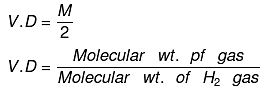Mole Concept and Basic Concepts | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
MOLE CONCEPT
Definition of mole: One mole is a collection of those many entities as there are number of atoms exactly in 12 gm of C - 12 isotope.
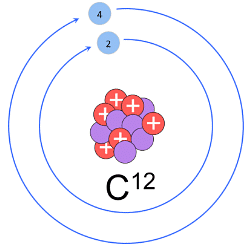
Fig. C-12 isotope
Or 1 mole = collection of 6.02 × 1023 species
6.02 × 1023 = NA = Avogadro's No.
1 mole of atoms is also termed as 1 gm-atom, 1 mole of ions is termed as 1 gm-ion and 1 mole of molecule termed as 1 gm-molecule.
Methods of Calculations of mole:
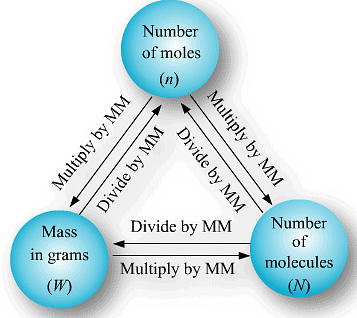
(a) If no. of some species is given, then no. of moles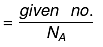
(b) If weight of a given species is given, then no of moles
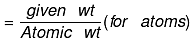
or

(c) If volume of a gas is given along with its temperature (T) and pressure (P)
use
where R = 0.0821 liter-atm/mol-K (when P is in atmosphere and V is in litre.)
1 mole of any gas at STP (0°C & 1 bar) occupies 22.7 litre.
1 mole of any gas at STP (0°C & 1 atm) occupies 22.4 litre.
Atom: Atom is smallest particle which can not be divided into its constituents.

Atomic weight: It is the weight of an atom relative to one twelfth of weight of 1 atom of C-12 isotope.
Relationship between gram and amu:
⇒ 1 amu = 1/12 wt of one C - 12 atom
⇒ for C, 1 mole C = 12 gm = 6.023 × 1023 atoms
⇒ wt. of 6.023 × 1023 atoms = 12 gm
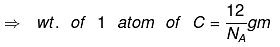
(NA → Avogadro's number = 6.23 × 1023)
⇒ 1 amu = 1/12 wt of one C - 12 atom
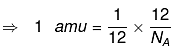
⇒ 1 amu = 1/NA g
So, 1 amu = 1.66 x 10-24 g
= 1.66 x 10-27 kg .
Elemental Analysis:
For 'n' mole of a compound (C3H7O2)
Moles of C = 3n
Moles of H = 7n
Moles of O = 2n
Example. Find the weight of water present in 1.61 g of Na2SO4. 10H2O
Solution. Moles of Na2SO4.10H2O = 0.005 moles
Moles of water = 10 × moles of Na2SO4. 10H2O = 10 × 0.05 = 0.05
wt. of water = 0.5 × 18 = 0.9 gm
Average atomic weight:
= % of isotope x molar mass of isotope.
The % obtained by above expression (used in above expression) is by number (i.e. its a mole%).
Molecular weight:
It is the sum of the atomic weight of all the constituent atoms.
(a) Average molecular weight= where ni = no. of moles of any compound and
mi = molecular mass of any compound.
Shortcut for % determination if average atomic weight is given for X having isotopes XA & XB.
Try working out of such a shortcut for XA, XB, XC
EMPIRICAL FORMULA and MOLECULAR FORMULA
Empirical formula: Formula depicting constituent atom in their simplest ratio.
Molecular formula: Formula depicting an actual number of atoms in one molecule of the compound.
Relation between the two: Molecular formula= Empirical formula × n
Check out the importance of each step involved in calculations of empirical formula.
Example. A molecule of a compound has 13 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atom, 3 oxygen atoms and 3.02 × 10-23 gm of other element. Find the molecular wt. of compound.
Solution. Wt. of the 1 molecule of a compound = 13 × 12 × 3 × 3.02 × 10-23
= 234.18 / NA = 234 amu.
Density:
(a) Absolute density
(b) Relative density
Vapor density: It is defined only for gas.
It is a density of gas with respect to H2 gas at same temp & pressure.
Density of Cl2 gas with respect to O2 gas
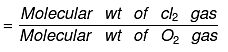
|
22 videos|162 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Mole Concept and Basic Concepts - Additional Study Material for JEE
| 1. What is the mole concept in JEE? |  |
| 2. What are the basic concepts of the mole in JEE? |  |
| 3. How do you calculate the number of moles in JEE? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between the mole and the gas laws in JEE? |  |
| 5. How is the mole concept used in stoichiometry problems in JEE? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|