DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Main): Motion in One Dimension- 3 | DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics PDF Download
Graphs
Ques 28: Displacement-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in figure.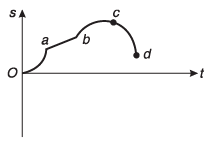
(a) Find the sign of velocity in regions oa, ab, be and cd.
(b) Find the sign of acceleration in the above region.
Ans: (a) positive, positive, positive, negative (b) positive, zero, negative, negative
Sol: OA : slope is + ive and increasing.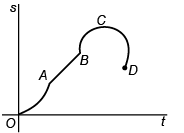
∴ velocity is + ive and acceleration is + ive.
AB : slope is + ive and constant
∴ velocity is +ive and acceleration is zero.
BC : sope is + ive and decreases.
∴ velocity is + ive and increasing.
CD : slope is –ive and increasing
∴ velocity is - ive and acceleration is - ive.
Ques 29: Let us call a motion as:
M1 → if velocity and acceleration both are positive.
M2 → if velocity is positive but acceleration is negative.
M3 → if velocity and acceleration both are negative.
M4 → if velocity is negative but acceleration is positive.
(a) State, in which of the above four motions, magnitude of velocity is increasing and in which it is decreasing.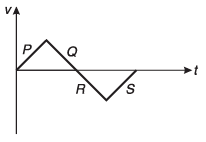
(b) v-t graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in figure. The whole graph is made up of four straight lines P, Q, R and S. These four straight lines indicate four type of motions (M1.. , M4) discussed above. State, which straight line corresponds to which type of motion.
Ans: (a) In M1 and M3 magnitude is increasing, in M2 and M4 magnitude is decreasing
(b) P → M1; Q → M2; R → M3; S → M4
Sol: 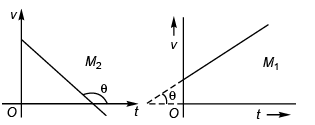
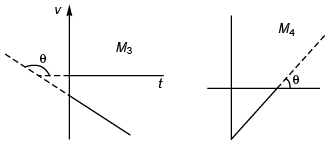
In M1 and M3 : 0° < θ < 90°
∴ slope is + ive i.e., acceleration is + ive.
In M2 and M4 : 90° < θ < 180°
∴ slope is - ive i.e., acceleration is - ive.
(a) M1 : Magnitude of velocity is increasing.
M2 : Magnitude of velocity is decreasing.
M3 : Magnitude of velocity is increasing.
M4 : Magnitude of velocity is decreasing.
M1 and M3.
(b) P → M1
Q → M2
R → M3
S → M4
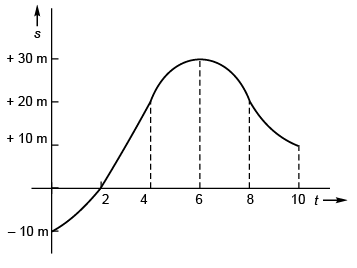
Ques 30: Velocity-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is shown in figure. At time t = 0, s = - 10 m. Plot corresponding a-t and s-t graphs.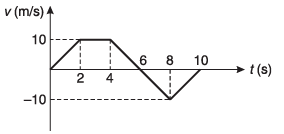
Ans: 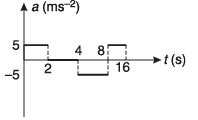
Sol: Case I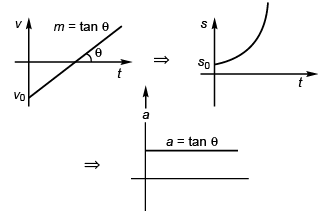
v = mt - v0 (st-line)
∴ ∫ ds = ∫ (mt - v0) dt
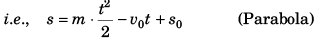
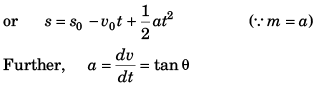
As for 0° < q < 90°
tan θ is + ive, a is + ive.
Case II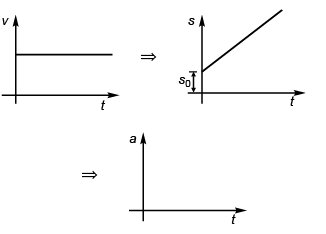
v = k (constant) (st line parallel to time-axis)
⇒ ∫ ds = ∫ k dt
s = kt + s0
Further, a = dv/dt = 0
Case III.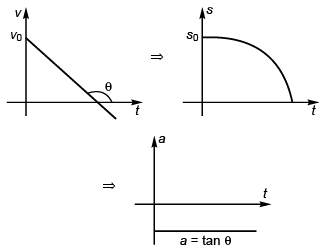
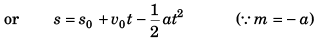
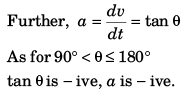
Time-displacement graph | |||
Time | Area under the graph | Initial Displacement | Net displacement |
at 0 s | 0 m | - 10 m | - 10 m |
2 s | 10 m | - 10 m | 0 m |
4 s | 30 m | - 10 m | + 20 m |
6 s | 40 m | - 10 m | + 30 m |
8 s | 30 m | - 10 m | + 20 m |
10 s | 20 m | - 10 m | + 10 m |
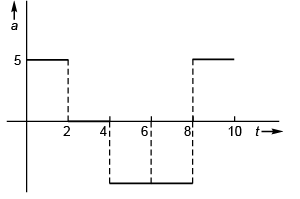
Time-acceleration graph | ||
time | slope | acceleration |
0 - 2 s | 5 | 5 m/s2 |
2 - 4 s | zero | 0 m/s2 |
4 - 6 s | - 5 | - 5 m/s2 |
6 - 8 s | - 5 | - 5 m/s2 |
8 - 10 s | + 5 | + 5 m/s2 |
Ques 31: Velocity-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is shown in figure. At time t = 0, s = 20 m. Plot a-t and s-t graphs of the particle.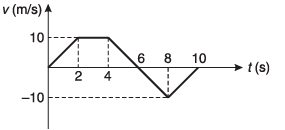
Ans: 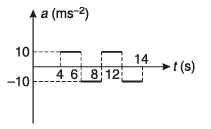
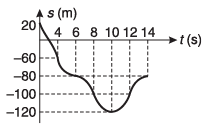
Sol: a = slope of v-t graph.
S = area under v-t graph.
Corresponding graphs are drawn in the answer sheet.
Ques 32: Velocity-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is shown in figure. In the time interval from t = 0 to t = 14s, find: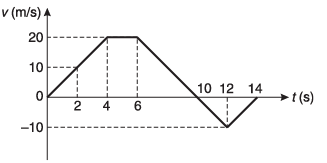
(a) average velocity and
(b) average speed of the particle
Ans: (a) (50/7) ms-1
(b) 10 ms-1
Sol: 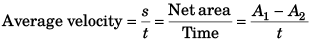
Ques 33: Acceleration-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in figure. At time t = 0, velocity of the particle is zero. Find: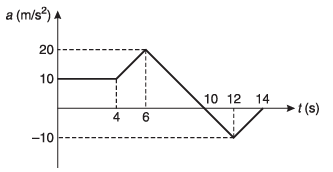
(a) average acceleration in a time interval from t = 6s to t = 12s,
(b) velocity of the particle at t = 14s.
Ans: (a) 5 ms-2
(b) 90 ms-1
Sol: Average acceleration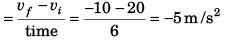
vf - vi = Area under a-t graph.
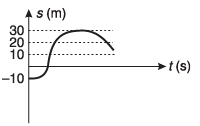
Ques 34: Velocity-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is shown in figure. At time t = 0, displacement of the particle from mean position is 10 m. Find: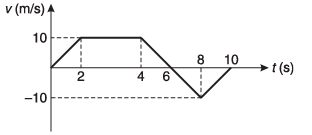
(a) acceleration of particle at t = Is, 3s and 9 s.
(b) position of particle from mean position at t = 10s.
(c) write down s-t equation for time interval:
(i) 0 < / < 2s,
(ii) 4s < t < 8s
Ans: (a) 5 ms-2, zero, 5 ms-2
(b) s = 30 m
(c) (i) s = 10 + 2.5 t2
(ii) s = 40 + 10 (t - 4) - 2.5 (t - 4)2
Sol: (a) Acceleration = slope of v-t graph.
(b) rf - ri = s = area under v-t graph.
(c) Equations are written in answer sheet.
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Main): Motion in One Dimension- 3 - DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics
| 1. What is the importance of understanding motion in one dimension for the JEE Main exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the motion in one dimension section of the JEE Main exam? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the concept of displacement in motion in one dimension? |  |
| 4. How can I determine the velocity of an object in motion in one dimension? |  |
| 5. How are the equations of motion used in solving problems related to motion in one dimension for the JEE Main exam? |  |
















