and effective way to recall key historical events, helping to connect complex ideas with simple memory aids for better understanding and retention.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What was Sorrieu’s vision for democratic and social republics in Europe? |  |
| 2. How did the French Revolution contribute to the rise of nationalism? |  |
| 3. What were the key factors that contributed to the making of nationalism in Europe? |  |
| 4. How did the unification of Germany and Italy occur, and what were its consequences? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between nationalism and imperialism in the context of European history? |  |

















