NCERT Based Activity: Measurement of Length and Motion | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Activity 5.1: Let us Measure
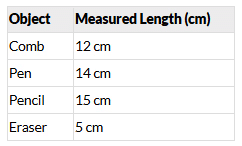
Select some objects around you, such as a comb, a pen, a pencil, and an eraser to measure their lengths. Measure their lengths one by one using a metre scale and note down the measurements in Table 5.2. Measuring Lengths
Measuring Lengths
 Conclusion:
Conclusion:- Measurement requires a fixed standard unit like centimetres or metres.
- Using different body parts (handspan, foot length) can give inconsistent results.
Q: Compare the lengths measured by you with that of your friends. Are the measured lengths the same or slightly different? If not the same, discuss the possible reasons for the differences.
Ans:
The measured lengths may be slightly different due to factors like:
- Measurement Technique: Variations in where and how the scale is read.
- Scale Alignment: Misalignment of the object with the scale.
- Human Error: Differences in reading accuracy.
- Different Tools: Using different measuring instruments (ruler vs. metre scale).
- Scale Calibration: Slight variations in scale accuracy.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature changes or material expansion.
Activity 5.2: Let us explore
Look around and prepare a list of five objects that are in motion and five objects that are at rest. Record your observations in Table 5.3. Think about how you decided whether an object was in motion or at rest. Write your explanation (justification) in Table 5.3.
 Table 5.3: Observing things around you
Table 5.3: Observing things around you
Compare and analyse your justifications. How can one decide if an object is in motion or at rest?
Ans: 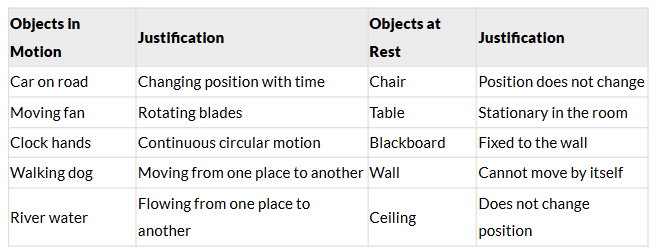
Conclusion:
- Objects in motion change position over time relative to a reference point.
- Objects at rest do not change position relative to a reference point
Activity 5.3: Let us explore
- Take an eraser and drop it from a certain height.
- Observe its motion.
- Does it move along a straight line? When an orange drops from the tree, does it move in a straight line? Have you seen the Republic Day parade? Recall the march-past of students during the parade. Do they move on a straight-line path? When a heavy box is pushed, it may also move along a straight line (Fig. 5.14).
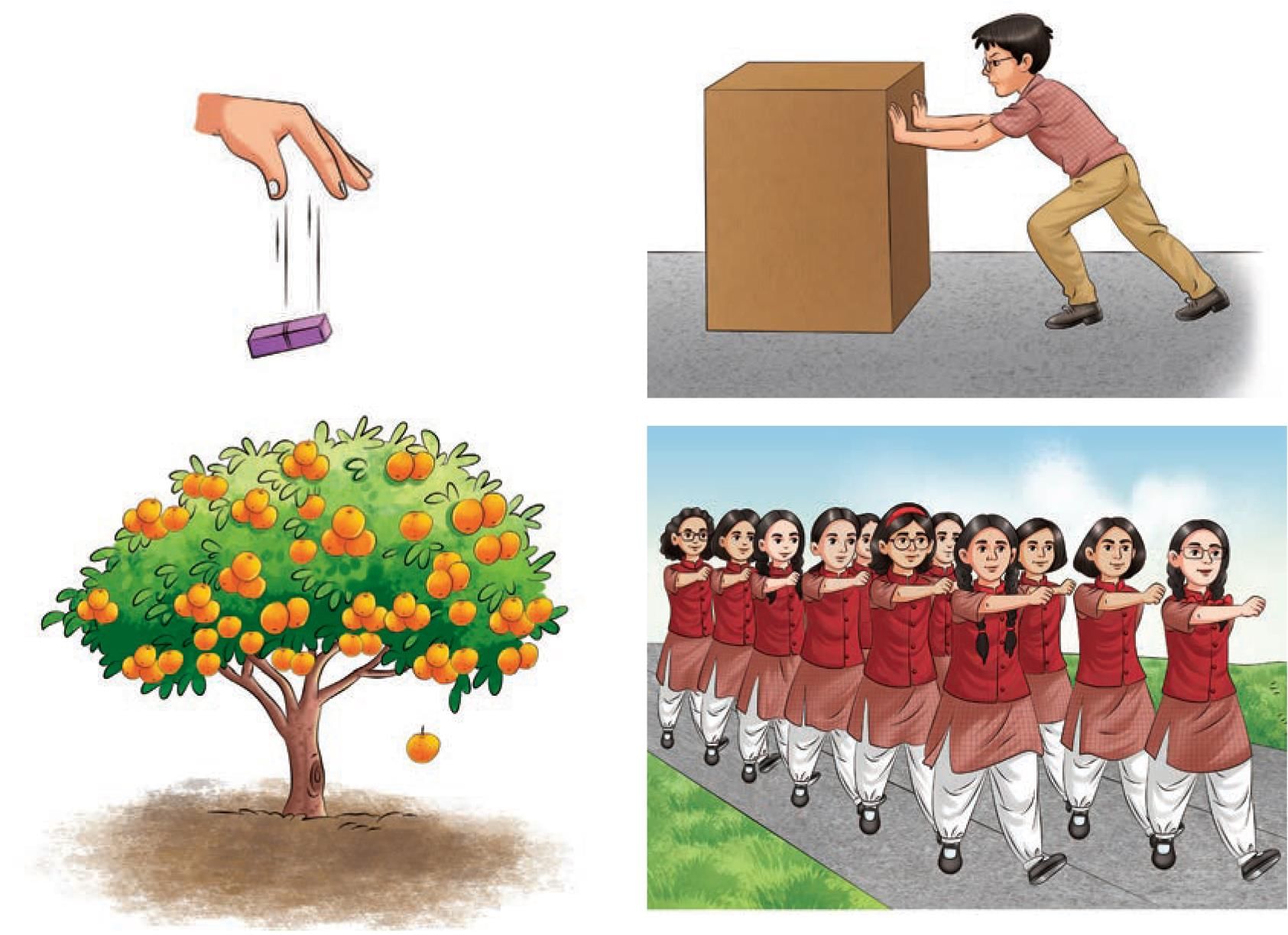 Fig. 5.15: Circular motion
Fig. 5.15: Circular motion
But do things always move along a straight line? You might have enjoyed playing on swings and merry-go-rounds. Are these types of motion also linear motion?
Ans: 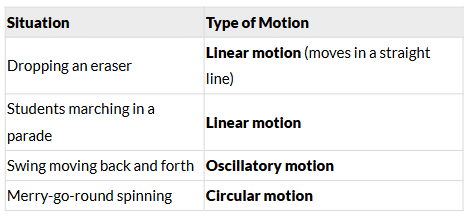
Conclusion:
- Linear motion: When an object moves in a straight path.
- Circular motion: When an object moves in a circular path.
- Oscillatory motion: When an object moves back and forth.
Activity 5.4: Let us investigate
- Tie an eraser (or a potato) at one end of a thread.
- Hold the other end of the thread with your hand and whirl it (Fig. 5.15).
- Observe its motion.
- Is the motion of the eraser the same as that of a merry-go-round?
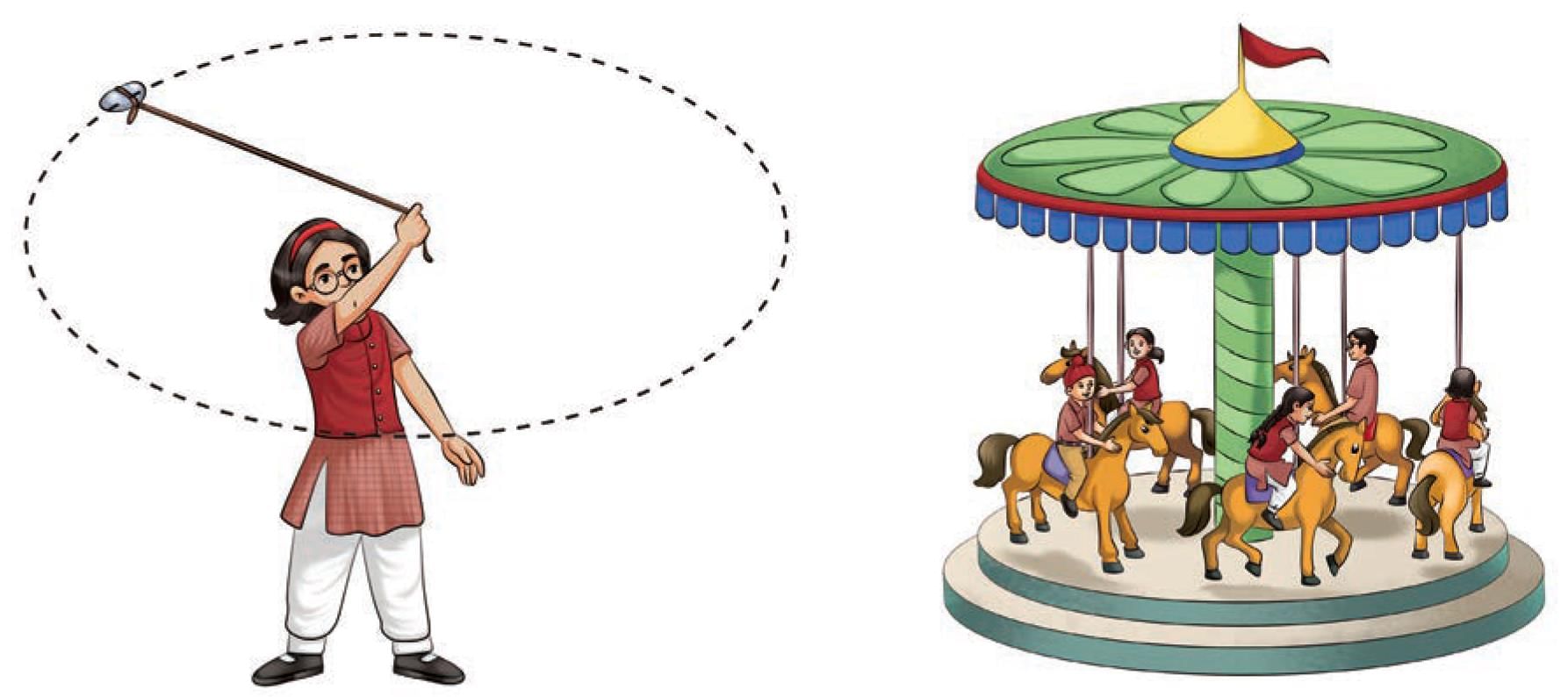 Fig. 5.15: Circular motionAns:
Fig. 5.15: Circular motionAns:
Observation:
- The eraser moves in a circular path around the centre.
Conclusion:
- Circular motion occurs when an object moves around a fixed point.
- Examples: Ferris wheel, spinning fan blades, planets orbiting the sun
Activity 5.5: Let us investigate
- Tie an eraser (or a potato) at one end of a thread.
- Hang the eraser by holding the other end of the thread (Fig. 5.16). Keep your hand steady.
- Using the other hand, take the eraser slightly to one side and then release (Fig. 5.16).
- Does it start moving to and fro? Is its motion similar to the motion of a swing?
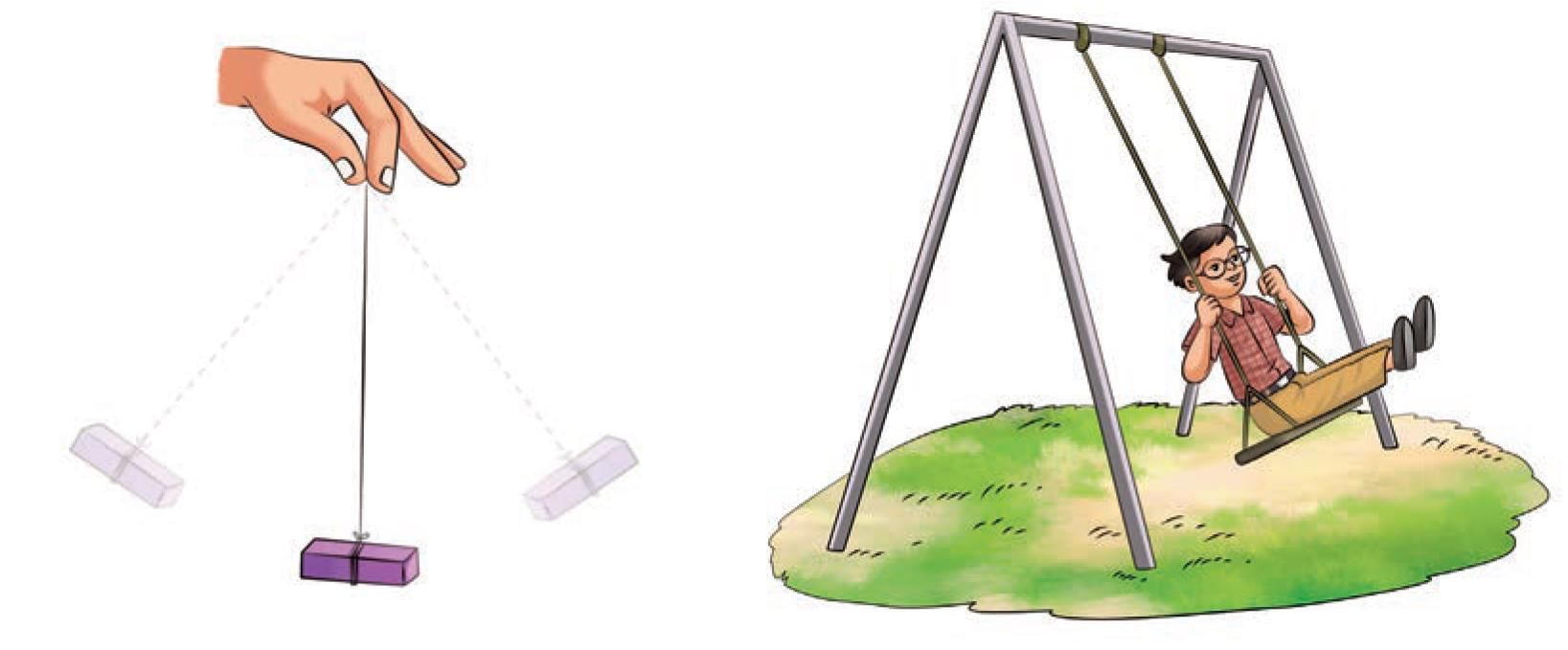 Fig. 5.16: Oscillatory motion
Fig. 5.16: Oscillatory motion
Ans:
Observation:
- The eraser moves to and fro about its original position.
Conclusion:
- Oscillatory motion occurs when an object moves back and forth.
- Examples: Pendulum, swing, vibrating guitar string.
Activity 5.6: Let us investigate
- Take a thin metal strip of about 50 cm long.
- Hold its one end pressed to a table. You may use a few books or a brick to hold it (Fig. 5.17).
- Press the free end of the strip slightly and let it go.
- Observe the motion of this end of the strip. Does it move up and down? This is also an example of oscillatory motion.
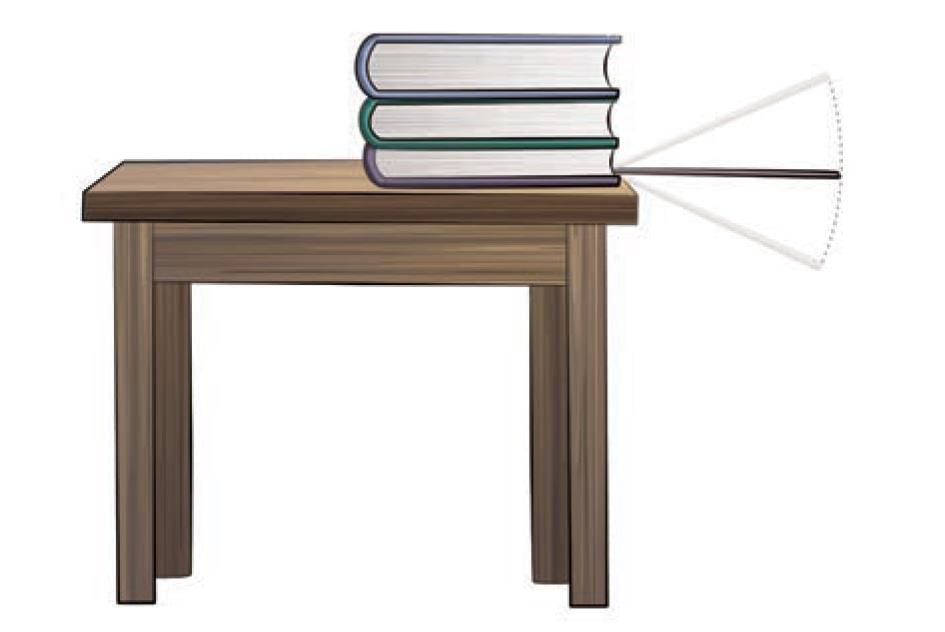 Fig. 5.17: Oscillatory motion of a metal strip
Fig. 5.17: Oscillatory motion of a metal strip
Ans:
Observation:
- The free end of the strip moves up and down repeatedly.
Conclusion:
- Oscillatory motion can occur in flexible objects.
- Examples: Guitar strings, trampoline, ruler flicked on a table edge.
Activity 5.7: Let us identify
- Look at the picture of a children’s park (Fig. 5.18) or visit a children’s park.
- Observe different kinds of motions. Classify them as linear, circular or oscillatory motion.
- List them in Table 5.4. Give your justification for why you put each in a certain category.
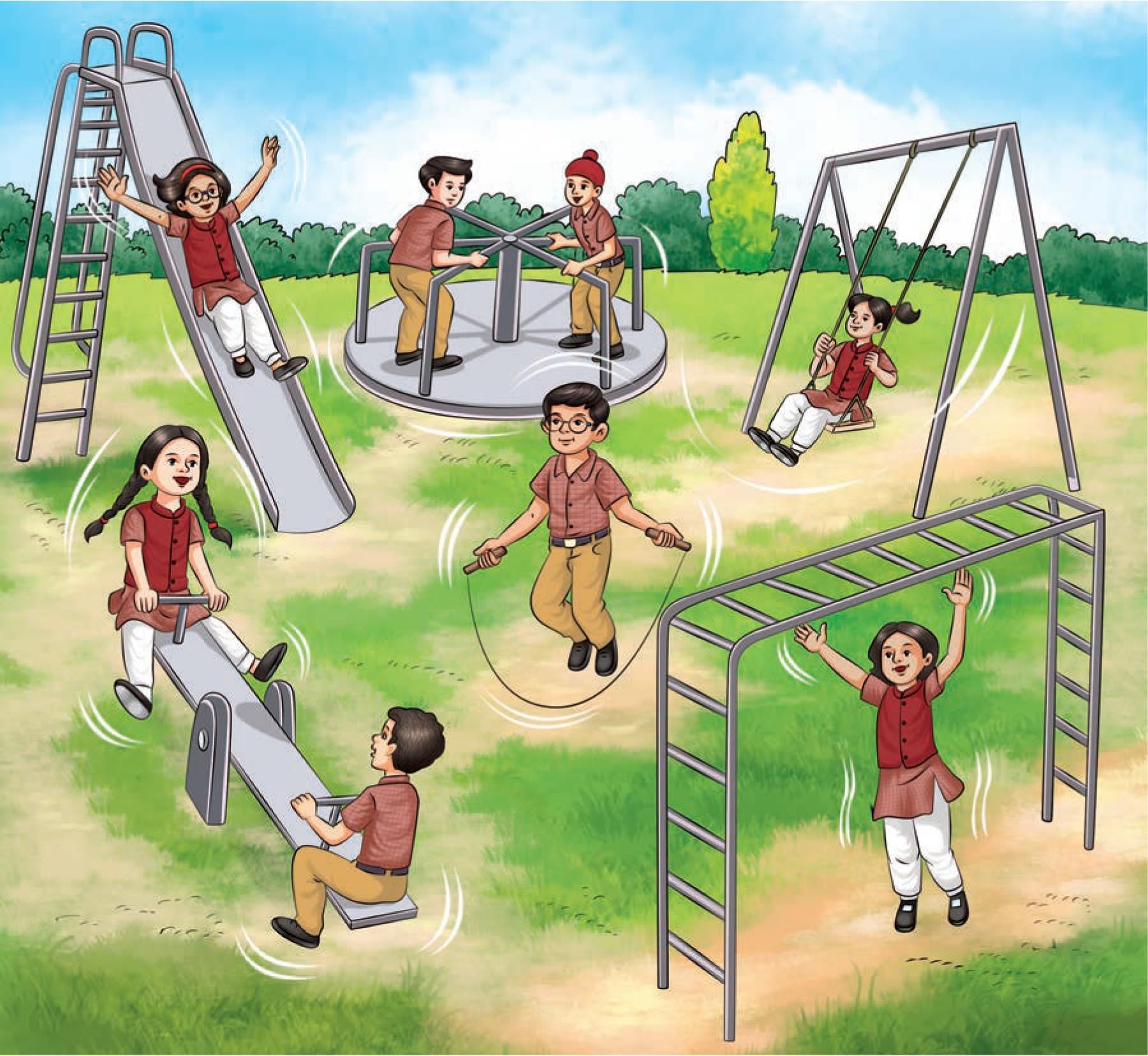 Fig. 5.18: Types of motion observed in a children’s park
Fig. 5.18: Types of motion observed in a children’s park
 Table 5.4: Types of Motion
Table 5.4: Types of Motion
Ans: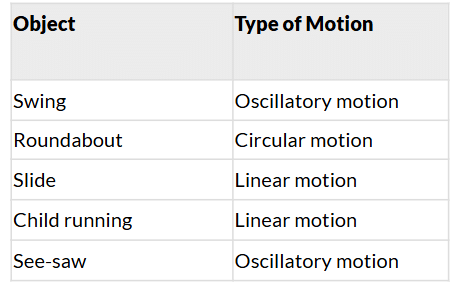
Conclusion:
- Different objects show different types of motion.
- Some motions are periodic (repeat at regular intervals).
|
69 videos|289 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Measurement of Length and Motion - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of motion explored in the activities? |  |
| 2. How can I measure the length of a curved line accurately? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of using a bicycle wheel to estimate distance? |  |
| 4. How can I measure the height of a friend accurately? |  |
| 5. What is oscillatory motion, and how is it demonstrated in the activities? |  |
















