Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT > NCERT Based Activity: Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones
NCERT Based Activity: Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Activity 6.1: Let us try and find out
- Take two transparent glass or plastic pipes of the same length (about 25 cm), but of different diameters, as shown in Fig. 6.5.
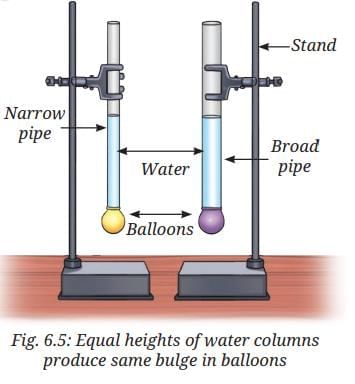
- Take two good-quality rubber balloons. Attach them to one end of each pipe.
- Clamp the pipes on a stand as shown in Fig. 6.5.
- Now, fill both the pipes with water up to the same level about halfway.
- Observe what happens to the balloons.
- Do both balloons bulge? Do they bulge to the same extent?
Answer: Both balloons bulge to the same extent. This happens because the pressure exerted by the water column is responsible, and equal water column heights produce equal bulges despite different pipe diameters. - Pour some more water in any one of the pipes used in Fig. 6.5. Observe the bulge of the balloon. Repeat this process a few times, adding more water each time and noting the extent of bulge as shown in Fig. 6.6.
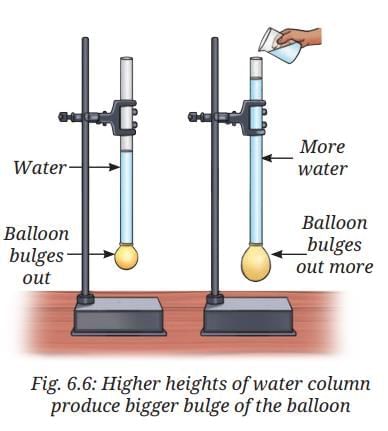
- Do you see any relation between the amount of bulge of the rubber balloon and the height of the water column in the pipe?
Answer: The bulge of the balloon increases as the height of the water column increases. This indicates that the pressure at the bottom of the pipe increases with the height of the water column. - What will happen to the bulge of the balloon if we increase the height of the water column?
Answer: The bulge of the balloon will increase if the height of the water column is increased, as the pressure exerted by the liquid depends on the height of its column. - Suppose you are living on the second floor of a three-storeyed building and an overhead water tank is placed on the top floor. Will you or your friend on the first floor receive a more powerful stream of tap water? Give reasons.
Answer: The friend on the first floor will receive a more powerful stream of tap water. This is because water pressure increases with depth (height of the water column above the point). Since the first floor is at a lower level than the second floor, the height of the water column above it is greater. Thus, the water pressure on the first floor tap is higher, giving a stronger stream.
Activity 6.2: Let us find out
- Take a used plastic bottle and remove its cap. Make four small holes near the bottom around the sides using a needle or a nail. Make sure that the holes are at the same height from the bottom as shown in Fig. 6.7. (If you find it difficult to make a hole, you can slightly heat the needle and poke it to make holes.)
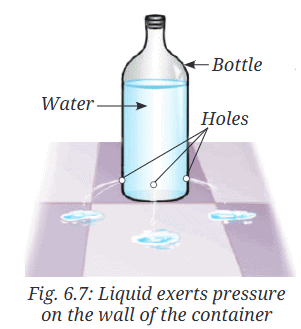
- Seal the holes with a tape and fill the bottle with water.
- Now, remove the tape from all holes at the same time.
- What do you observe?
Answer: Water flows out through the holes on the sides of the bottle, indicating that water exerts pressure on the sides of the container.
Activity 6.3: Let us explore
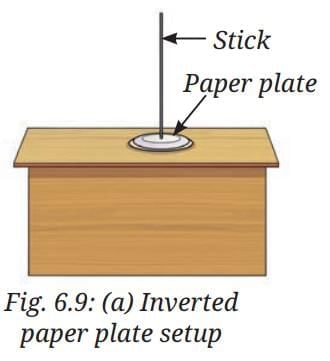
- Take a paper plate, invert it and attach a stick to it as shown in Fig. 6.9a. Place it on a plain surface.
- Take two identical sheets of chart paper about 70 cm × 56 cm each. Fold one sheet twice and make a hole in the centre of the folded chart paper sheet — big enough for the stick to come out. Place the folded sheet on top of the inverted paper plate as shown in Fig. 6.9b.

- Now, try to lift the paper plate covered with a folded sheet using the stick.
- Observe how much effort is needed to lift it.
- Now, place the second unfolded chart paper sheet in place of the folded sheet. Make a hole at the centre of this chart paper for the stick to pass through. Cover the paper plate with the unfolded chart paper as shown in Fig. 6.9c.
- Lift the paper plate again and feel the effort needed in doing so.
- In which case is the lifting easier, with the folded or the unfolded chart paper covering the paper plate?
Answer: Lifting is easier with the folded chart paper covering the paper plate. More effort is needed with the unfolded chart paper due to the increased area, indicating that air exerts pressure that increases with the area of the covering sheet.
Activity 6.4: Let us perform
- Take a good-quality rubber sucker. Press it firmly against a smooth flat surface (Fig. 6.11).

- Do you realize that it sticks to the surface?
Answer: The sucker sticks to the surface and is difficult to pull off because pressing it removes most of the air between its cup and the surface, reducing the air pressure inside. - Now, try to pull it off. Do you find it difficult to pull it off?
Answer: The higher atmospheric pressure outside keeps it stuck, and a strong force is needed to overcome this pressure difference.
Activity 6.5: Let us observe
- Take two similar balloons made of thin rubber, and a drinking straw.
- Insert one end of the straw into one balloon and secure it with a rubber band or thread.
- Now inflate the second balloon and hold its mouth with your fingers, so that air does not escape.
- Insert the free end of the straw into the neck of the inflated balloon and secure it with a rubber band or thread. Make sure that the air does not leak from the balloon as the straw is inserted in it. Now you have one end of the straw inside the inflated balloon and the other end inside the uninflated balloon as shown in Fig. 6.12.
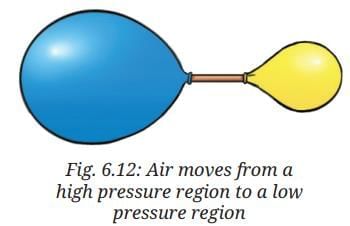
- Predict what would happen to the balloons.
- Observe what happens to both the balloons. Did it happen as predicted? Do you observe any change in the size of the balloons? Write down your observations.
Answer: The inflated balloon decreases in size, and the uninflated balloon increases in size as air moves from the high-pressure inflated balloon to the low-pressure uninflated balloon. The flow stops when both balloons attain almost the same size due to equalized pressure.
What can be the reason for the change in the sizes of the balloons?
Answer: The change occurs because air moves from a region of high air pressure (inflated balloon) to a region of low air pressure (uninflated balloon) until the pressures equalize.
Activity 6.6: Let us observe
- Take two balloons of the same size.
- Inflate both balloons and tie strings to them.
- Hang the two balloons from a stick, leaving a gap of 6–10 cm (Fig. 6.13).
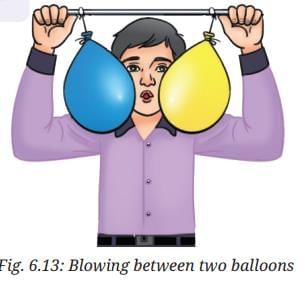
- Now, blow air into the narrow space between the balloons.
- What happens to the balloons? Note down your observations.
- Now blow harder and observe.
Answer: The balloons move towards each other when air is blown between them, creating a low-pressure area. Blowing harder increases the speed at which they approach each other, indicating that high-speed winds are accompanied by reduced air pressure.
The document NCERT Based Activity: Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
59 videos|235 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the definition of pressure in the context of weather and climate? |  |
Ans. Pressure in meteorology refers to the weight of the air above a specific point on the Earth's surface. It is typically measured in millibars (mb) or inches of mercury (inHg). High pressure indicates descending air, leading to clear skies, while low pressure suggests rising air, which can result in clouds and precipitation.
| 2. How do winds form and what factors influence their direction? |  |
Ans. Winds form due to the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun, causing differences in air pressure. The primary factors influencing wind direction include the Coriolis effect, which causes winds to curve due to the Earth's rotation, and local geographical features such as mountains and valleys which can channel wind flows.
| 3. What roles do storms play in the Earth's weather system? |  |
Ans. Storms are crucial for the Earth's weather system as they redistribute heat and moisture across the planet. They can bring much-needed rainfall to dry areas, help in regulating temperatures, and contribute to the overall balance of ecosystems. However, they can also lead to extreme weather conditions that may cause damage and disrupt human activities.
| 4. What are cyclones, and how do they develop? |  |
Ans. Cyclones are large-scale air mass systems that rotate around a center of low atmospheric pressure. They develop over warm ocean waters, where the heat and moisture from the water surface increase the air temperature, leading to rising air and the formation of clouds and storms. The Coriolis effect helps in the rotation of these systems.
| 5. How can we observe and measure changes in weather patterns over time? |  |
Ans. Changes in weather patterns can be observed using various tools and technologies, such as weather satellites, radar systems, and ground-based weather stations. Meteorologists analyze data collected from these instruments to identify trends and variations in temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation, allowing for accurate forecasting and understanding of climate change.
Related Searches
















