NCERT Based Activity: Exploring Forces | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Activity 5.1: Let us explore
Take a large cardboard box. Try moving the box in as many different ways as you can think of. Did you move the box in any other way than shown in Fig. 5.1?
Ans: Yes, the box can be moved in many ways—by pushing, pulling, sliding, or lifting. In all cases, a push or pull is applied, which is called a force in science.
Activity 5.2: Let us analyse
Think of situations where a force is applied and list them in Table 5.1. Analyse each situation and write the effect of the force.
Ans: A force can cause a moving object to stop, change its speed, change direction of motion, or change its shape.
Activity 5.3: Let us investigate
- Take an object with a flat base (such as an empty lunch box/ geometry box/ a notebook) and place it on a table or floor.
- Gently push it and observe. Does it stop after travelling some distance? Is there a force acting on it which brings it to rest?
Answer: Yes, the object stops after travelling some distance due to a force acting on it. - Now repeat by pushing the object in the opposite direction. Does it stop again after travelling some distance?
Answer: Yes, it stops again when pushed in the opposite direction.
Activity 5.4: Let us explore
- Try Activity 5.3 again, but this time place the same object on different surfaces, such as glass, cloth, wood, ceramic tile, and sand.
- Does the object stop after travelling the same distance as in Activity 5.3?
Answer: No, the object does not stop after travelling the same distance on all surfaces. - Does the object stop at the same distance on all surfaces?
- Answer: The stopping distance varies depending on the nature of the surface, with greater friction on rough surfaces.
Activity 5.5: Let us test
- Take two ring magnets and a wooden stick.
- While holding the stick in a vertical position over a wooden table, insert one ring magnet onto the stick (Fig. 5.7).

- Now insert the second ring magnet above it such that the like poles of the two magnets face each other. Does the second magnet stay floating above the first magnet?
Answer: Yes, the second magnet stays floating when like poles face each other. - Try pushing the second magnet down gently. Do you feel a force on it?
- Now, reverse the poles of both the magnets. Does the second magnet still remain floating?
Answer: Yes, a force is felt when pushing it down. No, it does not remain floating when poles are reversed.
Activity 5.6: Let us experiment
- Take a plastic scale or a plastic straw, a piece of polythene, and small pieces of paper.
- Rub plastic scale/straw vigorously with polythene.
- Do not touch the rubbed part with your hand or any metal object.
- Now, bring it close to the small pieces of paper placed on a table, taking care not to touch the paper pieces (Fig. 5.8). Do you notice something surprising?
Answer: Yes, the paper pieces are attracted to the rubbed plastic scale/straw and stick to it.
Activity 5.7: Let us experiment
- Take two balloons, a length of thread, and a woollen cloth.
- Inflate two balloons and hang them in such a way that they do not touch each other as shown in Fig. 5.9a.
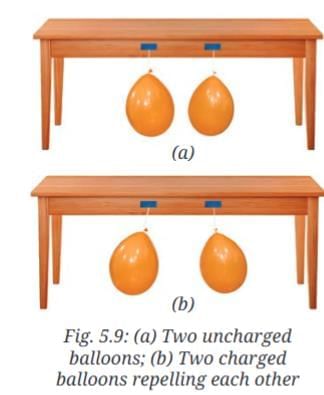
- Rub both balloons with the woollen cloth and release them. Be careful not to touch the rubbed balloons with your fingers. What do you observe?
- Now bring the woollen cloth used for rubbing the balloons close to one of the rubbed balloons. What happens?
Answer: The balloons move away from each other as if repelling. The balloon moves towards the woollen cloth as if attracting.
Activity 5.8: Let us observe
- Take a ball and throw it vertically upwards. Does it come down?
Answer: Yes, it comes down. - Now throw it again, but this time harder. Does it still fall back down to the ground?
Answer: Yes, it still falls back down.
Activity 5.9: Let us explore
- Take a spring and a few objects of different masses, such as a pencil box, a tiffin box, and a small stone.
- Hang one end of the spring from a nail. From the other end, hang an object and observe the spring. Does the spring stretch?
Answer: Yes, the spring stretches. - Now hang the other objects, one by one and notice the stretch in the spring each time. Is the stretch caused by each object the same
Answer: No, the stretch is different for different objects.
Activity 5.10: Let us observe
Look at the spring balance in Fig. 5.13. What is the maximum weight it can measure?
Ans: The spring balance can measure up to 10 N.
Activity 5.11: Let us calculate
Look at the spring balance shown in Fig. 5.13 and note down the following:
- How much is the weight difference indicated between the two bigger marks?
Answer: The weight difference between 0 and 01 N or between 01 N and 02 N is 1 N. - How many divisions (shown by smaller marks) are there between these two bigger marks?
Answer: There are 5 divisions between these marks. - How much weight does one small division indicate?
Answer: One small division can read 1 N / 5 = 0.2 N.
Activity 5.12: Let us measure
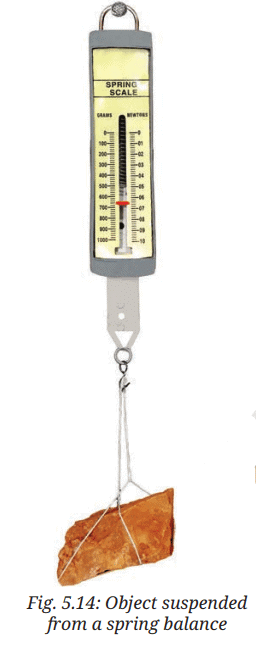
Take a spring balance and a few objects. Keep in mind that the objects should not be heavier than the maximum value of weight the spring balance can measure, otherwise it may get damaged.
Suspend the objects one by one from the hook (Fig. 5.14). Read the scale for weight carefully and record your observations in the Table 5.2.
Ans: Weights to be measured and recorded based on actual observation
Activity 5.13: Let us investigate
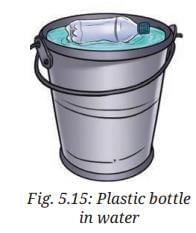
- Take an empty plastic bottle (with its lid closed tightly) and a bucket full of water.
- Push the bottle in the water (Fig. 5.15). Do you feel an upward push? Release the bottle. Does it bounce up?
Answer: Yes, an upward push is felt. Yes, it bounces back to the surface.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Exploring Forces - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the different types of forces explored in Class 8 science? |  |
| 2. How does frictional force affect motion? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of gravitational force? |  |
| 4. How can we demonstrate the effects of magnetic force? |  |
| 5. What methods can be used to measure forces in experiments? |  |















