NCERT Exemplar: Principles of Inheritance & Variation | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. All genes located on the same chromosome:
(a) Form different groups depending upon their relative distance
(b) Form one linkage group
(c) Will not from any linkage groups
(d) Form interactive groups that affect the phenotype
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Linkage groups: A linkage group is a group of the linked gene (on the same chromosome) and corresponds to the genome of an organism like a human has 23 linkage groups, pea and Neurospora have 7 linkage groups, Drosophila has 4 linkage groups.
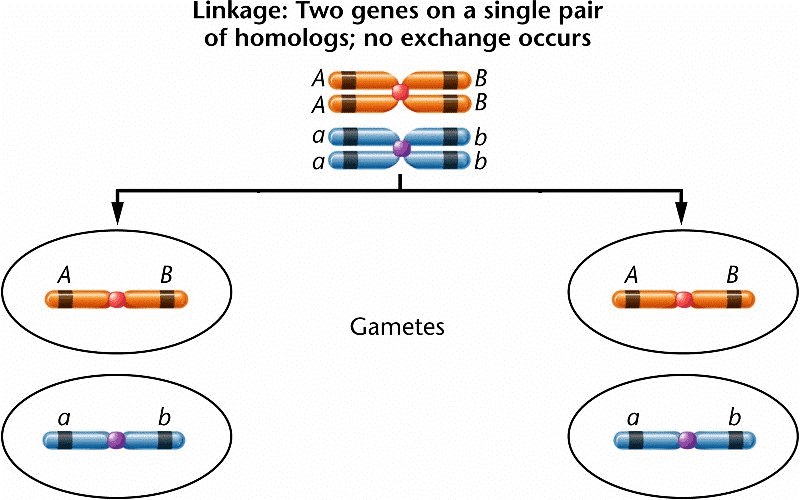
Q2. Conditions of a karyotype 2n + 1, 2n –1 and 2n + 2, 2n – 2 are called:
(a) Aneuploidy
(b) Polyploidy
(c) Allopolyploidy
(d) Monosomy
Ans: (a)
Solution:
Failure of segregation of chromatids during the cell division cycle results in the gain or loss of a chromosome(s), called aneuploidy. Aneuploidy arises due to the non-disjunction of the homologous chromosome.
Aneuploidy is of four types:
- Monosomy = 2n – 1
- Nullisomy = 2n – 2
- Trisomy = 2n + 1
- Tetrasomy = 2n + 2
Q3. Distance between the genes and percentage of recombination shows:
(a) A direct relationship
(b) An inverse relationship
(c) A parallel relationship
(d) No relationship
Ans: (a)
Solution:
Distance between the genes and percentage of recombination shows a direct relationship.
Q4. If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is:
(a) Autosomal dominant
(b) Autosomal recessive
(c) Sex-linked dominant
(d) Sex-linked recessive
Ans: (d)
Solution:
Sex-linked recessive disease: A genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny.
Example:
- Haemophilia/Bleeder’s disease
- Colour-blindness
- Congenital night blindness
- DMD (Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy)
- G-6-P dehydrogenase deficiency
Q5. In sickle cell anaemia glutamic acid is replaced by valine. Which one of the following triplets codes for valine?
(a) G G G
(b) A A G
(c) G A A
(d) G U G
Ans: (d)
Solution:
The substitution of amino acid in the globin protein results due to the single base substitution at the sixth codon of the beta-globin gene from GAG (Glutamic acid) to GUG (Valine).
Q6. Person having genotype IA IB would show the blood group as AB. This is because of:
(a) Pleiotropy
(b) Co-dominance
(c) Segregation
(d) Incomplete dominance
Ans: (b)
Solution:
| Blood Group | Genotype | Example |
| AB | IAIB | Co-dominance |
| A or B | IAi or IBi | Dominance |
Q7. ZZ / ZW type of sex determination is seen in:
(a) Platypus
(b) Snails
(c) Cockroach
(d) Peacock
Ans: (d)
Solution:
| Type of sex determination | Example |
| ZZ/Zw | Birds ( Peacock etc.) |
| XO type or (XX-XO type) | Insects, grasshopper and cockroach |
| XY type or (XX-XY type) | Human, Drosophila and Melandrium |
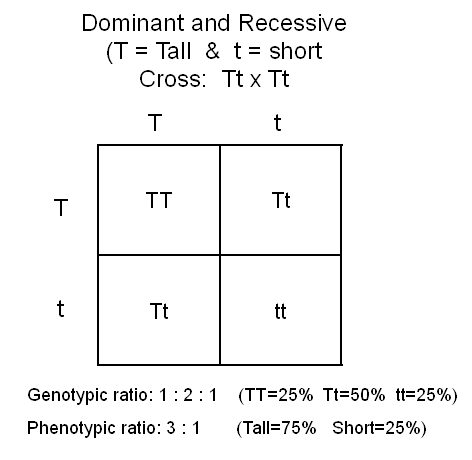
Q8. A cross between two tall plants resulted in offspring having few dwarf plants. What would be the genotypes of both the parents?
(a) TT and Tt
(b) Tt and Tt
(c) TT and TT
(d) Tt and tt
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Q9. In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9:3:3:1 ratio it denotes that:
(a) The alleles of two genes are interacting with each other
(b) It is a multigenic inheritance
(c) It is a case of multiple allelism
(d) The alleles of two genes are segregating independently
Ans: (d)
Solution:
Based upon such observations on dihybrid crosses (crosses between plants differing in two traits) Mendel proposed a second set of generalisations that we call Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment. The law states that “When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters”.
Q10. Which of the following will not result in variations among siblings?
(a) Independent assortment of genes
(b) Crossing over
(c) Linkage
(d) Mutation
Ans: (a)
Solution:
- Linkage will not result in variations among siblings.
- A sibling is one of two or more individuals having one or both parents in common. The emotional bond between siblings is often complicated and is influenced by factors such as parental treatment, birth order, personality, and personal experiences outside the family. Identical twins share 100% of their DNA. Full siblings are first-degree relatives and, on average, share 50% of their genes out of those that vary among humans. Half-siblings are second-degree relatives and have, on average, a 25% overlap in their human genetic variation.
Q11. Mendel’s Law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the:
(a) Non-homologous chromosomes
(b) Homologous chromosomes
(c) Extra nuclear genetic element
(d) Same chromosome
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Mendel’s Law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the homologous chromosomes.
Q12. Occasionally, a single gene may express more than one effect. The phenomenon is called:
(a) Multiple allelism
(b) Mosaicism
(c) Pleiotropy
(d) Polygeny
Ans: (c)
Solution:
Occasionally, a single gene may express more than one effect. The phenomenon is called pleiotropy.
Q13. In a certain taxon of insects, some have 17 chromosomes and the others have 18 chromosomes. The 17 and 18 chromosome-bearing organisms are:
(a) Males and females, respectively
(b) Females and males, respectively
(c) All males
(d) All females
Ans: (a)
Solution:
The 17 and 18 chromosome-bearing organisms are males and females respectively because it comes under XO-type of sex determination.
Males have only 1 chromosome besides the autosomes whereas females have a pair of X chromosomes besides the autosomes.
Q14. The inheritance pattern of a gene over generations among humans is studied by the pedigree analysis. Character studied in the pedigree analysis is equivalent to:
(a) Quantitative trait
(b) Mendelian trait
(c) Polygenic trait
(d) Maternal trait
Ans: (b)
Solution:
The character studied in the pedigree analysis is equivalent to the Mendelian trait.
Q15. It is said that Mendel proposed that the factor controlling any character is discrete and independent. His proposition was based on the
(a) Results of F3 generation of a cross.
(b) Observations that the offspring of a cross made between the plants having two contrasting characters shows only one character without any blending.
(c) Self-pollination of F1 offsprings
(d) Cross-pollination of F1 generation with recessive parent
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Mendel proposed that the factor Controlling any character is discrete and independent. His proposition was based on the observations that the offspring of a cross made between the plants having two contrasting characters shows only one character without any blending.
Q16. Two genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are linked. In a dihybrid cross involving these two genes, the F1 heterozygote is crossed with homozygous recessive parental type (aa bb). What would be the ratio of offspring in the next generation?
(a) 1 : 1 : 1: 1
(b) 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
(c) 3 : 1
(d) 1 : 1
Ans: (d)
Solution:
Two genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are linked. In a dihybrid cross involving these two genes, the Fj heterozygote is crossed with homozygous recessive parental type (aa bb). The ratio of offspring in the next generation will be 1 :1.
Q17. In the F2 generation of a Mendelian dihybrid cross the number of phenotypes and genotypes are:
(a) Phenotypes - 4; genotypes - 16
(b) Phenotypes - 9; genotypes - 4
(c) phenotypes - 4; genotypes - 8
(d) phenotypes - 4; genotypes - 9
Ans: (d)
Solution:
In the F2 generation of a Mendelian dihybrid cross, the number of phenotypes and genotypes are 4, 9 respectively.
Q18. Mother and father of a person with ‘O’ blood group have ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively. What would be the genotype of both mother and father?
(a) Mother is homozygous for ‘A’ blood group and father is heterozygous for ‘B’
(b) Mother is heterozygous for ‘A’ blood group and father is homozygous for ‘B’
(c) Both mother and father are heterozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively
(d) Both mother and father are homozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively
Ans: (c)
Solution:
Genotype of mother: IA i
Genotype of father: IB i
Both mother and father are heterozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. What is the cross between the progeny of F1 and the homozygous recessive parent called? How is it useful?
Ans: When a progeny of F1 is crossed with the homozygous recessive parent, it is called test cross. Such a cross is useful to determine the genotype of an unknown, i.e., whether it is heterozygous, or homozygous dominant for the trait.
Q2. Do you think Mendel’s laws of inheritance would have been different if the characters that he chose were located on the same chromosome?
Ans: If Mendel chose characters that were located on the same chromosome then Mendel would not find the law of independent assortment.
Q3. Enlist the steps of controlled cross-pollination. Would emasculation be needed in a cucurbit plant? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans: Steps of controlled cross-pollination:
Selection of parents → Emasculation → Bagging → Collection of pollen from male parent → Dusting the pollen on stigma → Re-bagging
Emasculation could not be needed in a cucurbit plant because it has unisexual flowers.
Q4. A person has to perform crosses for the purpose of studying the inheritance of a few traits/characters. What should be the criteria for selecting the organisms?
Ans: Criteria for selecting the organism are:
- Shorter life span
- To produce large number of progeny
- Clear differentiation of sex/traits
- Many types of hereditary variations
Q5. The pedigree chart given below shows a particular trait which is absent in parents but present in the next generation irrespective of sexes. Draw your conclusion on the basis of the pedigree.
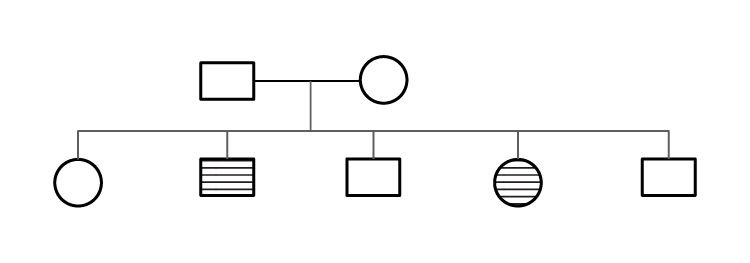 Ans: The trait is autosome linked and recessive in nature. Both the parents are carriers (i.e., heterozygous) hence among offspring few show the trait irrespective of sex. The other offsprings are either normal or carrier.
Ans: The trait is autosome linked and recessive in nature. Both the parents are carriers (i.e., heterozygous) hence among offspring few show the trait irrespective of sex. The other offsprings are either normal or carrier.
Q6. In order to obtain the F1 generation, Mendel pollinated a pure-breeding tall plant with a pure breeding dwarf plant. But forgetting the F2 generation, he simply self-pollinated the tall F1 plants. Why?
Ans: Genotype of 50% of the offspring would resemble one parent and the rest the other parent. All the F1, offsprings of the cross are heterozygous so allowing self-pollination is sufficient to raise F2 offspring. Also, Mendel intended to understand the inheritance of the selected trait over generations.
Q7. “Genes contain the information that is required to express a particular trait.” Explain.
Ans. The genes present in an organism show a particular trait by way of forming a certain product. This is facilitated by the process of transcription and translation (according to the central dogma of genetics).
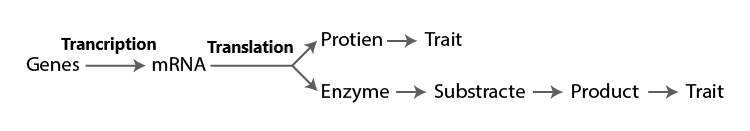
Q8. How are alleles of a particular gene differ from each other? Explain its significance.
Ans: Alleles of a particular gene differ from each other on the basis of certain changes (i.e., mutations) in the genetic material (segment of DNA or RNA). Different alleles of a gene increase the variability or variation among the organisms.
Q9. In a monohybrid cross of plants with red and white-flowered plants, Mendel got only red-flowered plants. On self-pollinating these F1 plants got both red and white-flowered plants in 3:1 ratio. Explain the basis of using RR and rr symbols to represent the genotype of plants of the parental generation.
Ans: On crossing red and white flower only red colour flower appeared in the F1 generation. But the white colour flower again appears in the F2 generation which is raised out of the F1 individuals only. Mendel reasoned that there is a factor of each and every character. Accordingly, there has to be one factor (R) for red flower and other one factor (r) for white flower. In case, an organism possesses only one copy of the gene then the possibility of reappearance of white flower in the F2 generation of the given cross is not there. Also, the ratio (3 : 1 of red and white) indicates that each organism must possess two copies of a particular gene.
Q10. For the expression of traits, genes provide only the potentiality and the environment provides the opportunity. Comment on the veracity of the statement.
Ans: The phenotype of individuals is a result of the combined effect of environment and genotype.
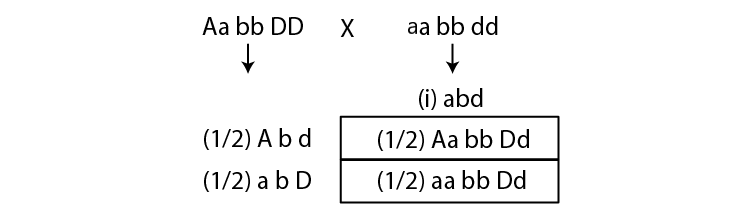
Q11. A, B, D are three independently assorting genes with their recessive alleles a, b, d, respectively. A cross was made between individuals of Aa bb DD genotype with aa bb dd. Find out the type of genotypes of the offspring produced.
Ans: The given cross is Aa bb dd X aa bb dd. Accordingly, the type of offspring produced would:
Q12. In our society, a woman is often blamed for not bearing a male child. Do you think it is right? Justify.
Ans: 50 per cent of sperm carry the X chromosome while the other 50 percent carry the Y. After fusion of the male and female gametes the zygote would carry either XX or YY depending on whether the sperm carrying X or Y fertilised the ovum. The sex of the baby is determined by the father and not by the mother.
It is unfortunate that in our society women are blamed for producing female children and have been ostracised and ill-treated because of this false notion.
Q13. Discuss the genetic basis of wrinkled phenotype of pea seed.
Ans: Wrinkled phenotype of pea seed is due to the small grain size produced by double recessive allele (bb).
Q14. Even if a character shows multiple allelism, an individual will only have two alleles for that character. Why?
Ans: A diploid organism has only two alleles of a character, although it has more than two alleles. Multiple alleles can be found only when population studies are made.
Q15. How does a mutagen induce mutation? Explain with example.
Ans: A mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA. Different mutagens act on the DNA differently. Powerful mutagens may result in chromosomal instability, causing chromosomal breakages and rearrangement of the chromosomes such as translocation, deletion, and inversion.
Ionizing radiations such as X-rays, gamma rays and alpha particles may cause DNA breakage and other damages. Ultraviolet radiations with wavelength above 260 nm are absorbed strongly by bases, producing pyrimidine dimers. Radioactive decay, such as 14C in DNA which decays into nitrogen.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. In a Mendelian monohybrid cross, the F2 generation shows identical genotypic and phenotypic ratios. What does it tell us about the nature of alleles involved? Justify your answer.
Ans: In a monohybrid cross, starting with parents which homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive, F1, would be heterozygous for the trait and would express the dominant allele. But in the case of incomplete dominance, a monohybrid cross shows the result as follows.
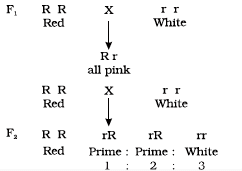
Phenotypic ratio → Red : Pink : White :: 1 : 2 : 1
Genotypic ratio → RR : Rr: rr : .1:2:1
Here the genotypic and phenotypic ratios are the same. So, we can conclude that when genotypic and phenotypic ratios are the same, the alleles show incomplete dominance.
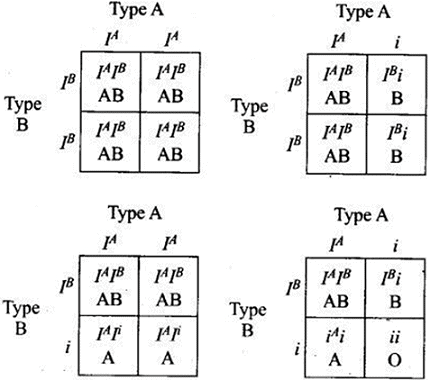
Q2. Can a child have blood group O if his parents have blood group ‘A’ and ‘B’? Explain.
Ans: If parents are heterozygous then the child can have O blood group but if the parents are homozygous then the child cannot have O blood group.
Q3. What is Down’s syndrome? Give its symptoms and cause. Why is it that the chances of having a child with Down’s syndrome increases if the age of the mother exceeds forty years?
Ans: Down’s syndrome is a human genetic disorder caused due to trisomy of chromosome no. 21. Such individuals are aneuploid and have 47 chromosomes (2n + 1). The symptoms include mental retardation, growth abnormalities, constantly open mouth, dwarfness etc. The reason for the disorder is the non-disjunction (failure to separate) of the homologous chromosome of pair 21 during meiotic division in the ovum. The chances of having a child with Down’s syndrome increase with the age of the mother (+40) because ova are present in females. Since their birth and therefore older cells are more prone to chromosomal non-disjunction because of various physico-chemical exposures during the mother’s lifetime.
Q4. How was it concluded that genes are located on chromosomes?
Ans: Morgan confirmed Mendelian laws of inheritance and the hypothesis that genes are located on chromosomes. Morgan had discovered that eye colour in Drosophila expressed a sex-linked trait. All first-generation offspring of a mutant white-eyed male and a normal red-eyed female would have red eyes because every chromosome pair would contain at least one copy of the X chromosome with the dominant trait.
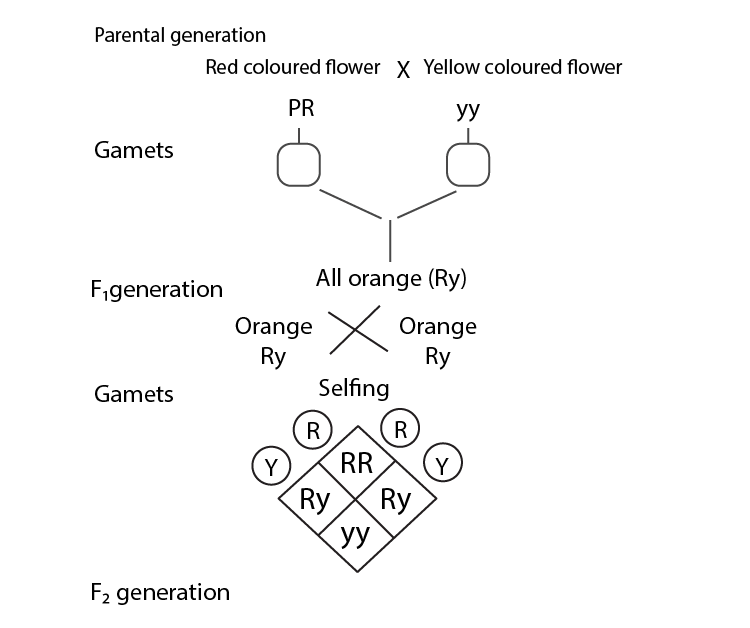
Q5. A plant with red flowers was crossed with another plant with yellow flowers. If F1 showed all flowers orange in colour, explain the inheritance.
Ans: This is due to the incomplete dominance as the F, do not resemble either of the two parents and is in between the two.
Q6. What are the characteristic features of a true-breeding line?
Ans: A true-breeding line for a trait is one that, has undergone continuous self¬pollination or brother-sister mating, showing stability in the inheritance of the trait for several generations.
Q7. In peas, tallness is dominant over dwarfness, and the red colour of flowers is dominant over the white colour. When a tall plant bearing red flowers was pollinated with a dwarf plant bearing white flowers, the different phenotypic groups were obtained in the progeny in numbers mentioned against them:
Tall, Red = 138
Tall, White = 132
Dwarf, Red = 136
Dwarf, White = 128
Mention the genotypes of the two parents and of the four offspring types.
Ans: The result shows that the four types of offspring are in a ratio of 1:1:1:1. Such a result is observed in a test-cross progeny of a dihybrid cross.
The cross can be represented as:
Tall & Red (Tt Rr) x Dwarf & White (ttrr)
| Offspring | tr |
| Tt Rr - Tall, Red | TR - TtRr - Tall Red |
| Tt rr - Tall, White | Tr - Ttrr - Tall White |
| Tt Rr - Dwarf, Red | tR - ttRr - Dwarf Red |
| tt rr - Dwarf, white | tr - ttrr - Dwarf White |
Q8. Why is the frequency of red-green colour blindness is many times higher in males than that in females?
Ans: For becoming colourblind, the female must have the allele for it in both her X-chromosomes; but males develop colourblindness when their sole X-chromosome has the allele for it.
Q9. If a father and son are both defective in red-green colour vision, is it likely that the son inherited the trait from his father? Comment.
Ans: Gene for colour blindness is X-chromosome linked, and sons receive their sole from their mother, not from their father. Male-to-male inheritances are not possible for X-linked traits in humans. In the given case the mother of the child must be a carrier (heterozygous) for the colour blindness gene.
Q10. Discuss why Drosophila has been used extensively for genetical studies.
Ans: Morgan worked with the tiny fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster, which were found very suitable for such studies, as:
- They could be grown on a simple synthetic medium (ripe banana) in the laboratory.
- They complete their life cycle in about two weeks.
- A single mating could produce a large number of progeny flies.
- There was a clear differentiation of the sexes—the male and female flies are easily distinguishable.
- It has many types of hereditary, variations that can be seen with low power microscopes.
Q11. How do genes and chromosomes share similarity from the point of view of genetical studies?
Ans: Similarities between Chromosomes and Genes:
- Both occur in pairs.
- Both segregate at the time of gamete formation such that only one of each pair is transmitted to a gamete.
- Independent pairs segregate independently of each other in both.
Q12. What is recombination? Discuss the applications of recombination from the point of view of genetic engineering.
Ans: The formation of new combinations of genes, either by crossing over or independent assortment is called recombination. Alfred Sturtevant used the frequency of recombination between gene pairs on the same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes and ‘mapped’ their position on the chromosome. Today genetic maps are extensively used as a starting point in the sequencing of whole genomes as was done in the case of the Human Genome Sequencing Project.
Q13. What is artificial selection? Do you think it affects the process of natural selection? How?
Ans: A process in the breeding of organisms by which the scientist chooses to only those forms having certain desirable characteristics is called artificial selection.
- Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. In natural selection, the difference in reproductive success based on a particular trait is driven by natural processes like predators, weather conditions, and environmental constraints.
- Artificial selection is imposed by humans on other organisms. It affects the process of natural selection through changes in environmental conditions.
Q14. With the help of an example differentiate between incomplete dominance and co-dominance.
Ans:
Incomplete Dominance | Co-Dominance | ||
| 1. | Effect of one of the two alleles is more conspicuous | 1. | Effect of both the alleles are equally conspicuous. |
| 2. | It produces a mixture of the expression of two alleles | 2. | There is no mixing of the effect of the two alleles. |
| 3. | The F1 does not resemble either of the parents. | 3. | The F1 resembles both the parents. |
| Example: Flower colour in dog flower | Example: ABO blood grouping in humans | ||
Q15. It is said, that the harmful alleles get eliminated from the population over a period of time, yet sickle cell anaemia is persisting in the human population. Why?
Ans: The harmful alleles get eliminated from the population over a period of time, yet sickle cell anaemia is persisting in the human population because SCA is a harmful condition which is also a potential saviour from malaria.
Those with the benign sickle trait possess resistance to malarial infection. The pathogen that causes the disease spends part of its cycle in the red blood cells and triggers an abnormal drop in oxygen levels in the cell. In carriers, this drop is sufficient to trigger the full sickle-cell reaction, which leads to infected cells being rapidly removed from circulation and strongly limiting the infection’s progress. These individuals have great resistance to infection and have a greater chance of surviving outbreaks. This resistance to infection is the main reason the SCA allele and SCA disease still exist. It is found in the greatest frequency in populations where malaria was and often still is a serious problem.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. In a plant, tallness is dominant over dwarfness and red flower is dominant over white. Starting with the parents work out a dihybrid cross. What is the standard dihybrid ratio? Do you think the values would deviate if the two genes in question are interacting with each other?
Ans: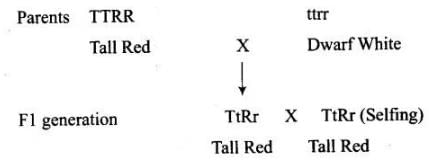
F2 generation
Gametes | TR | Tr | tR | tr |
TR | TTRR tall red | TTRr tall red | TtRR tall red | TtRr tall red |
Tr | TTRr tall red | Ttrr tall white | TtRr tall red | Ttrr tall white |
tR | TtRR tall red | TtRr tall red | ttRR dwarf red | ttRr dwarf red |
tr | TtRr tall red | Ttrr tall white | ttRr dwarf red | ttrr dw arf white |
Yes, the ratio will deviate if the two genes are interacting with each other. In this condition, the genes do not independently assort with each other. So, the ratio will be changed from 9:3:3: 1.
Q2. a. In humans, males are heterogametic and females are homogametic. Explain. Are there any examples where males are homogametic and females heterogametic?
b. Also describe as to, who determines the sex of an unborn child? Mention whether the temperature has a role in sex determination.
Ans:
(a) The term homogametic and heterogametic refer to the organism depending upon whether all the gametes contain one type of sex chromosome (Homo = same) or two different types of sex chromosomes (Hetero = different). Humans show XX/XY type of sex determination, i.e. Females contain two copies of the X chromosome and males contain one X and one Y chromosome. Therefore, ova produced by females contain the same sex chromosome, i.e. X. On the other hand, the sperms contain two different types of chromosomes, i. e. 50% of sperms have X and 50% have Y chromosomes open from half the autosomes (Meiosis). Therefore, the sperms are different with respect to the composition of the sex chromosome. In the case of humans, females are considered to be homogametic while males are heterogametic. Yes, there are examples where males are homogametic and females are heterogametic. In some birds, the mode of sex determination is denoted by ZZ (males) and ZW (females),
(b) As a rule the heterogametic organism determines the sex of the unborn child. In the case of humans, since males are heterogametic it is the father and not the mother who decides the sex of the child. In some animals like crocodiles, lower temperatures favour the hatching of female offspring and higher temperatures lead to the hatching of male offspring.
Q3. A normal visioned woman, whose father is colour blind, marries a normal visioned man. What would be the probability of her sons and daughters being colour blind? Explain with the help of a pedigree chart.
Ans:
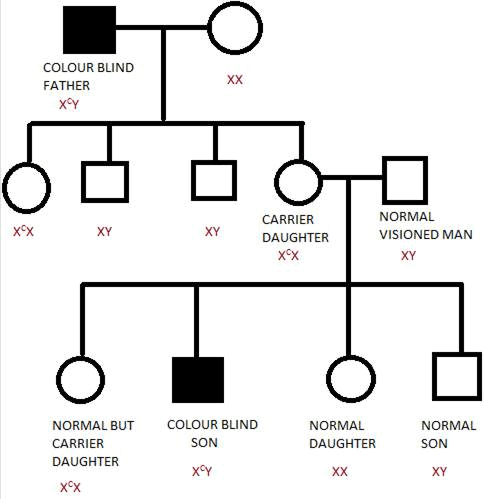 All daughters are normal visioned; 50% of sons are likely to be colour blind.
All daughters are normal visioned; 50% of sons are likely to be colour blind.
Q4. Discuss in detail the contributions of Morgan and Sturvant in the area of genetics.
Ans Experimental verification of the chromosomal theory of inheritance by Thomas Hunt Morgan (Father of experimental genetics) and his colleagues, led to discovering the basis for the variation that sexual reproduction produced. Morgan worked with the tiny fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster, which were found very suitable for such studies.
- Morgan carried out several dihybrid crosses in Drosophila to study genes that were sex-linked. The crosses were similar to the dihybrid crosses carried out by Mendel in peas. For example, Morgan hybridised yellow-bodied, white-eyed females to brown-bodied, red-eyed males and intercrossed their F, progeny.
- He observed that the two genes did not segregate independently of each other and the F2 ratio deviated very significantly from the. 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio (expected when the two genes are independent). Morgan and his group knew that the genes were located on the X chromosome and saw quickly that when the two genes in a dihybrid cross were situated on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations were much higher than the non-parental type.
- Morgan attributed this due to the physical association or linkage of the two genes and coined the term linkage to describe this physical association of genes on a chromosome and the term recombination to describe the generation of non-parental gene combinations.
- His student Alfred Sturtevant used the frequency of recombination between gene pairs on the same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes and ‘mapped’ their position on the chromosome. Today genetic maps are extensively used as a starting point in the sequencing of whole genomes as was done in the case of the Human Genome Sequencing Project.
Q5. Define aneuploidy. How is it different from polyploidy? Describe the individuals having following chromosomal abnormalities.
a. Trisomy of 21st Chromosome
b. XXY
c. XO
Ans Failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division cycle results in the gain or loss of a chromosome(s), called aneuploidy. – Difference between aneuploidy and polyploidy
1. Failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division cycle results in the gain or loss of a chromosome(s), called aneuploidy. Failure of cytokinesis after telophase stage of cell division results in an increase in a whole set of chromosomes in an organism and,this phenomenon is known as polyploidy.
2. Polyploidy occurs due to altering a set of chromosome numbers such as 2n, 3n, 5n, whereas aneuploidy occurs due to altering a particular chromosome or part of a chromosome such as 2n + 1 (trisomic) and 2n – 1 (monosomic).
3. Aneuploidy can be seen in humans as a genetic disorder; for example, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome and Down syndrome, whereas polyploidy is common in plants.
(i) Down’s Syndrome (Mongolism)
- The cause of this genetic disorder is the presence of an additional copy of chromosome number 21 (trisomy of 21) due to the non-disjunction of chromosomes during sperm or ova formation.
- The affected individual is short-statured with a small round head, furrowed tongue and partially open mouth. Palm is broad with a characteristic palm crease.
- Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
(ii) Klinefelter’s Syndrome
- This genetic disorder is also caused due to the presence of an additional copy of X-chromosome resulting in a karyotype of 47, XXY.
- Such an individual has overall masculine development, however, the feminine development (development of breast, i.e., Gynaecomastia) is also expressed. Such individuals are sterile males.
(iii) Turner’s Syndrome
Such a disorder is caused due to the absence of one of the X chromosomes, i.e., 45 with XO. Such females are sterile as ovaries are rudimentary besides other features including lack of other secondary sexual characters.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the main principles of inheritance according to Mendel's experiments? |  |
| 2. How does variation occur in a population? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of test crosses in genetics? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of genotype and phenotype? |  |
| 5. What role do chromosomes play in inheritance? |  |
















