NCERT Based Activity: Living Creatures: Exploring Their Characteristics | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Activity 10.1: Let us record |

|
| Activity 10.2: Let us experiment |

|
| Activity 10.3: Let us design |

|
| Activity 10.4: Let us explore |

|
| Activity 10.5: Let us analyse |

|
| Activity 10.6: Let us analyse |

|
Activity 10.1: Let us record
- We are surrounded by numerous things. Just look around in your classroom and you may find many examples—the pencil that you are holding, the book that you are reading or the pigeon near the window.
- List them in Table 10.1 and identify each of them as living or non-living on the basis of your understanding in column II.
- Write a reason for grouping them as living or non living in column III.
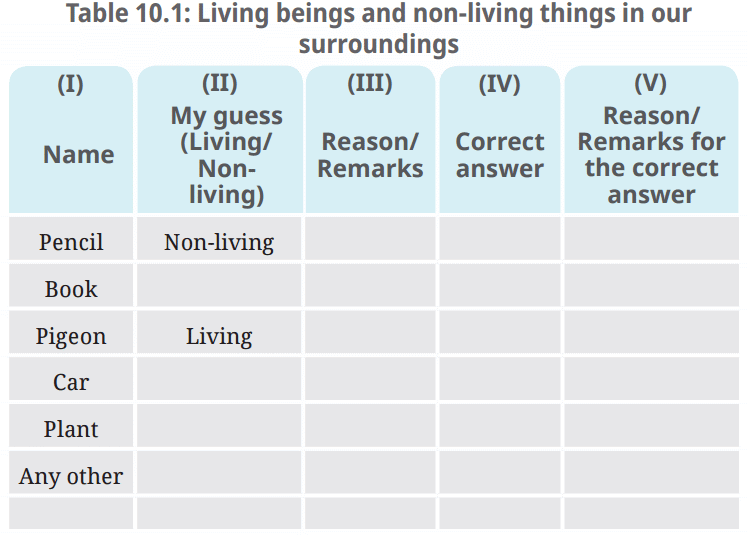
Q: List them in Table 10.1 and identify each of them as living or non-living on the basis of your understanding in column II. Write a reason for grouping them as living or non living in column III.
Ans: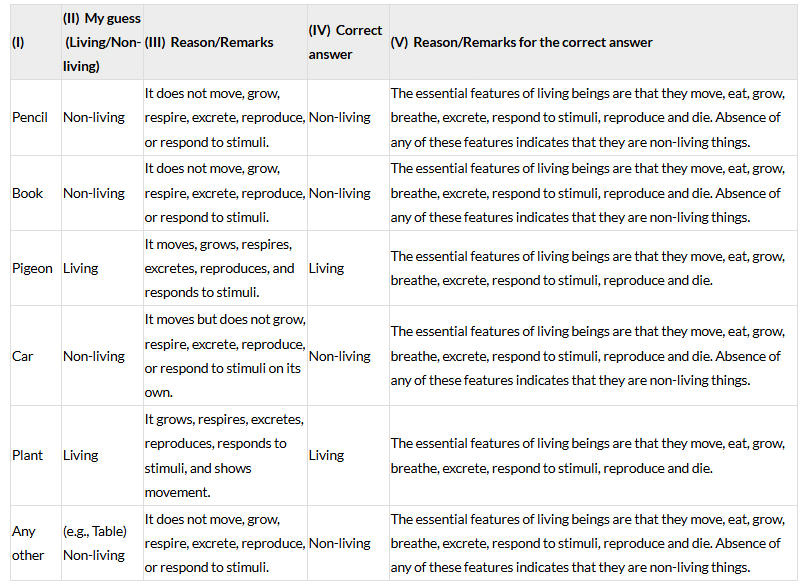
Ans: A seed is living. Seeds require water for germination. Water enables the seeds to carry out the processes necessary for their growth. The outer covering of the seed is called seed coat. Water softens the seed coat and helps the tiny embryo inside it to develop into a plant.
Activity 10.2: Let us experiment
- Take four identical pots filled with garden soil. Sow four bean seeds in each pot. Now, keep these pots in the following conditions for 15 days.
- Pot A: Do not water the soil. Place this pot in direct sunlight.
- Pot B: Add excess water to the soil such that water is always present above the soil. Keep adding water on a regular basis if water reduces. Place this pot in direct sunlight.
- Pot C: Keep the soil in this pot slightly moist by adding a moderate amount of water on a regular basis. Place this pot in a dark location.
- Pot D: Maintain the soil in this pot slightly moist by adding a moderate amount of water on a regular basis. Place this pot in direct sunlight.
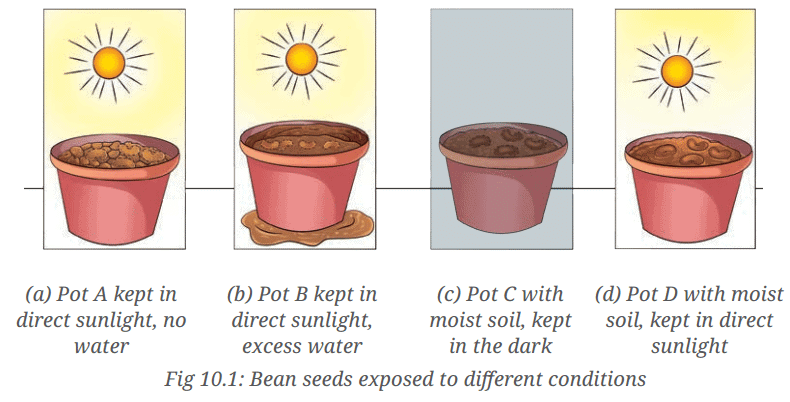
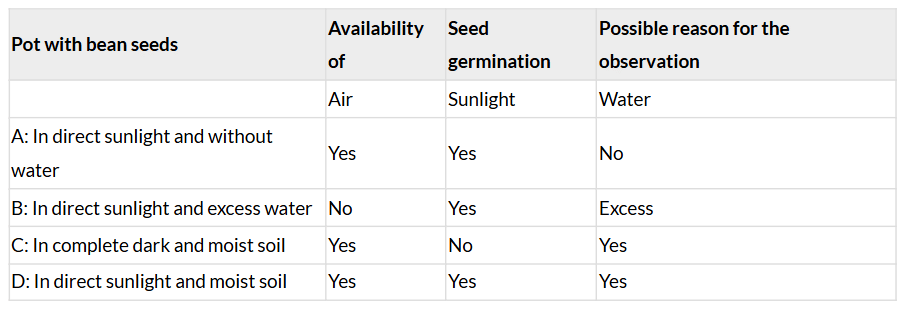
- Indicate the availability of air, sunlight and water for the seeds in each of these cases in Table 10.2.
- When a seed turns into a sprout, it is said to have germinated. Predict whether the seeds in each pot will germinate. Record your predictions for each pot kept under different conditions in Table 10.2.
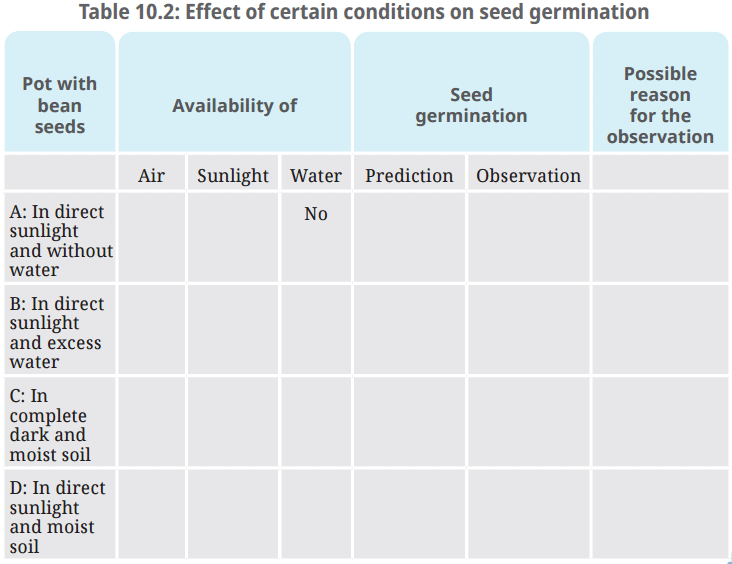
Q: Indicate the availability of air, sunlight and water for the seeds in each of these cases in Table 10.2. Predict whether the seeds in each pot will germinate. Record your predictions for each pot kept under different conditions in Table 10.2. Regularly observe the pots for 7-10 days to check the status of germination of the seeds. Record your observations in Table 10.2. Write possible reasons in favour of your observations in Table 10.2.
Ans:
Q: Compare your predictions with your observations.
Ans: Observations match with predictions.
Q: Do you think sunlight is necessary for germination of seeds?
Ans: For the bean seeds, presence of light is not essential for their germination.
Q: Do the seeds in all the pots receive air, water and sunlight?
Ans: Seeds in Pot A receive air and sunlight but no water. Seeds in Pot B receive sunlight and excess water but no air. Seeds in Pot C receive air and water but no sunlight. Seeds in Pot D receive air, sunlight, and water.
Q: Is there any pot in which air is not available to the seeds? If so, why is it not available?
Ans: In Pot B, air is not available to the seeds because excess water does not allow air to reach the seeds.
Q: What happens to the seeds in the pot where water is provided in excess?
Ans: Seeds do not germinate.
Q: Which seeds receive both air and water?
Ans: Seeds in Pot C and Pot D receive both air and water.
Q: Identify the pots where you can notice the germination of seeds.
Ans: Germination of seeds is noticed in Pot C and Pot D.
Q: Do your observations match with your predictions?
Ans: Observations match with predictions.
Q: Based on your observations, state the conditions which favour seed germination.
Ans: Germination of bean seeds requires the right amount of water and air.
Q: Which of the following are essential for seed germination—air, water and sunlight?
Ans: Germination of bean seeds requires the right amount of water and air.
Q: Compare the available conditions in each pot.
Ans: Seeds in Pot A receive air and sunlight but no water. Seeds in Pot B receive sunlight and excess water but no air. Seeds in Pot C receive air and water but no sunlight. Seeds in Pot D receive air, sunlight, and water.
Q: Why do seeds require these conditions for germination?
Ans: Seeds require water for germination. Water enables the seeds to carry out the processes necessary for their growth. The outer covering of the seed is called seed coat. Water softens the seed coat and helps the tiny embryo inside it to develop into a plant. Seeds need air for germination. They use the air available in the spaces between soil particles.
Q: Do you think that the absence of one or more of these conditions will affect seed germination?
Ans: The absence of one or more of these conditions will affect seed germination.
Activity 10.3: Let us design
- Take some bean or gram seeds and allow them to germinate on a moist cloth or a moist tissue paper.
- Let them germinate until each of them develop into a seedling having a small root and a small shoot.
- Now, take three glass beakers or tumblers, and label them as A, B and C.
- Take three glass plates and attach a thick blotting paper to one side of each plate using a thick soft cotton thread.
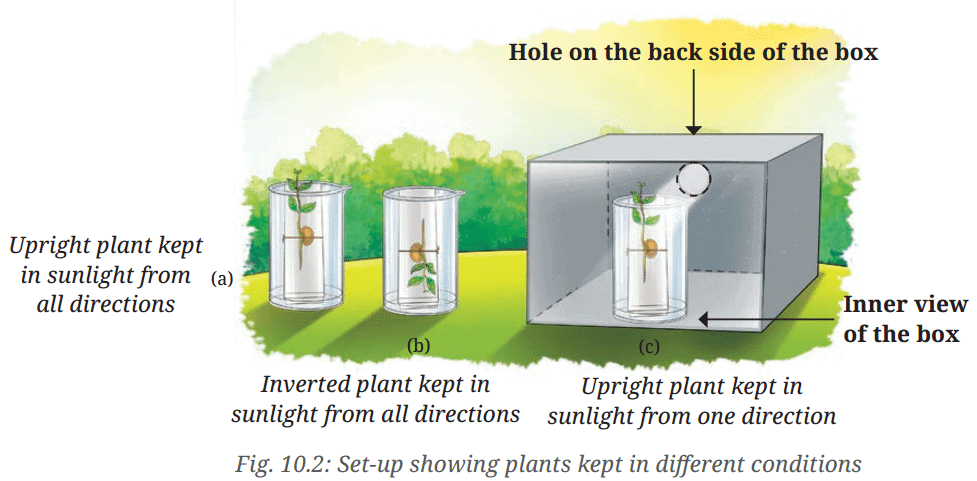
- Fix one seedling on each plate using a thick soft cotton thread, as shown in Fig. 10.2, ensuring that the plant is not damaged.
- Now, place one glass plate upright with a seedling attached into each of the beaker A and beaker C, as shown in Fig. 10.2a and Fig. 10.2c.
- In beaker B, arrange the plate such that the shoot of a seedling is directed downwards and the root is directed upwards, as shown in Fig. 10.2b.
- Pour water into all the three beakers to ensure that the seedling in each beaker remains above the water level.
- In each case, let the bottom of the blotting paper get completely wet by soaking in the water. In this way, the seedling will get the moisture from the wet blotting paper.
- Place beaker A and beaker B in sunlight as shown in Fig. 10.2a and Fig. 10.2b.
- Position beaker C as shown in Fig. 10.2c. Place a cardboard box in such a way that the seedling gets light from one direction only through a small circular hole.
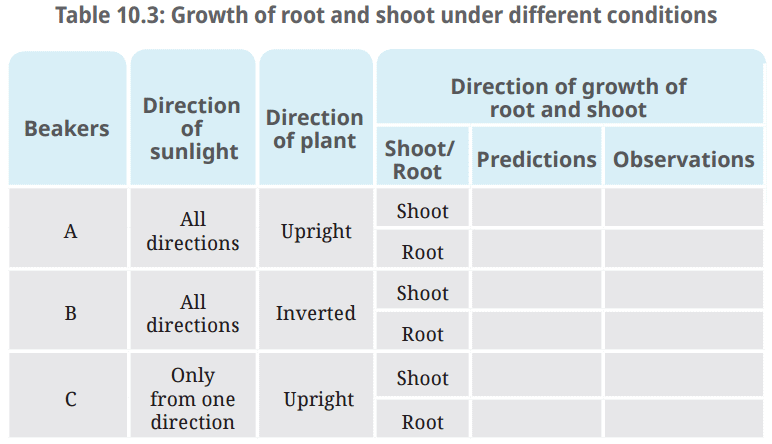
Q: Fill Table 10.3 with your predictions and observations.
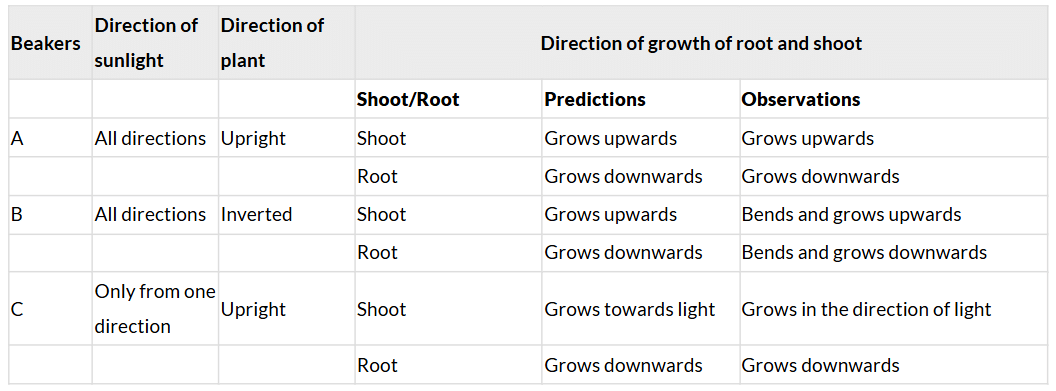
Q: What is the direction of growth of root and shoot in beakers A, B and C based on your observations?
Ans: When the plant is kept upright, the root grows downwards and the shoot grows upwards. When the plant is kept inverted, the root bends and grows downwards. Also, the shoot bends and grows upwards. When the plant gets sunlight only from one direction, the shoot grows in the direction of light while the root continues to grow downwards.
Q: Do your predictions match your observations?
Ans: Predictions match observations.
Q: What do you conclude from this activity?
Ans: Shoots of plants grow upward and exhibit movement towards sunlight but roots of plants grow downwards.
Activity 10.4: Let us explore
- Plant a bean seed and provide suitable conditions for its growth. Observe regularly for three months.
- Record your observations in Table 10.4 as and when changes become visible.
- Note the date when any change is observed. Record answers for the following questions-
Q: Record your observations in Table 10.4 as and when changes become visible. Note the date when any change is observed. Make sketches of various changes that you observe in Table 10.4.
Ans: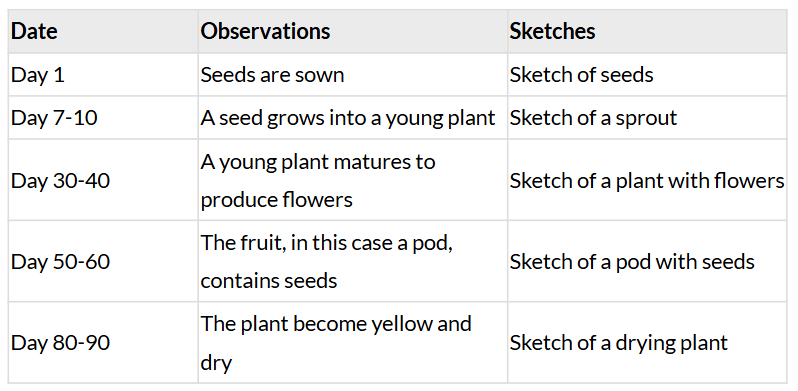
Q: How long does it take for any change to occur?
Ans: It takes 7-10 days for a seed to grow into a young plant.
Q: After how many days does the first flower appear?
Ans: The first flower appears after 30-40 days.
Q: After some parts of the flower have dried, can you see any further growth?
Ans: Yes, you can see further growth.
Q: Which structure do the remaining parts of flower develop into?
Ans: The remaining parts of flower develop into a pod.
Q: Can you notice a pod or a fruit with seeds develop from a flower?
Ans: Yes, you can notice a pod or a fruit with seeds develop from a flower.
Q: What happens to the plant after the fruits containing seeds are formed?
Ans: The plant become yellow and dry even when you continue watering it.
Activity 10.5: Let us analyse
- Let us solve an interesting puzzle.
- How will you decide which stage (larva or pupa) comes immediately after the egg stage?
- Suppose you are given a container with water from a puddle containing larvae and pupae. Design an activity to find out the correct sequence of these stages.
You can take help of the following activity designed by Avadhi to create your own activity-
- Step 1: I have a water container with mosquito larvae and pupae.
- Step 2: I will separate 4-5 larvae and pupae into two separate containers with the same water.
- Step 3: I will observe them every day until I see them changing to the next stage.
- Step 4: If the larvae change into pupae, it would mean that the larval stage comes before the pupal stage or vice-versa.
- Step 5: I will keep watching both the containers to see in which one a mosquito appears first.
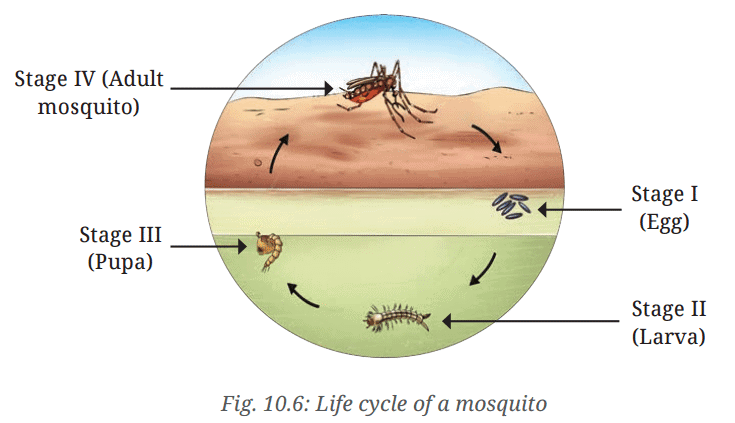
Q: How will you decide which stage (larva or pupa) comes immediately after the egg stage?
Ans: These observations will help us to learn the correct sequence of growth. If the larvae change into pupae, it would mean that the larval stage comes before the pupal stage.
Q: Suppose you are given a container with water from a puddle containing larvae and pupae. Design an activity to find out the correct sequence of these stages.
Ans:
- Step 1: I have a water container with mosquito larvae and pupae.
- Step 2: I will separate 4-5 larvae and pupae into two separate containers with the same water.
- Step 3: I will observe them every day until I see them changing to the next stage.
- Step 4: If the larvae change into pupae, it would mean that the larval stage comes before the pupal stage or vice-versa.
- Step 5: I will keep watching both the containers to see in which one a mosquito appears first.
Q: Now, suppose you are given a container filled with water from a puddle which contains larvae and pupae. Without separating them from the container, how would you design an activity to decide which stage, out of the two, gives way to the next?
Ans:
- Step 1: I have a water container with mosquito larvae and pupae.
- Step 2: I will observe the container every day to monitor the larvae and pupae.
- Step 3: I will record when larvae change into pupae or when pupae transform into adult mosquitoes.
- Step 4: If larvae are observed changing into pupae, it indicates that the larval stage comes before the pupal stage.
- Step 5: If pupae are observed transforming into adult mosquitoes, it confirms that the pupal stage comes after the larval stage.
Activity 10.6: Let us analyse
- Avadhi and Aayush are dressed up in full sleeves shirts and full pants today. It has been raining intermittently for a week. They are going out with their classmates for an activity. After a brief walk led by their science teacher, they reach a shallow pond. It is surrounded by trees and tall grasses. The teacher cautions them to watch everything from a distance without causing any disturbance. You may also go to a small water body during the rainy season with a facilitator and explore it by taking due safety precautions.
- You may notice a white jelly-like substance on the surface of water towards the edge of the pond (Fig. 10.7). This may also be attached to plants growing in or around the water. This jelly-like substance is actually a cluster of eggs of a frog and is known as spawn.
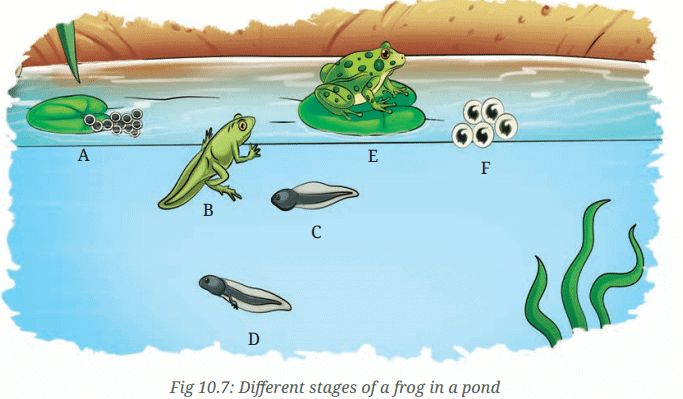
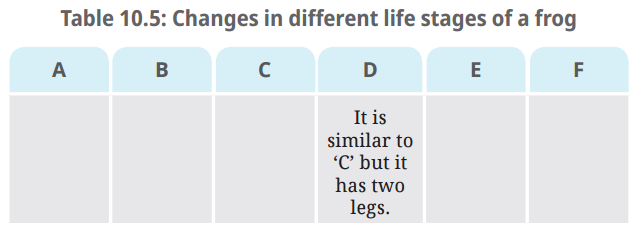
- Observe the features of all the stages of a frog shown in Fig. 10.7. How will you decide the sequence of the given stages (A, B, C, D, E, F)? Some of the stages show distinct changes in their initial and final shapes. Record these changes in Table 10.5.
- Based on the observations listed in Table 10.5, draw the life cycle of a frog. Compare the figure drawn by you with Fig. 10.8.
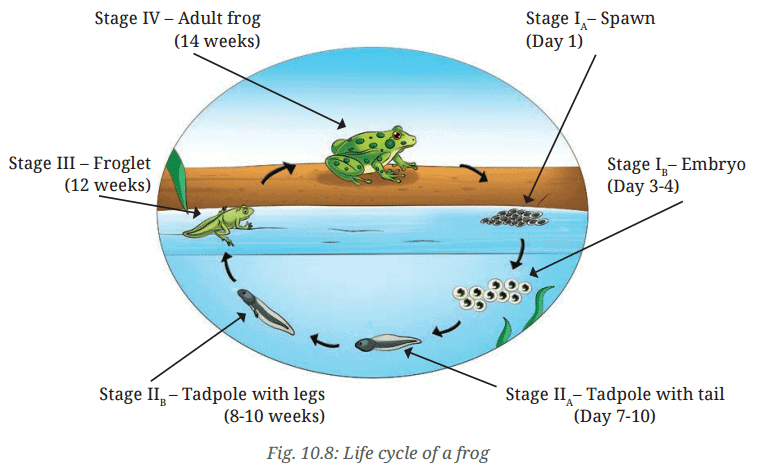
Q: Observe the features of all the stages of a frog shown in Fig. 10.7. How will you decide the sequence of the given stages (A, B, C, D, E, F)?
Ans: You will find four stages in the life cycle of a frog—the egg stage, which progresses to the embryo stage; the tadpole stage, consisting of an early stage with a tail and no legs, and a late stage with hind legs; the froglet stage, and the adult frog stage.
Q: Record these changes in Table 10.5.
Ans: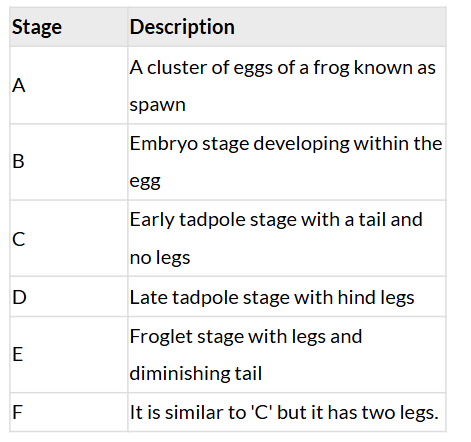
Ans: The life cycle of a frog includes the egg stage, which progresses to the embryo stage; the tadpole stage, consisting of an early stage with a tail and no legs, and a late stage with hind legs; the froglet stage, and the adult frog stage.
Q: How are these eggs of a frog different from the other eggs that you may have seen?
Ans: These eggs of a frog are different as they are a white jelly-like substance known as spawn, attached to plants or floating on the surface of water.
Q: Which stage has the shortest duration?
Ans: The froglet stage has the shortest duration.
Q: Is there a change in the habitat during the various stages in the life cycle of a frog?
Ans: Tadpoles grow gradually and start looking like little frogs called froglets. They still live in water but begin to spend some time on land. They become fully developed adult frogs who live both in water and on land.
Q: How do the special features support that stage?
Ans: Tadpoles develop legs but still have tails. Tails help them swim in water. They continue to grow and lose their tails completely. Their legs become strong to help them jump and land.
|
69 videos|288 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Living Creatures: Exploring Their Characteristics - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the key characteristics of living creatures? |  |
| 2. How do we classify living organisms? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of studying living creatures in science? |  |
| 4. How do living creatures adapt to their environment? |  |
| 5. What role do living organisms play in the ecosystem? |  |




















