NCERT Exemplar: Human Health & Diseases | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Q.1. The term 'Health' is defined in many ways. The most accurate definition of the health would be:
(a) Health is the state of body and mind in a balanced condition
(b) Health is the reflection of a smiling face
(c) Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being
(d) Health is the symbol of economic prosperity.
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Health is not just the absence of disease. It is a state of complete physical, mental, social and psychological well-being.
Q.2. The organisms which cause diseases in plants and animals are called:
(a) Pathogens
(b) Vectors
(c) Insects
(d) Worms
Ans. (a)
Solution.
A wide range of organisms belonging to bacteria, viruses, fungi protozoans, helminthes, etc., could cause diseases in man. Such disease causing organisms are called pathogens.
Q.3. The clinical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
(a) ELISA
(b) ESR
(c) PCR
(d) Widal
Ans. (d)
Solution.
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is Widal-Test.
Q.4. Diseases are broadly grouped into infectious and non-infectious diseases.
In the list given below, identify the infectious diseases.
i. Cancer
ii. Influenza
iii. Allergy
iv. Small pox
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) iii and iv
(d) ii and iv
Ans. (d)
Solution.
| Non infectious diseases | Infectious diseases |
| Cancer | Influenza |
| Allergy | Small Pox |
Q.5. The sporozoites that cause infection when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are formed in:
(a) liver of the person
(b) RBCs of mosquito
(c) salivary glands of mosquito
(d) Intestine of mosquito
Ans. (d)
Solution.
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person being are formed in intestine of mosquito.
Q.6. The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by:
(a) House fly
(b) Aedes mosquito
(c) Cockroach
(d) Female Anopheles
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Dengue and chikunguniya are transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes.
Q.7. Many diseases can be diagnosed by observing the symptoms in the patient. Which group of symptoms are indicative of pneumonia?
(a) Difficulty in respiration, fever, chills, cough, headache
(b) Constipation, abdominal pain, cramps, blood clots
(c) Nasal congestion and discharge, cough, constipation, headache
(d) High fever, weakness, stomach pain, loss of appetite and constipation
Ans. (a)
Solution.
- Difficulty in respiration, fever, chills, cough, headache: Pneumonia
- Constipation, abdominal pain, cramps, blood clots: Amoebiasis
- Nasal congestion and discharge, cough, sorethroat, headache: Common cold
- High fever, weakness, stomach pain, loss of appetite and constipation: Typhoid
Q.8. Cancer causing genes are called:
(a) Structural genes
(b) Expressor genes
(c) Oncogenes
(d) Regulatory genes
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Oncogenes are the cancer causing genes.
Q.9. In malignant tumors, the cells proliferate, grow rapidly and move to other parts of the body to form new tumors. This stage of disease is called:
(a) Metagenesis
(b) Metastasis
(c) Teratogenesis
(d) Mitosis
Ans. (b)
Solution.
In malignant tumors, the cells proliferate, grow rapidly and move to other parts of the body to form new tumors. This stage of disease is called metastasis.
Q.10. When an apparently healthy person is diagnosed as unhealthy by a psychiatrist, the reason could be that:
(a) The patient was not efficient at his work
(b) The patient was not economically prosperous
(c) The patient shows behavioural and social maladjustment
(d) He does not take interest in sports
Ans. (c)
Solution.
When an apparently healthy person- is diagnosed as unhealthy by a psychiatrist, the reason could be that the patient shows behavioural and social maladjustment.
Q.11. Which of the following are the reason(s) for Rheumatoid arthritis? Choose the correct option.
i. The ability to differentiate pathogens or foreign molecules from self cells increases.
ii. Body attacks self cells
iii. More antibodies are produced in the body
iv. The ability to differentiate pathogens or foreign molecules from self cells is lost
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iv
(c) iii and iv
(d) i and iii
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune diseases in which
- Body attacks self cells
- The ability to differentiate pathogens or foreign molecules from self cells is lost
Q.12. AIDS is caused by HIV. Among the following, which one is not a mode of transmission of HIV?
(a) Transfusion of contaminated blood
(b) Sharing the infected needles
(c) Shaking hands with infected persons
(d) Sexual contact with infected persons
Ans. (c)
Solution.
- Transfusion of contaminated blood
- Sharing the infected needles
- Sexual contact with infected persons
Q.13. 'Smack' is a drug obtained from the:
(a) Latex of Papaver somniferum
(b) Leaves of Cannabis sativa
(c) Flowers of Dhatura
(d) Fruits of Erythroxyl coca
Ans. (a)
Solution.
- Smack’ is a drug obtained from the latex of Papaver somniferum.
- Smack are brown sugar, the common name of Heroin.
- Heroin is obtained by acetylation of morphine.
Q.14. The substance produced by a cell in viral infection that can protect other cells from further infection is:
(a) Serotonin
(b) Colostrum
(c) Interferon
(d) Histamine
Ans. (c)
Solution.
The substance produced by a cell in viral infection that can protect other cells from further infection is interferon.
Q.15. Transplantation of tissues/organs to save certain patients often fails due to rejection of such tissues/organs by the patient. Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections?
(a) Auto-immune response
(b) Humoral immune response
(c) Physiological immune response
(d) Cell-mediated immune response
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Transplantation of tissues/organs to-save certain patients often fails due to rejection of such tissues/organs by the patient. Cell-mediated immune response is responsible for such rejections.
Q.16. Antibodies present in colostrum which protect the new born from certain diseases is of
(a) Ig G type
(b) Ig A type
(c) Ig D type
(d) Ig E type
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Antibodies present in colostrum which protect the new bom from certain diseases is of Ig A type.
Q.17. Tobacco consumption is known to stimulate secretion of adrenaline and nor-adrenaline. The component causing this could be:
(a) Nicotine
(b) Tannic acid
(c) Curamin
(d) Catechin
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Tobacco consumption is known to stimulate secretion of adrenaline and nor-adrenaline. The component causing this could be nicotine. Morphine, cocaine, codeine and nicotine are all alkaloids.
Q.18. Antivenom against snake poison contains:
(a) Antigens
(b) Antigen-antibody complexes
(c) Antibodies
(d) Enzymes
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Anti-venom against snake poison contains antibodies.
Q.19. Which of the following is not a lymphoid tissue?
(a) Spleen
(b) Tonsils
(c) Pancreas
(d) Thymus
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Spleen, Tonsils and Thymus are lymphoid tissue while pancreas is mixed gland.
Q.20. Which of the following glands is large sized at birth but reduces in size with ageing?
(a) Pineal
(b) Pituitary
(c) Thymus
(d) Thyroid
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Thymus glands is large sized at birth but reduces in size with ageing.
Q.21. Haemozoin is a:
(a) Precursor of hemoglobin
(b) Toxin released from Streptococcus infected cells
(c) Toxin released from Plasmodium infected cells
(d) Toxin released from Haemophilus infected cells
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Haemozoin is a toxin released from Plasmodium infected cells.
Q.22. Which of the following is not the causal organism for ringworm?
(a) Microsporum
(b) Trichophyton
(c) Epidermophyton
(d) Macrosporum
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton are the causal organism for ringworm while Macrosporum is a brown alga.
Q.23. A person with sickle cell anemia is
(a) More prone to malaria
(b) More prone to typhoid
(c) Less prone to malaria
(d) Less prone to typhoid
Ans. (c)
Solution.
A person with sickle cell anemia is less prone to malaria.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Certain pathogens are tissue/organ specific. Justify the statement with suitable examples.
Ans. Salmonella typhi causes typhoid and infects small intestine while intestinal endoparasite causes amoebic dysentery and infects large intestine.
Q.2. The immune system of a person is suppressed. In the ELISA test, he was found positive to a pathogen.
(a) Name the disease the patient is suffering from.
(b) What is the causative organism?
(c) Which cells of body are affected by the pathogen?
Ans. (a) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
(b) Human Immuno deficiency virus (HIV)
(c) Helper T-lymphocytes (TH or T4)
Q.3. Where are B-cells and T-cells formed? How do they differ from each other?
Ans. Both B-cells and T-cells are formed in bone marrow. B-cells matures in bone marrow while T-cells matures in thymus. B-cells provides humoral immunity and T-cells provides cell mediated immunity (CMI).
Q.4. Given below are the pairs of pathogens and the diseases caused by them. Which out of these is not a matching pair and why?
| (a) Virus | common cold |
| (b) Salmonella | typhoid |
| (c) Microsporum | filariasis |
| (d) Plasmodium | malaria |
Ans. Pair is mismatched. Microsporum causes ringworm disease.
Q.5. What would happen to immune system, if thymus gland is removed from the body of a person?
Ans. Thymus is the primary lymphoid organ. In thymus gland, immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. If thymus gland is removed from the body of a person, his immune system becomes weak. As a result the person’s body becomes prone to infectious diseases,
Q.6. Many microbial pathogens enter the gut of humans along with food. What are the preventive barriers to protect the body from such pathogens? What type of immunity do you observe in this case?
Ans. (i) The mucus coating of the epithelium lining of the gut helps in trapping microbes entering the body.
(ii) Saliva in the mouth and hydrochloric acid in gastric juice secreted by stomach prevent microbial growth. This type of immunity is innate immunity.
Q.7. Why is mother's milk considered the most appropriate food for a new born infant?
Ans. Mother’s milk is considered as the most appropriate food for a new born infant because the yellowish fluid colostrum secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation has abundant antibodies (IgA) to protect the infant.
Q.8. What are interferons? How do interferons check infection of new cells?
Ans. Interferons are natural proteins produced by the cells of immune system in response to foreign agents such as viruses, tumor cells and parasites and protect non-infected cells from further infection. Interferons inhibit the viral replication within host cells, activate natural killer cells and macrophages, increases antigen presentation to lymphocytes, and induce the resistance of host cells to viral infection. When the antigen is presented to matching T-cells’ and B-cells, these cells multiply and remove the foreign substance.
Q.9. In the figure, structure of an antibody molecule is shown. Name the parts A, B and C.
Show A, B and C in the diagram.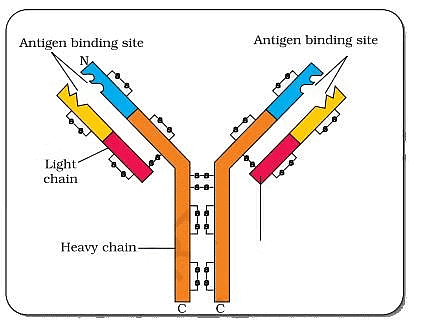 Ans. A — Constant region of heavy chain,
Ans. A — Constant region of heavy chain,
B — Constant region of light chain,
C — Variable region of light and heavy chain
Q.10. If a regular dose of drug or alcohol is not provided to an addicted person, he shows some withdrawal symptoms. List any four such withdrawal symptoms.
Ans. The withdrawal symptoms are:
(a) Anxiety
(b) Shakiness
(c) Nausea
(d) Sweating
Q.11. Why is it that during changing weather, one is advised to avoid closed, crowded and air conditioned places like cinema halls etc.?
Ans. During changing weather, one is advised to avoid closed, crowded and air- conditioned placed like cinema halls, etc., because during this period the infectious agents are more humorous and prevalent to which we are more vulnerable.
Q.12. The harmful allele of sickle cell anemia has not been eliminated from human population. Such afflicted people derive some other benefit. Discuss.
Ans. The harmful alleles get eliminated from population over a period of time, yet sickle cell anaemia is persisting in human population because SCA is a harmful condition which is also a potential saviour from malaria.
Those with the benign sickle trait possess a resistance to malarial infection. The pathogen that causes the disease spends part of its cycle in the red blood cells and triggers an abnormal drop in oxygen levels in the cell. In carriers, this drop is sufficient to trigger the full sickle-cell reaction, which leads to infected cells being rapidly removed from circulation and strongly limiting the infection’s progress. These individuals have a great resistance to infection and have a greater chance of surviving outbreaks. This resistance to infection is the main reason the SCA allele and SCA disease still exist. It is found in greatest frequency in populations where malaria was and is still often a serious problem.
Q.13. Lymph nodes are secondary lymphoid organs. Explain the role of lymph nodes in our immune response.
Ans. Lymph nodes are small solid structures located at different points along the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes trap the microorganisms or other antigens, which happen to get into the lymph and tissue fluid. Antigens trapped in the lymph nodes are responsible for the activation of lymphocytes present there and cause the immune response.
Q.14. Why is an antibody molecule represented as H2L2?
Ans. Each antibody molecule is made of the two heavy chains (H2) and two light chains (L2), hence represented as H2 L2.
Q.15. What does the term 'memory' of the Immune system mean?
Ans. When body encounters a pathogen for the first time produce a response called 1° response. 1° response is of low intensity. When body encounters the same pathogen subsequently then body elicits 2° response. 2° response is highly intensified. This is due to the fact that our body have memory of the first encounter.
Q.16. If a patient is advised Anti Retroviral Therapy, which infection is he suffering from? Name the causative organism.
Ans. The patient is suffering from AIDS. The causative organism for AIDS is HIV (Human Immuno deficiency Virus).
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Differentiate between active immunity and passive immunity.
Ans.
| Active Immunity | Passive Immunity |
| 1. It is produced due to interaction with pathogen or antigen. | 1. It is produced due to pre-formed antibodies. |
| 2. A time gap occurs for development, so it is slow acting. | 2. It develops immediately, so it provides quick immune response. |
| 3. It is long lasting. | 3. It lasts for some time. |
| 4. Antibodies are produced by the body in response to pathogen or antigen. | 4. Antibodies are obtained from out ide. |
Q.2. Differentiate between benign tumor and malignant tumor.
Ans.
- Benign tumors normally remain confined to their original location and do not spread to other parts of the body and cause little damage.
- Malignant tumors are a mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic or tumor cells. Neoplastic cells grow very rapidly, invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues. As these cells actively divide and grow they also starve the normal cells by competing for vital nutrients.
- Cells sloughed from such tumors reach distant sites through blood, and wherever they get lodged in the body, they start a new tumor there. This property called metastasis is the most feared property of malignant tumors.
Q.3. Do you consider passive smoking is more dangerous than active smoking? Why?
Ans. Yes, passive smoking is also dangerous as the active smoking because the person is exposed to the same harmful effects of smoking like emphysema, bronchitis, lung cancer, urinary bladder cancer or even peptic ulcer.
Q.4. “Prevention is better than cure”. Comment
Ans. Prevention is better than cure is true as in same cases the disease is non- curable like AIDS and Hepatitis-B, and in some cases’ the treatment causes financial problems in the family.
Q.5. Explain any three preventive measures to control microbial infections.
Ans. (i) Maintenance of personal and public hygiene is very important for prevention and control of many infectious diseases. Measures for personal hygiene include keeping the body clean; consumption of clean drinking water, food, vegetables, fruits, etc. Public hygiene includes proper disposal of waste and excreta; periodic cleaning and disinfection of water reservoirs, pools, cesspools and tanks and observing standard practices of hygiene in public catering.
(ii) In cases of air-borne diseases such as pneumonia and common cold, in addition to the above measures, close contact with the infected persons or their belongings should be avoided.
(iii) For diseases such as malaria and filariasis that are transmitted through insect vectors, the most important measure is to control or eliminate the vectors and their breeding places. This can be achieved by avoiding stagnation of water in and around residential areas, regular cleaning of household coolers, use of mosquito nets, introducing fishes like Gambusia in ponds that feed on mosquito larvae, spraying of insecticides in ditches, drainage areas and swamps, etc. In addition, doors and windows should be provided with wire mesh to prevent the entry of mosquitoes.
Q.6. In the given flow diagram, the replication of retrovirus in a host is shown.
Observe and answer the following questions.
(a) Fill in (1) and (2)
(b) Why is the virus called retrovirus?
(c) Can the infected cell survive while viruses are being replicated and released?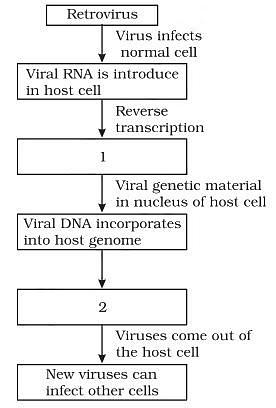 Ans. (a) (i) Viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase.
Ans. (a) (i) Viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase.
(ii) New viral RNA is produced by infected cell.
(b) HIV is called retrovirus because it forms DNA from RNA by reverse transcription.
(c) Yes, infected cell can survive while viruses are being replicated and released.
Q.7. “Maintenance of personal and public hygiene is necessary for prevention and control of many infectious diseases”. Justify the statement giving suitable examples.
Ans. Measures for personal hygiene include keeping the body clean; consumption of clean drinking water, food, vegetables, fruits, etc. Public hygiene includes proper disposal of waste and excreta; periodic cleaning and disinfection of water reservoirs, pools, cesspools and tanks, and observing standard practices of hygiene in public catering. These measures are particularly essential where the infectious agents are transmitted through food and water such as typhoid, amoebiasis and ascariasis.
Q.8. The following table shows certain diseases, their causative organisms and symptoms. Fill the gaps.
| Name of the Disease | Causative organism | Symptoms | |
| (i) | Ascariasis | Ascaris | ____ |
| (ii) | ____ | Trichophyton | Appearance of dry, scaly lesions on various parts of the body |
| (iii) | Typhoid | ____ | High fever, weakness, headache, stomach pain, constipation. |
| (iv) | Pneumonia | Streptococcus pneumoniae | ____ |
| (v) | ____ | Rhino viruses | Nasal congestion and discharge, sorethroat, cough, headache |
| (vi) | Filariasis | ____ | Inflammation in lower limbs |
Ans.
| (i) | Ascariasis | Ascaris | Internal bleeding, muscular pain, fever, anemia and blockage of the intestinal passage |
| (ii) | Ringworm | Trichophyton | Appearance of dry, scaly lesions on various parts of the body |
| (iii) | Typhoid | Salmonella typhi | High fever, weakness, headache, stomach pain, constipation |
| (iv) | Pneumonia | Streptococcus pneumoniae | Fever, chills, cough and headache |
| (v) | Common cold | Rhino viruses | Nasal congestion and discharge, sore throat, cough, headache |
| (vi) | Filariasis | W. bancrofti and W. malayi | Inflammation in lower limbs |
Q.9. The outline structure of a drug is given below.
(a) Which group of drugs does this represent?
(b) What are the modes of consumption of these drugs?
(c) Name the organ of the body which is affected by consumption of these drugs. 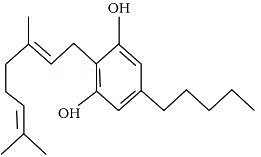 Ans.
Ans.
(a) Cannabinoids
(b) Generally taken by inhalation and oral ingestion
(c) Affect the cardiovascular system of the body
Q.10. Give the full form of CT and MRI. How are they different from each other? Where are they used?
Ans. CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful to detect cancers of the internal organs. Computed tomography uses X-rays to generate a three-dimensional image of the internals of an object. MRI uses strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissue.
Q.11. Many secondary metabolites of plants have medicinal properties. It is their misuse that creates problems. Justify the statement with an example.
Ans. Several plants, fruits and seeds having hallucinogenic properties and have been used for hundreds of years in folk-medicine, religious ceremonies and rituals all over the globe. When these are taken for a purpose other than medicinal use or in amounts/frequency that impairs one’s physical, physiological or psychological functions, it constitutes drug abuse.
Q.12. Why cannabinoids are banned in sports and games?
Ans. As these days cannabinoids are being abused by some sports persons to increase their performance, that is why cannabinoids are banned in sports and games.
Q.13. What is secondary metabolism?
Ans. Secondary metabolism is a term for pathways and small molecule products of metabolism that are not absolutely required for the survival of the organism. Examples of the products include antibiotics and pigments.
Q.14. Drugs and alcohol give short-term 'high' and long-term ‘damages’, Discuss.
Ans. Curiosity, need for adventure and excitement, and experimentation, constitute common causes, which motivate youngsters towards drug and alcohol use. A child’s natural curiosity motivates him/her to experiment. This is complicated further by effects that might be perceived as benefits, of alcohol or drug use. Thus, the first use of drugs or alcohol may be out of curiosity or experimentation, but later the child starts using these to escape facing problems. Of late, stress, from pressures to excel in academics or examinations, has played a significant role in persuading the youngsters to try alcohol and drugs. The perception among youth that it is ‘cool’ or progressive to smoke, use drugs or alcohol, is also in a way a major cause for youth to start these habits. Television, movies, newspapers, internet also help to promote this perception. Other factors that have been seen to be associated with drug and alcohol abuse among adolescents are unstable or unsupportive family structures and peer pressure.
Q.15. Diseases like dysentery, cholera, typhoid etc., are more common in over crowded human settlements. Why?
Ans. Diseases like dysentery, cholera, typhoid etc., are more common in overcrowded human settlements because these are infectious diseases that can transmitted from one person to another. In overcrowded settlements there is more chances of transmission of disease from one person to other.
Q.16. From which plant cannabiniods are obtained? Name any two cannabinoids. Which part of the body is effected by consuming these substances?
Ans. Cannabinoids are obtained from the inflorescence of the plant Cannabis sativa. Marijuana, hashish, charas, ganja are some of the cannabinoids. These chemicals interact with cannabinoid receptors of the body, mainly present in the brain. Cardiovascular system is affected adversely.
Q.17. In the metropolitan cities of India, many children are suffering from allergy/asthma. What are the main causes of this problem. Give some symptoms of allergic reactions.
Ans. Allergy is the exaggerated response of the immune system of certain antigens present in the environment. In metropolitan cities lifestyle is responsible for lowering of immunity and sensitivity to allergens. More polluted environment increases the chances of allergy in children. Some symptoms of allergic reactions are sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing.
Q.18. What is the basic principle of vaccination? How do vaccines prevent microbial infections? Name the organism from which hepatitis B Vaccine is produced.
Ans. The principle of vaccination is based on the property of ’memory’ of the immune system. In vaccination, a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogens or inactivated/live but weakened pathogens is introduced into the body. The antigens generate the primary immune response by producing antibodies. The vaccines also generate the memory B-cells and T-cells. When the vaccinated person is attacked by the same pathogens, the existing memory B-cells or T-cells recognise the antigen quickly and overwhelm the invaders with massive production of lymphocytes and antibodies. Hepatitis B vaccine is produced from yeast.
Q.19. What is cancer? How is a cancer cell different from the normal cell? How do normal cells attain cancerous nature?
Ans. An abnormal and uncontrolled division of cells is termed as Cancer. The cancerous cells are different from the normal cells in the following ways.
| Cancer Cells | Normal Cells |
| 1. Cancer cells divide in an uncontrolled manner. | 1. Normal cells divide in a controlled manner. |
| 2. The cells do not show contact inhibition. | 2. The cells show contact inhibition. |
| 3. Life span is indefinite. | 3. Life span is definite. |
In our body, the growth and differentiation of cells is highly controlled and regulated. The normal cells show a property called contact inhibition.
The surrounding cells inhibits uncontrolled growth and division of cells. The normal cells lose this property and become cancerous cells giving rise to masses of cells called tumors. Transformation of normal cells into cancerous cells is induced by some physical, chemical and biological agents (carcinogens).
Q.20. A person shows strong unusual hypersensitive reactions when exposed to certain substances present in the air. Identify the condition. Name the cells responsible for such reactions. What precaution should be taken to avoid such reactions.
Ans. Allergy. Mast Cells are responsible for such reactions. To avoid such reactions following precautions must be taken:
(i) The use of drugs like antihistamine, adrenalin and steroids quickly reduce the symptoms of allergy.
(ii) Avoid contact with substances to which a person is hypersensitive.
Q.21. For an organ transplant, it is an advantage to have an identical twin. Why?
Ans. Very often, when some human organs like heart, eye, liver, kidney fail to function satisfactorily, transplantation is the only remedy to enable the patient to live a normal life. Then a search begins—to find a suitable donor.
Grafts from just any source—an animal, another primate, or any human beings cannot be made since the grafts would be rejected sooner or later. Tissue matching, blood group matching are essential before undertaking any graft/transplant and even after this the patient has to take immuno-suppresants all his/her life. The body is able to differentiate ‘self ’ and ‘nonself’ and the cell-mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection. In an identical twin there is no chance of rejection of transplanted organ, so it is advantageous.
Q.22. What are lifestyle diseases? How are they caused? Name any two such diseases.
Ans. Lifestyle diseases are defined as diseases linked with the way people live their life. This is commonly caused by alcohol, drug and smoking abuse as well as lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating. Diseases that impact on our lifestyle are heart disease, stroke and obesity.
Q.23. If there are two pathogenic viruses, one with DNA and other with RNA, which would mutate faster? And Why?
Ans. Both DNA and RNA are able to mutate. In fact, RNA being unstable, mutate at a faster rate. Consequently, viruses having RNA genome and having shorter life span mutate and evolve faster.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Represent schematically the life cycle of a malarial parasite.
Ans.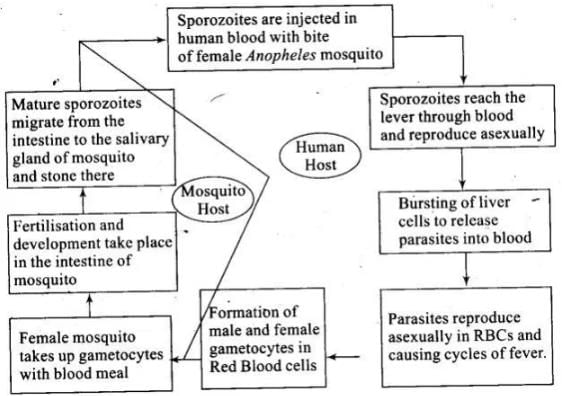
Q.2. Compare the life style of people living in the urban areas with those of rural areas and briefly describe how the life style affects their health.
Ans. Urban areas
The social environment: Urban environments are more likely to see higher rates of crime and violence.
The physical environment: In densely populated urban areas, there is often a lack of facilities and outdoor areas for exercise. In addition, air quality is often lower in urban environments which can contribute to chronic diseases such as asthma. In the developing world, urban dwellers often live in large slums which lack basic sanitation and utilities such as water and electricity. Access to health and social service: Persons of lower socioeconomic status are more likely to live in urban areas and are more likely to lack health insurance. The high prevalence of individuals without health insurance or citizenship creates a greater burden on available systems.
Rural areas
The social environment: Rural dwellers have significantly poorer health status than urban elders. Also, rural residents smoke more, exercise less, have less nutritional diets.
The physical environment: Rural women especially less educated women, are more sedentary than urban women. While poor air quality and crime rates are likely to be less of an issue in rural areas, insufficiencies in the built environment make it difficult for rural residents to exercise and maintain healthy habits.
Access to health and social service: Evidence indicates that rural residents have limited access to health care. Some rural areas have a higher proportion of uninsured and individually insured residents than urban areas.
Q.3. Why do some adolescents start taking drugs. How can this be avoided?
Ans. The reasons why adolescents and youngsters take to consumption of drugs are:
(i) Curiosity of child motivates him/her to experiment.
(ii) Need for adventure and excitement.
(iii) Peer group pressure
(iv) Desire to do more physical and mental work.
(v) To overcome frustration and depression, due to failure in examinations or in other activities.
(vi) Unstable or unsupportive family structures.
The following measures can be taken to avoid taking drugs:
(i) Avoid undue pressure on child to perform beyond his/her capability in studies, sports ox any other activities.
(ii) Education and counselling are very important to face problem of stress and failure in life.
(iii) Seeking help from parents, elders and peers. This would help the young to share their feelings and concern.
(iv) Looking for danger signs and taking appropriate measures to treat them.
(v) Seeking professional and medical help for de-addiction and rehabilitation.
Q.4. In your locality, if a person is addicted to alcohol, what kind of behavioural changes do you observe in that person? Suggest measures to over come the problem.
Ans. The immediate adverse effects of drugs and alcohol abuse are manifested in the form of reckless behaviour, vandalism and violence. Excessive doses of drugs may lead to coma and death due to respiratory failure, heart failure or cerebral hemorrhage. A Combination of drugs or their intake along with alcohol generally results in overdosing and even deaths. The most common warning signs of drug and alcohol abuse among youth include drop in academic performance, unexplained absence from school/college, lack of interest in personal hygiene, withdrawal, isolation, depression,, fatigue, aggressive and rebellious behaviour, deteriorating relationships with family and friends, loss of interest in hobbies, change in sleeping and eating habits, fluctuations in weight, appetite, etc. There may even be some far-reaching implications of drug/alcohol abuse. If an abuser is unable to get money to buy drugs/alcohol he/she may turn to stealing. The adverse effects are just not restricted to the person who is using drugs or alcohol. At times, a drug/ alcohol addict becomes the cause of mental and financial distress to his/her entire family and friends.
The age-old adage of ‘prevention is better than cure’ holds true here also. It is also true that habits such as smoking, taking drug or alcohol are more likely to be taken up at a young age, more during adolescence. Hence, it is best to identify the situations that may push an adolescent towards use of drugs or alcohol, and to take remedial measures well in time. In this regard, the parents and the teachers have a special responsibility. Parenting that combines with high levels of nurturance and consistent discipline, has been associated with lowered risk of substance (alcohol/drugs/tobacco) abuse. Some of the measures mentioned here would be particularly useful for prevention and control of alcohol and drugs abuse among adolescents.
Q.5. What are the methods of cancer detection? Describe the common approaches for treatment of cancer.
Ans. Cancer detection and diagnosis: Early detection of cancers, is essential as it allows the disease to be treated successfully in many cases. Cancer detection is based on biopsy and histopathological studies of the tissue and blood and bone marrow tests for increased cell counts in the case of leukemias. In biopsy, a piece of the suspected tissue cut into thin sections is stained and examined under microscope (histopathological studies) by a pathologist. Techniques like radiography (use of X-rays), CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful to detect cancers of the internal organs. Computed tomography uses X-rays to generate a three-dimensional image of the internals of an object. MRI uses strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissue.
- Antibodies against cancer-specific antigens are also used for detection of certain cancers. Techniques of molecular biology can be applied to detect genes in individuals with inherited susceptibility to certain cancers. Identification of such genes, which predispose an individual to certain cancers, may be very helpful in prevention of cancers. Such individuals may be advised to avoid exposure to particular carcinogens to which they are susceptible (e.g., tobacco smoke in case of lung cancer).
- Treatment of cancer: The common approaches for treatment of cancer are surgery, radiation therapy and immunotherapy. In radiotherapy, tumor cells are irradiated lethally, taking proper care of the normal tissues surrounding the-tumor mass. Several chemotherapeutic drugs are used to kill cancerous cells. Some of these are specific for particular tumors. Majority of drugs have side effects like hair loss; anemia, etc. Most cancers are treated by combination of surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Tumor cells have been shown to avoid detection and destruction by immune system. Therefore, the patients are given substances called biological response modifiers such as a-interferon which activates their immune system and helps in destroying the tumor.
Q.6. Drugs like LSD, barbiturates, amphetamines, etc., are used as medicines to help patients with mental illness. However, excessive doses and abusive usage are harmful. Enumerate the major adverse effects of such drugs in humans.
Ans. Drugs like barbiturates, amphetamines, benzodiazepines, and other similar drugs, that are normally used as medicines to help patients cope with mental illnesses like depression and insomnia, are often abused. Morphine is a very effective sedative and painkiller, and is very useful in patients who have undergone surgery. Several plants, fruits and seeds having hallucinogenic properties have been used for hundreds of years in folk-medicine, religious ceremonies and rituals all over the globe. When these are taken for a purpose other than medicinal use or in amounts/frequency that impairs one’s physical, physiological or psychological functions, it constitutes drug abuse.
Q.7. What is Pulse Polio Programme of Government of India? What is OPV?
Why is it that India is yet to eradicate Polio?
Ans. Pulse Polio is an immunisation campaign established by the government of India to eliminate poliomyelitis (polio) in India by vaccinating all children under the age of five years against the polio virus. The project fights poliomyelitis through a large-scale pulse vaccination programme and monitoring for polio cases.
- In 1995, following the Global Polio Eradication Initiative of the World Health Organization (1988), India launched Pulse Polio immunisation program with Universal Immunization Program which aimed at 100% coverage.
- The last reported cases of wild polio in India were in West Bengal and Gujarat on 13 January 2011. On 27 March 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared India a polio free country, since no cases of wild polio had been reported in for three years.
- Polio vaccines are the vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio).One type uses inactivated poliovirus and is given by injection (IPV), while the other type uses weakened poliovirus and is given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization recommends all children be vaccinated against polio. The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the world. The oral polio vaccine was developed by Albert Sabin and came into commercial use in 1961.
Q.8. What are recombinant DNA vaccines? Give two examples of such vaccines. Discuss their advantages.
Ans. A recombinant vaccine is a vaccine produced through recombinant DNA technology. This involves inserting the DNA encoding an antigen that stimulates an immune response into bacterial or mammalian cells.
Recombinant DNA technology has allowed the production of antigenic polypeptides of pathogen in bacteria or yeast. Vaccines produced using jthis approach allow large scale production and hence greater availability for immunisation, e.g., hepatitis B vaccine (Recombivax HB) produced from yeast. As of June 2015 one human DNA vaccine had been approved for human use, the single-dose Japanese encephalitis vaccine called IMOJEV, released in 2010 in Australia.
Advantages of recombinant DNA vaccines:
1. No risk for infection
2. Ease of development and production
3. Stability for storage and shipping
4. Cost-effectiveness
5. Expression and purification of recombinant proteins
6. Long-term persistence of immunogen
7. In vivo expression ensures protein more closely resembles normal eukaryotic structure, with accompanying post-translational modifications.
|
78 videos|280 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Human Health & Diseases - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the common symptoms of human diseases? |  |
| 2. How can infectious diseases be transmitted from one person to another? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of preventing the spread of human diseases? |  |
| 4. How can one strengthen their immune system to fight against diseases? |  |
| 5. What are the major differences between infectious and non-infectious diseases? |  |