Multilevel Queue (MLQ) CPU Scheduling | Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
It may happen that processes in the ready queue can be divided into different classes where each class has its own scheduling needs. For example, a common division is a foreground (interactive) process and background (batch) processes. These two classes have different scheduling needs. For this kind of situation Multilevel Queue Scheduling is used. Now, let us see how it works.
Ready Queue is divided into separate queues for each class of processes. For example, let us take three different types of process System processes, Interactive processes and Batch Processes. All three process have there own queue. Now, look at the below figure.
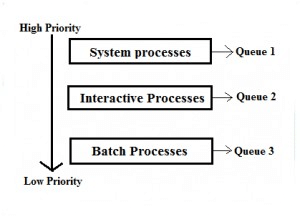
All three different type of processes have there own queue. Each queue have its own Scheduling algorithm. For example, queue 1 and queue 2 uses Round Robin while queue 3 can use FCFS to schedule there processes.
Scheduling among the queues: What will happen if all the queues have some processes? Which process should get the cpu? To determine this Scheduling among the queues is necessary.
There are two ways to do so:
- Fixed priority preemptive scheduling method: Each queue has absolute priority over lower priority queue. Let us consider following priority order queue 1 > queue 2 > queue 3. According to this algorithm no process in the batch queue(queue 3) can run unless queue 1 and 2 are empty. If any batch process (queue 3) is running and any system (queue 1) or Interactive process(queue 2) entered the ready queue the batch process is preempted.
- Time slicing: In this method each queue gets certain portion of CPU time and can use it to schedule its own processes. For instance, queue 1 takes 50 percent of CPU time queue 2 takes 30 percent and queue 3 gets 20 percent of CPU time.
Example Problem: Consider below table of four processes under Multilevel queue scheduling. Queue number denotes the queue of the process.
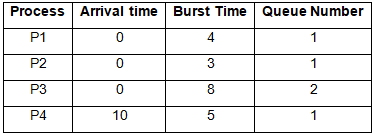
Priority of queue 1 is greater than queue 2. queue 1 uses Round Robin (Time Quantum = 2) and queue 2 uses FCFS.
Below is the gantt chart of the problem:

At starting both queues have process so process in queue 1 (P1, P2) runs first (because of higher priority) in the round robin fashion and completes after 7 units then process in queue 2 (P3) starts running (as there is no process in queue 1) but while it is running P4 comes in queue 1 and interrupts P3 and start running for 5 second and after its completion P3 takes the CPU and completes its execution.
Advantages:
- The processes are permanently assigned to the queue, so it has advantage of low scheduling overhead.
Disadvantages:
- Some processes may starve for CPU if some higher priority queues are never becoming empty.
- It is inflexible in nature.
Multilevel Feedback Queue Scheduling (MLFQ) CPU Scheduling
This Scheduling is like Multilevel Queue(MLQ) Scheduling but in this process can move between the queues. Multilevel Feedback Queue Scheduling (MLFQ) keep analyzing the behavior (time of execution) of processes and according to which it changes its priority. Now, look at the diagram and explanation below to understand it properly.
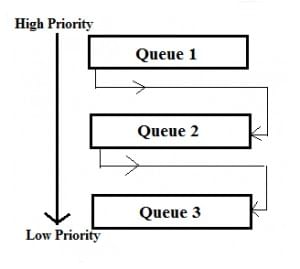
Now let us suppose that queue 1 and 2 follow round robin with time quantum 4 and 8 respectively and queue 3 follow FCFS. One implementation of MFQS is given below:
- When a process starts executing then it first enters queue 1.
- In queue 1 process executes for 4 unit and if it completes in this 4 unit or it gives CPU for I/O operation in this 4 unit than the priority of this process does not change and if it again comes in the ready queue than it again starts its execution in Queue 1.
- If a process in queue 1 does not complete in 4 unit then its priority gets reduced and it shifted to queue 2.
- Above points 2 and 3 are also true for queue 2 processes but the time quantum is 8 unit. In a general case if a process does not complete in a time quantum than it is shifted to the lower priority queue.
- In the last queue, processes are scheduled in FCFS manner.
- A process in lower priority queue can only execute only when higher priority queues are empty.
- A process running in the lower priority queue is interrupted by a process arriving in the higher priority queue.
Well, above implementation may differ for example the last queue can also follow Round-robin Scheduling.
Problems in the above implementation: A process in the lower priority queue can suffer from starvation due to some short processes taking all the CPU time.
Solution: A simple solution can be to boost the priority of all the process after regular intervals and place them all in the highest priority queue.
What is the need of such complex Scheduling?
- Firstly, it is more flexible than the multilevel queue scheduling.
- To optimize turnaround time algorithms like SJF is needed which require the running time of processes to schedule them. But the running time of the process is not known in advance. MFQS runs a process for a time quantum and then it can change its priority(if it is a long process). Thus it learns from past behavior of the process and then predicts its future behavior. This way it tries to run shorter process first thus optimizing turnaround time.
- MFQS also reduces the response time.
Example: Consider a system which has a CPU bound process, which requires the burst time of 40 seconds. The multilevel Feed Back Queue scheduling algorithm is used and the queue time quantum ‘2’ seconds and in each level it is incremented by ‘5’ seconds.Then how many times the process will be interrupted and on which queue the process will terminate the execution?
Solution:
- Process P needs 40 Seconds for total execution.
- At Queue 1 it is executed for 2 seconds and then interrupted and shifted to queue 2.
- At Queue 2 it is executed for 7 seconds and then interrupted and shifted to queue 3.
- At Queue 3 it is executed for 12 seconds and then interrupted and shifted to queue 4.
- At Queue 4 it is executed for 17 seconds and then interrupted and shifted to queue 5.
- At Queue 5 it executes for 2 seconds and then it completes.
- Hence the process is interrupted 4 times and completes on queue 5.
Advantages:
- It is more flexible.
- It allows different processes to move between different queues.
- It prevents starvation by moving a process that waits too long for lower priority queue to the higher priority queue.
Disadvantages:
- For the selection of the best scheduler, it require some other means to select the values.
- It produces more CPU overheads.
- It is most complex algorithm.
|
10 videos|99 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Multilevel Queue (MLQ) CPU Scheduling - Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is multilevel queue CPU scheduling? |  |
| 2. How does multilevel queue CPU scheduling work? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of multilevel queue CPU scheduling? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges of implementing multilevel queue CPU scheduling? |  |
| 5. Can multilevel queue CPU scheduling be combined with other scheduling algorithms? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|

















