NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Cell - Structure & Functions | Science Olympiad Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Choose the correct statement with respect to unicellular organisms:
(a) in unicellular organisms, tissues work in co-ordination to perform different functions.
(b) unicellular organisms do not require food.
(c) unicellular organisms respire and reproduce.
(d) all unicellular organisms move by cilia.
Ans: c
Explanation:
Unicellular are single-celled organisms where single cell performs basic functions such as respiration, digestion and reproduction. Option a) is wrong because tissues are a group of cells in unicellular there will be only one cell. Option b) is wrong because organisms require food for their survival like any other organisms. Different unicellular uses different organism for locomotion. Example: Cilia, Pseudopodia.
Q.2. Majority of cells cannot be seen directly with our naked eyes because:
(a) organisms are generally unicellular
(b) cells are microscopic
(c) cells are present only inside the body
(d) cells are grouped into tissues
Ans: b
Explanation:
Cells are basic unit if life whose size is very small to be seen by our naked eye. Cell varies from nanometer to micrometre which requires a microscope to visualize. Hence they are called microscopic structures.
Q.3. Read the different combinations of terms given below:
(a) cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, plastid
(b) cell wall, nucleus, ribosome, chromosome
(c) the cell membrane, mitochondria, ribosome, chromosome
(d) the cell membrane, ribosome, mitochondria, chloroplast.
The correct combination of terms with reference to an animal cell is _____.
Ans: c
Explanation:
Option a) and b) are wrong because they have a cell wall which is present only in plant cells. Option d) is wrong because it has chloroplast which is absent in animal cells. Hence the answer is c)
Q.4. Which one of the following term is not a part of the nucleus?
(a) ribosome
(c) chromosome
(b) nucleolus
(d) gene
Ans: a
Explanation:
Ribosomes are the organelles that float in the cytoplasm. Chromosomes are the structures present in the nucleus which are composed of genes. The nucleolus is a part of the nucleus which helps in protein synthesis.
Q.5. A suitable term for the various components of cells is
(a) tissue
(b) cell organelles
(c) chromosomes
(d) genes
Ans: b
Explanation:
The tissue is a group of cells which work together to perform a certain function. Chromosomes are thread-like structure present in the nucleus which constitutes all the genes. Gene is a unit of inheritance in living organisms. It controls the transfer of a hereditary characteristic from parents to offspring. Genes are made of DNA.
Q.6. The jelly-like fluid substance present in cells is called
(a) protoplasm
(b) chromosome
(c) chloroplast
(d) cytoplasm
Ans: d
Explanation:
It is the jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various other components, or organelles, of cells are present in the cytoplasm. These are mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc.
Q.7. Read the following pairs of examples of organisms:
(a) moss and sponge
(b) yeast and Amoeba
(c) bacteria and a blue-green alga
(d) penicillium and Spirogyra
The pair that belongs to the group prokaryotes is_____
Ans: c
Explanation:
Prokaryotes are the organism which lacks a true nucleus and cell organelles. Other options provided are contained eukaryotes hence answer is c)
Q.8. Read the following terms and select the pair that is related to the inheritance of characters.
(a) cell wall and cell membrane
(b) chromosome and mitochondria
(c) chloroplast and cell membrane
(d) chromosome and genes
Ans: d
Explanation:
Chromosomes and gene are responsible for the inheritance of characters. Chromosomes are present in the nucleus. Genes are the parts of chromosomes which consist of DNA.
Q.9. Choose the correct statement:
(a) Genes are located in the chromosomes.
(b) The cell is located in the nucleus.
(c) Chromosomes are located in the nucleolus.
(d) Cell membrane surrounds the nucleus.
Ans: a
Explanation:
Genes are the units of inheritance located in the chromosomes. The nucleus is located in cells but not cell is located in the nucleus. Chromosomes are present in the nucleus, not nucleolus. The nucleus is surrounded by the nucleus membrane, not cell membrane.
Q.10. The green colour of leaves is due to presence of the pigment_____
(a) chlorophyll
(b) ribosomes
(c) mitochondria
(d) chloroplast
Ans: a
Explanation:
Chlorophyll is a pigment present in the chloroplasts. Chlorophyll is responsible for the green colour of leaves. Chlorophyll can absorb energy from the sun and helps in converting it to chemical energy.
Q.11. The unit of measurement used for expressing dimension (size) of cells is:
(a) centimetre
(b) millimetre
(c) micrometre
(d) metre
Ans: c
Q.12. The most important function of the cell membrane is that it:
(a) controls the entry and exit of materials from cells.
(b) controls only the entry of materials into cells.
(c) controls only the exit of materials from cells.
(d) allows entry and exit of materials without any control.
Ans: a
Explanation:
Cell membrane facilitates entry and exit of material from cells. The cell membrane also provides shapes to the cells.
Q.13. Paheli accidentally placed her hand over a flame and immediately pulled it back. She felt the sensation of heat and reacted due to the action of
(a) blood cells
(b) skin surface
(c) nerve cells
(d) nucleus of cells
Ans: c
Explanation:
Paheli felt the sensation of heat and reacted due to the response to the stimulus by the nerve cells. Nerve cell are specialized cells, which receives and transmits signals from one part to other cells that react to stimuli by generating signals through the axons
Q.14. Which of the following cell organelle is found in all plant cells, animal cells and also in bacterial cells?
(a) chloroplast
(b) cell wall
(c) cell membrane
(d) nucleus
Ans: c
Explanation:
Chloroplast and cell wall present only in plant cells. The nucleus is absent in bacterial cell, therefore, the answer is (c) cell membrane.
Q.15. The thread-like structures present in the nucleus are
(a) nucleolus
(b) chromosomes
(c) genes
(d) ribosomes
Ans: b
Explanation:
The nucleolus is a spherical body present on the nucleus. Genes are present on chromosomes which help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring. Ribosomes are present in the cytoplasm. Hence the answer is (b) chromosomes.
Q.16. Identify the statement which is true for cells.
(a) Cells can be easily seen with naked eyes.
(b) Insect’s egg is not a cell.
(c) A single cell can perform all the functions in a unicellular organism.
(d) The size and shape of cells is uniform in multicellular organisms
Ans: c
Explanation:
Cells can only be seen with microscopes hence option a) is wrong. Insect’s egg is a cell so option b) is wrong. Cells in multicellular organism are in different size and shape therefore option d) is wrong.
Q.17. Which of the following is not a cell?
(a) Red Blood Corpuscle (RBC)
(b) bacterium
(c) spermatozoa
(d) virus
Ans: d
Explanation:
The virus is considered as intermediate between living and non-living. It is not considered as cell because it cannot replicate or perform life processes outside the host cell.
Q.18. Which of the following feature will help you in distinguishing a plant cell from an animal cell?
(a) cell wall
(b) cell membrane
(c) mitochondria
(d) nucleus
Ans: a
Explanation:
The cell wall is present only in plant cell whereas cell wall, mitochondria and nucleus are present in both plant and animal cells. Hence cell wall help in distinguishing a plant cell from an animal cell.
Q.19. Under a microscope Paheli observes a cell that has a cell wall but no distinct nucleus. The cell that she observes is
(a) a plant cell
(b) an animal cell
(c) a nerve cell
(d) a bacterial cell
Ans: d
Explanation:
Bacterial cell is a prokaryote and it lacks a distinct nucleus and cell organelles. Hence the answer is (d) a bacterial cell.
Q.20. Cheek cells do not have _______
(a) cell membrane
(b) nucleus
(c) golgi apparatus
(d) plastids
Ans: d
Explanation:
Plastids are present only in plant cells. Cheeks cells are present only in animals hence the answer is (d) plastids.
Q.21. Identify the correct statement.
(a) Tissue is a group of dissimilar cells.
(b) An organ consists of similar cells.
(c) Vacuoles are not found in plant cells.
(d) Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus.
Ans: d
Explanation:
Prokaryotes are the organism which lack a true nucleus and cell organelles.
Q.22. Which of the following statements are not true for eukaryotic cells?
(a) They do not have a nuclear membrane.
(b) They have a well-organised nucleus.
(c) They have a nuclear membrane.
(d) Blue-green algae are eukaryotic cells
Ans: d
Explanation:
Blue-green algae is a bacteria which comes under prokaryotes hence statement d) is wrong.
Q.23. Identify the correct statement about cells.
(a) All the cells have nucleus.
(b) Cells of an organ have similar structure.
(c) Cells of tissue have a similar structure.
(d) The shape of all types of cells is round.
Ans: c
Explanation:
Only eukaryotic cells have well-defined nucleus hence option a) is wrong. Cells of an organ comprise of different types of the cell so statement b) is wrong. Cells are of different shapes and size hence option d) is wrong.
Q.24. The table given below has certain terms and four blank spaces named A, B, C and D.
From the options given below choose the correct combination of terms.
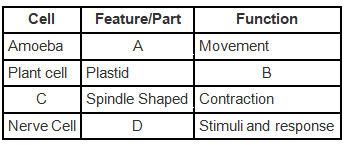 (a) A-Pseudopodia; B-Respirations; C-Muscle cell; D-Branched
(a) A-Pseudopodia; B-Respirations; C-Muscle cell; D-Branched
(b) A-Pseudopodia; B-Photosynthesis; C-Muscle cell; D-Branched
(c) A-Contractile vacuole; B-Photosynthesis; C-Blood cell; D-Spindle shaped
(d) A-Pseudopodia; B-Photosynthesis; C-Cheek cell; D-Spindle shaped
Ans: b
Explanation:
(a) The pseudopods are used by Amoeba for movement and as a tool to capture prey.
(b) Plastids are major organelles found in the plant cells, which contain chlorophyll can carry out photosynthesis.
(c) Muscle are spindle-shaped cells, which are involved in contraction and relaxation.
(d) Nerve cells are long, branched and active component of the nervous system, which functions by responding to stimuli.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. In leaves, name the cell organelle and pigment that is responsible for green colour.
Ans: Chloroplast and Chlorophyll
Q.2. The instrument used to observe cells is ________
Ans: Microscope
Q.3. We do not sense any pain when we clip our nails or cut our hair. Why?
Ans: Nails and hairs are made up of dead cells, which is not connected with nerve cells. Hence we do not feel the pain when we cut our nails or hair.
Q.4. In a cell, where are the genes located?
Ans: Genes are located in Chromosomes present within the nucleus.
Q.5. Amoeba and Paramecium belong to which category of organisms?
Ans: Protozoans
Q.6. What are the functions of the cell wall in plant cells?
Ans: Functions of cell-wall are as follows
- Acts as a protective layer.
- Provides shape to the cell.
- Control the cell expansion
- Preventing water loss from the cell.
- Provides strength and rigidity to the cell.
Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Is the following statement correct? If it is wrong, correct the statement Statement :
“Unicellular organisms do not respire, only multicellular organisms respire”
Ans: The statement is wrong because all kind of living organisms respire and undergo respiration process.
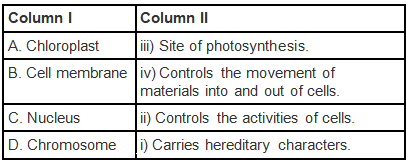
Q.2. Match the terms given in column I with their functions given in column II and fill the blanks given below the table:
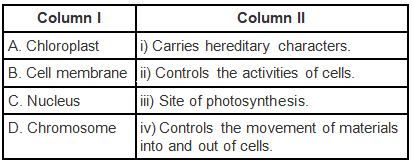
Ans:
Q.3. Observe the following diagram given as Figure.

Answer the following questions.
- Does it represent a plant cell or an animal cell?
- Does it represent a prokaryotic cell or a eukaryotic cell?
Ans:
- The figure represents an animal cell.
- This is a eukaryotic cell.
Q.4. Label the parts A to E in the given as figure diagram.
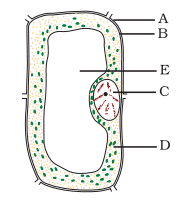
Ans:
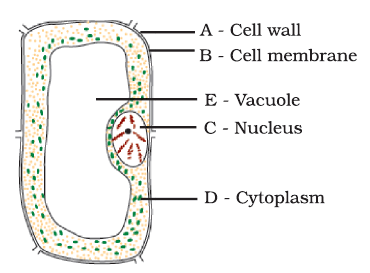
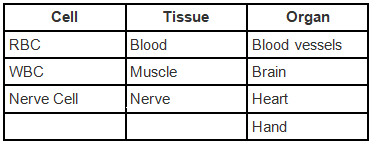
Q.5. Classify the following terms into cells, tissues and organs and write in the tabular column given below.
RBC, blood vessels, blood, WBC, Nerve cell, muscle, brain, heart, hand, nerve.
Ans:
Q.6. Read the following statements and write the appropriate term against each statement.
A. I control the functions of a cell. Who am I? ……………….
B. I am like a policeman. I do not allow anything and everything to get in and out of the cell. Who am I? ……………….
C. I transfer characters from parents to offsprings. Who am I? ……………….
Ans:
A- Nucleus;
B-Cell membrane;
C-Genes/Chromosomes
Q.7. Fill in the blanks with the terms given in the box below:
Nucleus, chromosomes, Cell wall, Cell membrane, Protoplasm, cytoplasm, ribsome, cell organelles
The outermost layer of plant cells is the (a) beneath which is the (b). The term (c) refers to the jelly-like substance containing all the (d). The (e) contains thread-like structures called (f).
Ans:
a-cell wall; b-cell membrane; c-cytoplasm; d-cell organelles; e-nucleus; f-chromosomes.
The outermost layer of plant cells is the (a) cell wall beneath which is the (b) cell membrane. The term (c) cytoplasm refers to the jelly-like substance containing all the (d) cell organelles. The (e) nucleus contains thread-like structures called (f) chromosomes.
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Cells consist of many organelles, yet we do not call any of these organelles as a structural and functional unit of living organisms. Explain.
Ans: Cell organelles like mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc, have specific functions and do specific functions, however, they can not be referred to the functional unit of the cell. This is because they will perform only specific functions within a living cell. They can not act as units. The nuclei, on the contrary, has an independent existence. it’s the littlest, structural and useful unit of life.
Q.2. Why do plant cells have an additional layer surrounding the cell membrane? What is this layer known as?
Ans: Plants do not have the property of moving, hence they need protection against variations in temperature, high wind speed, atmospheric moisture, etc. For this purpose, a plant cell has a special membrane call as the cell wall. This additional membrane also provides the shape for the plant cell.
Q.3. The size of the cells of an organism has no relation with the size of its body. Do you agree? Give the reason for your answer.
Ans: Size of the cells of an organism has no relation with the size of its body because the cell size of a rat and cell size of an elephant will not be different in size. The cell organelles like mitochondria, Golgi complex, ribosomes, nucleus, etc., have specific functions and carry out specific functions in a cell but they cannot be called as the structural and functional units of living organisms. This is because they can function only when present inside a living cell. They cannot act as independent units. The nuclei, on the contrary, has an independent existence. It is the smallest, structural and functional unit of life.
|
72 videos|141 docs|72 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Cell - Structure & Functions - Science Olympiad Class 8
| 1. What is the structure of a cell? |  |
| 2. What are the functions of the cell membrane? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the nucleus in a cell? |  |
| 4. What are organelles? Name a few organelles present in a cell. |  |
| 5. How do cells communicate with each other? |  |




















