NCERT Based Activity: Light: Mirrors and Lenses | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Activity 10.1: Let us explore
Take a shiny metallic spoon and hold its curved surface close to your face.
 1. Can you see your image in it?
1. Can you see your image in it?
Ans: Yes, you can see your image in the shiny metallic spoon as it acts like a mirror.
2. Notice the image of your face. Is it different from the image you see in a plane mirror?
Ans: Yes, the image is different; it is enlarged and erect when close, unlike the same-size erect image in a plane mirror.
3. While observing the image, slowly move the spoon away from your face. Do you observe any change in the image?
Ans: Yes, as the spoon moves away, the image becomes inverted and changes in size, initially enlarged then smaller.
4. Now flip the spoon and repeat the same steps.
Ans: On the outer side (convex), the image is erect but smaller (diminished), and it decreases slightly in size as moved away.
Explanation: The inner curved surface acts as a concave mirror, forming inverted images when far, and the outer as convex, always forming erect diminished images, demonstrating spherical mirror properties.
Activity 10.2: Let us distinguish
- Place concave and convex mirrors on a table with their reflecting surfaces facing upwards.
- Now view them from the side, keeping your eye at their level, to identify whether the reflecting surface is curved inwards or outwards (Fig. 10.4).
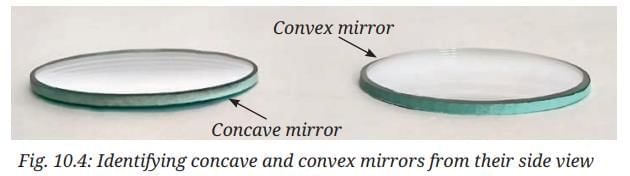
Ans: The concave mirror's reflecting surface curves inwards (like a cave), while the convex mirror's curves outwards (bulges out). Explanation: This side view helps distinguish concave (inward curve) from convex (outward curve) mirrors based on the shape of the reflecting surface.
Activity 10.3: Let us explore
Take a concave mirror, a convex mirror, two small wooden blocks or something similar to place the mirrors in an upright position, and a small toy or some other object.
1. Place the two mirrors side by side in an upright position on a table. Keep the object in front of them at a small distance (3–4 cm away) as shown in Fig. 10.5a. What kind of images do you see in each mirror?
Ans: In the concave mirror: enlarged, erect image. In the convex mirror: diminished, erect image.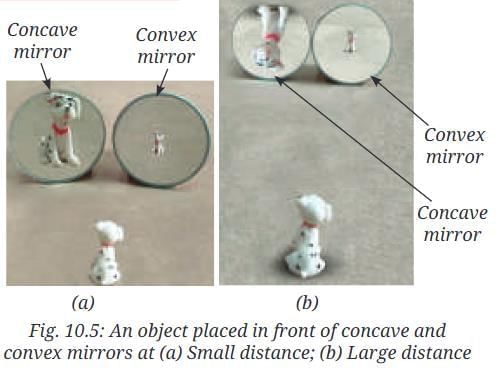
2. Are the images of the same size as the object? Are they erect? Do you see lateral inversion in the images? Write down your observations in your notebook.
Ans: Concave: larger than object, erect, lateral inversion present. Convex: smaller than object, erect, lateral inversion present.
3. Now slowly move the object away from the mirrors. What changes do you see in the images in both the mirrors? Do the images become smaller or larger? Do they continue to be erect? Again, note down your observations.
Ans: Concave: image inverts, initially enlarged then smaller. Convex: image remains erect, gets slightly smaller.
4. Repeat the steps with each mirror individually.
Ans: Same observations as above for each mirror separately.
5. Analyse your observations and draw conclusions.
Ans: Conclusion: Spherical mirrors form images that vary in size and orientation with distance, unlike plane mirrors (same size, erect). Concave: enlarged erect close, inverted far. Convex: always diminished erect. Lateral inversion in all.
Explanation: This activity demonstrates how image characteristics (size, orientation, inversion) in spherical mirrors depend on object distance, useful for applications like torches or vehicle mirrors.
Activity 10.4: Let us experiment
- Collect a plane mirror with stand, a torch, a comb, a paper clip to hold the comb upright, a sheet of white paper, and a strip of black paper.
- Make a thin slit by covering all openings of the comb using black paper, except for one in the middle.
- Spread a sheet of white paper on a table. Place the plane mirror upright on it.
- Using the thin slit and torch, obtain a thin beam of light along the paper and adjust it to fall upon the mirror as shown in Fig. 10.8a.
- Now, move the slit and torch slightly so that the beam of light falls at a different angle on the mirror. Does the reflected beam of light also shift? (Fig. 10.8b).
- Make the beam of light fall on the mirror at different angles and observe how the direction of the reflected beam changes.
- Draw a line showing the position of the plane mirror. Also, draw lines with arrows (rays) indicating the beam of light falling on the mirror and the reflected beam of light. Fig. 10.9a.
- Now remove the mirror. From the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror, draw a line making an angle of 90° to the line representing the mirror. This line is known as the normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, O (Fig. 10.9b).
- The angle between the normal and the incident ray is called the angle of incidence
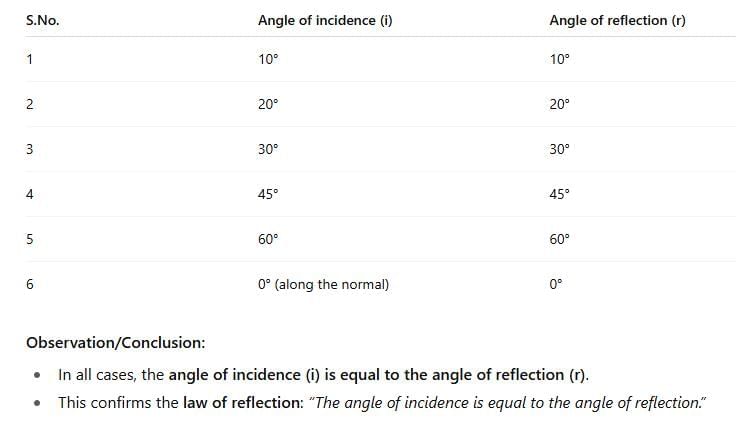
(i) (Fig. 10.9c). The angle between the normal and the reflected ray is known as the angle of reflection (r) (Fig. 10.9c). - On your drawing, measure the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection and note it in Table 10.1.
Table:
- Repeat the activity several times by changing the angle of incidence.
- Finally, let the incident beam fall on the mirror along the normal and observe the direction of the reflected beam. What would be the angle of incidence and angle of reflection in this case?
Answers:
Does the reflected beam of light also shift?
Answer: Yes, the reflected beam shifts as the incident beam angle changes.What would be the angle of incidence and angle of reflection in this case?
Answer: Both angles are zero when the incident beam falls along the normal.Do you notice that both angles in Table 10.1 are nearly equal?
Answer: Yes, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
Activity 10.5: Let us experiment
- Use the same setup as in Activity 10.4, but place a stiff sheet of chart paper flat on a table such that part of it extends beyond the edge of the table.
- Shine a beam of light on the mirror placed on the sheet and observe the reflected beam on the extended portion.
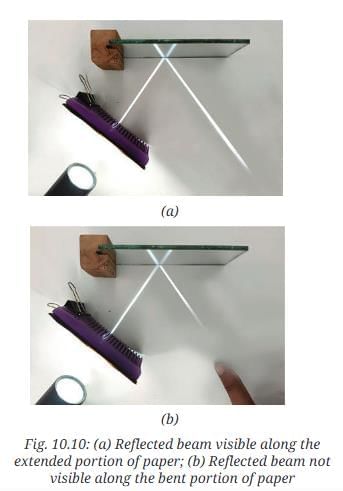
- Now, bend the extended part of the sheet along the edge of the table. Do you still see the reflected beam on the extended portion?
Answer: No, the reflected beam disappears when the sheet is bent but reappears when flattened. - Flatten the paper again and observe.
Activity 10.6: Let us explore
Collect a plane mirror, a concave mirror, a convex mirror, stand for mirrors, a torch, a comb, and a paper clip to hold the comb upright.
Use the same setup as Activity 10.4 again, but instead of a single slit, leave many openings of the comb uncovered to obtain multiple parallel beams of light.
Let the multiple parallel beams of light fall upon the plane mirror, concave mirror, and convex mirror, one by one. Observe the reflected beams. Is your observation similar to what is shown in Fig. 10.11 (b), (c), and (d)?
Answer: Yes, parallel beams reflect as parallel in a plane mirror, converge in a concave mirror, and diverge in a convex mirror.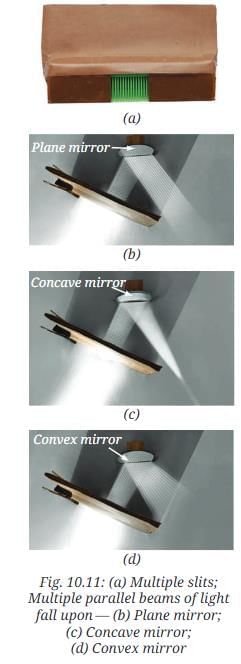
Activity 10.7: Let us explore
Take a concave mirror and a sheet of thin paper or newspaper.
Hold the concave mirror with its reflecting surface facing the Sun. Direct the light of the Sun reflected by the mirror on the sheet of paper.
Adjust the distance of the paper until you get a sharp bright spot on it.
Hold the mirror and the sheet of paper steady for a few minutes. Does the paper start to burn producing smoke?
Answer: Yes, the paper may start to burn and produce smoke due to concentrated sunlight.

Activity 10.8: Let us explore
Collect a flat strip of glass or clear plastic, such as a flat scale, few drops of oil, dropper, water, and a paper or book with some text printed on it.
Spread a few drops of oil on the surface of glass or plastic strip and rub it to leave a very thin coating.
Using a dropper or your finger, place a small drop of water on the oiled/waxed spot.

Examine the water drop. What is the shape of its surface? Is it flat or curved inward or curved outward?
Answer: The surface is curved outward.Place the paper underneath the glass/plastic strip such that the text is directly under the water drop.
Now, look down through the water drop at the text below. Do you find some change in the size of the letters just below the water drop? Do they look enlarged or smaller?
Answer: Yes, the letters look enlarged.
Activity 10.9: Let us experiment
Collect a convex lens, a concave lens, a lens holder, and a small object.
Take the convex lens and place it upright using its holder.
Place the object behind the convex lens.
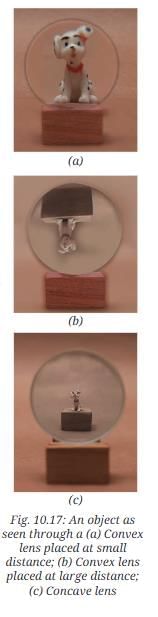
Look at the object through the lens from the other side of the lens and note your observations.
Now slowly move the object farther from the lens and keep observing how the image changes. How does the distance of the object from the convex lens affect how it looks?
Answer: At a small distance, the image is erect and enlarged; as the distance increases, it becomes inverted and initially enlarges then diminishes.Now repeat the steps using a concave lens.
Analyse your observations and compare the images seen through both lenses.
What conclusions do you draw?
Answer: A convex lens can produce erect and enlarged or inverted images depending on distance, while a concave lens always produces erect and diminished images.
Activity 10.10: Let us investigate
Collect a thin transparent glass plate, a convex lens, a concave lens, a torch and a comb to obtain multiple parallel beams of light, a paper clip to hold the comb upright, two identical books, and sheets of white paper.
Using two books placed adjacent to each other, fix the glass plate or lens upright in between them.
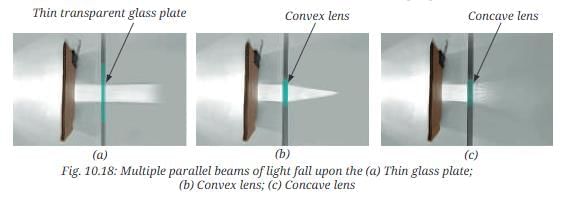
Spread paper sheets on both books.
Now let the multiple parallel beams of light fall upon the thin glass plate, convex lens, and concave lens one by one. Does the parallel beam of light pass through as it is in all three cases?
Answer: No, it passes unchanged through the glass plate, converges through the convex lens, and diverges through the concave lens.Record and analyse your observations.
Activity 10.11: Let us investigate
Repeat Activity 10.7 by putting a convex lens in the path of sunrays in place of a concave mirror. Could you burn the paper?

Answer: Yes, the convex lens can concentrate sunlight to burn the paper.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Light: Mirrors and Lenses - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the different types of mirrors and their uses? |  |
| 2. How do lenses work to form images? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between real and virtual images? |  |
| 4. How does the law of reflection apply to mirrors? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of mirrors and lenses in daily life? |  |















