NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Geometry | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
Exercise Page: 23
In each of the questions 1 to 16, out of four options only one is correct. Write the correct answer.
Q1: Number of lines passing through five points such that no three of them are collinear is
(a) 10
(b) 5
(c) 20
(d) 8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
From the question it is given that, number of lines passing through five points.
We know that, we need tow points to form a line.
Therefore, number of lines passing through five points = 5 × 2
= 10
Q2: The number of diagonals in a heptagon is
(a) 21
(b) 42
(c) 7
(d) 14
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
From the formula, diagonal = n(n – 3)/2
Where n = number of sides in a polygon.
There are 7 sides in a heptagon.
So, d = 7(7 – 3)/2
= 7(4)/2
= 28/2
= 14
Q3: Number of line segments in figure is
 (a) 5
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 15
(d) 20
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
From the figure, number of line segments are, AB, AC, AD, AE, BC, BD, BE, CD, CE, DE.
Therefore, there are 10 line segments in the given figure.
Q4: Measures of the two angles between hour and minute hands of a clock at 9 O’ clock are
(a) 60º, 300º
(b) 270º, 90º
(c) 75º, 285º
(d) 30º, 330º
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
We know that, measure of complete angle of clock is 360º.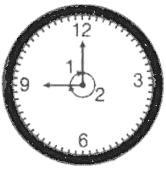
From the figure, we can say that angle at 2 = (9/12) × 360º= 270º
Then, angle at 1= 360º – 270º
= 90º
Therefore, measures of the two angles between hour and minute hands of a clock at 9 O’ clock are 270º and 90º.
Q5: If a bicycle wheel has 48 spokes, then the angle between a pair of two consecutive spokes is
(a) 5(1/2)
(b) 7(1/2)
(c) 2/11
(d) 2/15
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
We know that, bicycle wheel is in circular shape.
So, total angle of wheel is 360º.
From the question it is given that bicycle wheel has 48 spokes.
Then, the angle between a pair of two consecutive spokes is = 360º/48
= 7.5
= 7(1/2)
Q6: In the given figure, ∠XYZ cannot be written as
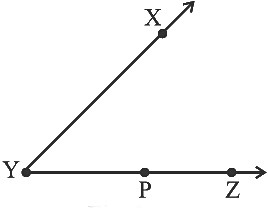 (a) ∠Y
(a) ∠Y
(b) ∠ZXY
(c) ∠ZYX
(d) ∠XYP
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Q7: In the given figure, if point A is shifted to point B along the ray PX such that PB = 2PA, then the measure of ∠BPY is
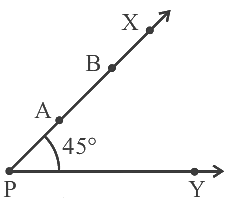
(a) greater than 45°
(b) 45°
(c) less than 45°
(d) 90°
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
As per the condition given the question, point A is shifted to point B along the ray PX such that PB = 2PA.
So, by shifting the point ‘A’ there is no change at the point ‘P’.
Therefore, the measure of ∠BPY is 45º.
Q8: The number of angles in the given figure is
 (a) 3
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)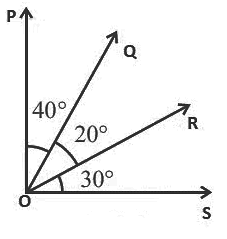 From the above figure,Angle are, ∠POS, ∠QOS, ∠ROS, ∠POQ, ∠QOR, ∠ROS.
From the above figure,Angle are, ∠POS, ∠QOS, ∠ROS, ∠POQ, ∠QOR, ∠ROS.
Therefore, number of angle formed are 6.
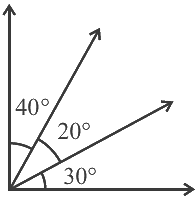
Q9: The number of obtuse angles in figure is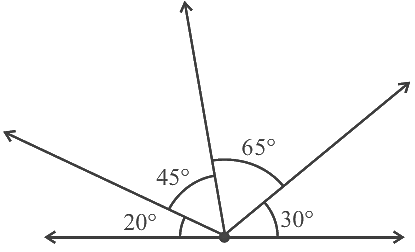 (a) 2
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Obtuse angle is defined as an angle formed is greater than 90o and less than 180o.
From the above figure,
Angle are, ∠ROP = ∠ROQ + ∠QOP
= 65º + 30º
= 95º
∠SOP = ∠ROQ + ∠QOP + ∠SOR
= 65º + 30º + 45º
= 140º
∠SOQ = ∠SOR + ∠ROQ
= 45º + 65º
= 110º
∠TOQ = ∠TOS + ∠SOR + ∠ROQ
= 20º+ 45º+ 65º
= 130º
Therefore, number of obtuse angle formed are 4.
Q10: The number of triangles in Fig. is
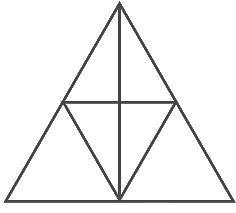
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 13
(d) 14
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)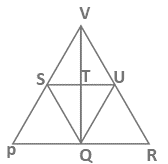
By observing the above figure, there are 13 triangles.
ΔPVR, ΔPSQ, ΔSQU, ΔSQT, ΔTQU, ΔQUR, ΔVSU, ΔVST, ΔVTU, ΔPQV, ΔRQV, ΔVSQ, ΔVUQ
Q11: If the sum of two angles is greater than 180°, then which of the following is not possible for the two angles?
(a) One obtuse angle and one acute angle
(b) One reflex angle and one acute angle
(c) Two obtuse angles
(d) Two right angles.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Because, sum of all angles of right angles is must be equal to 180º.
Q12: If the sum of two angles is equal to an obtuse angle, then which of the following is not possible?
(a) One obtuse angle and one acute angle.
(b) One right angle and one acute angle.
(c) Two acute angles.
(d) Two right angles.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Because, sum of all angles of right angles is must be equal to 180º.
Right angle triangle does not contain obtuse angle.
Obtuse angle is defined as an angle formed is greater than 90º and less than 180º.
Q13: A polygon has prime number of sides. Its number of sides is equal to the sum of the two least consecutive primes. The number of diagonals of the polygon is
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 10
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The two least consecutive prime numbers are, 2 and 3
Sum of two numbers = 2 + 3 = 5
By using formula = n(n – 3)/2
= 5(5 – 3)/2
= (5 × 2)/2
= 10/2
= 5
Q14: In the given figure, AB = BC and AD = BD = DC. The number of isosceles triangles in the figure is
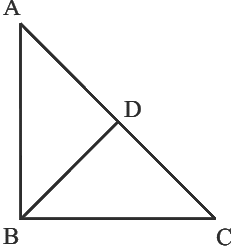
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
From the figure, ΔABC, ΔABD and ΔADC are right triangle.
Q15: In the given figure, ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC. The number of right triangles in the figure is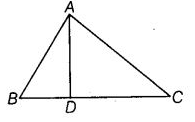
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
We have, ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC
∵ ∠BDA = ∠CDA = ∠BAC = 90°
∴ There are 3 right triangles formed in the given figure.
Q16: In the given figure, PQ ⊥ RQ, PQ = 5 cm and QR = 5 cm. Then ∆ PQR is
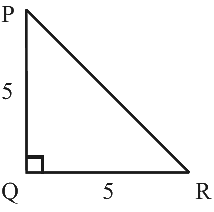
(a) a right triangle but not isosceles
(b) an isosceles right triangle
(c) isosceles but not a right triangle
(d) neither isosceles nor right triangle
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
From the question it is given that, PQ ⊥ RQ, PQ = 5 cm and QR = 5 cm.
We know that, isosceles triangle has two equal side.
Therefore, the given ΔPQR is an isosceles right triangle.
In questions 17 to 31, fill in the blanks to make the statements true:
Q17: An angle greater than 180° and less than a complete angle is called _______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
An angle greater than 180° and less than a complete angle is called reflex angle.
Q18: The number of diagonals in a hexagon is ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of diagonals in a hexagon is 9.
We know that, hexagon has 6 sides.
By using the formula, number of diagonals = n(n – 3)/2
= 6(6 – 3)/2
= 6(3)/2
= 18/2
= 9
Q19: A pair of opposite sides of a trapezium are ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
A pair of opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.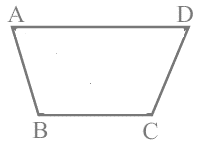
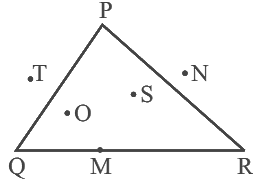
Q20: In the given figure, points lying in the interior of the triangle PQR are ______, that in the exterior are ______ and that on the triangle itself are ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
In Fig. points lying in the interior of the triangle PQR are O and S, that in the exterior are N and T and that on the triangle itself are M, P, Q and R.
Q21: In the given figure, points A, B, C, D and E are collinear such that AB = BC = CD = DE. Then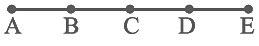 (a) AD = AB + ______
(a) AD = AB + ______
(b) AD = AC + ______
(c) mid point of AE is ______
(d) mid point of CE is ______
(e) AE = ______ × AB.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) AD = AB + BD
Where, BD = BC + CD
(b) AD = AC + CD
(c) mid point of AE is c
(d) mid point of CE is D
(e) AE = 4 × AB. [given]
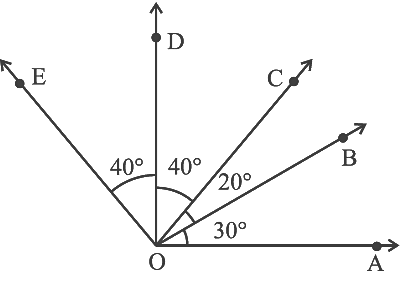
Q22: In the given figure.
(a) ∠AOD is a/an ______ angle
(b) ∠COA is a/an ______ angle
(c) ∠AOE is a/an ______ angle
 View Answer
View Answer 
From the figure,
(a) ∠AOD is a/an right angle.
Is anyone angle in the triangle is equal to 90º then the triangle is called right triangle.
∠AOD = ∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD
= 30º + 20º + 40º
(b) ∠COA is a/an acute angle
An acute angle is an angle formed between 0º to 90º.
∠COA = ∠COB + ∠BOA
= 20º + 30º
= 50º
(c) ∠AOE is a/an obtuse angle
An obtuse angle is an angle formed between 90º to 180º.
∠AOE = ∠EOD + ∠DOC + ∠COB + ∠BOA
= 40º + 40º + 20º + 30º
= 130º
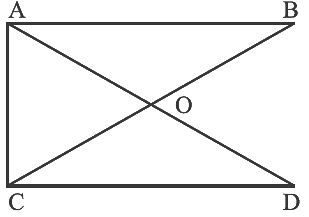
Q23: The number of triangles in figure is ______. Their names are ______________________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of triangles in Fig. is 5. Their names are ΔAOC, ΔCOD, ΔAOB, ΔACB, ΔACD.
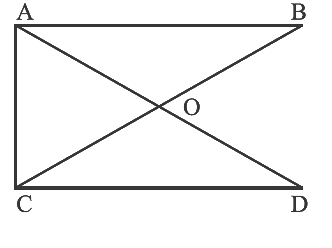
Q24: Number of angles less than 180° in figure is ______and their names are.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Number of angles less than 180° in Fig. is 12 and their names are ∠OAB, ∠OBA, ∠OAC, ∠OCA, ∠OCD, ∠ODC, ∠AOB, ∠AOC, ∠COD, ∠DOB, ∠BAC, ∠ACD.
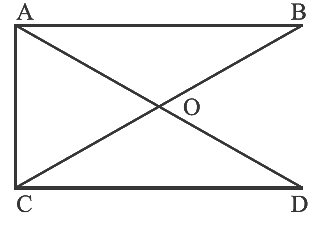
Q25: The number of straight angles in Fig. is ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of straight angles in Fig. is four.
The angles are, ∠AOD, ∠BOC, ∠COB, ∠DOA.
Q26: The number of right angles in a straight angle is ______ and that in a complete angle is ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of right angles in a straight angle is tow and that in a complete angle is four.
We know that, angle formed by straight angle = 180º
and angle formed by right angle = 90º
So, number of right angles = 180º/90º = 2
We know that, complete angle = 360º
So, number of right angles = 360º/90º = 4
Q27: The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. is ______.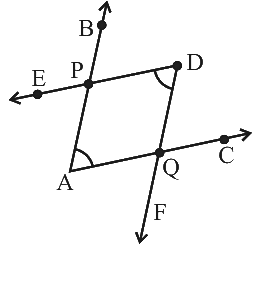
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. is two.
From the given figure, the common points are P and Q.
Q28: The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. is ______.
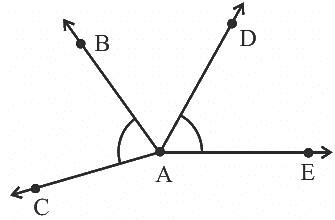
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. is one.
From the given figure, the common point is A.
Q29: The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. ______.
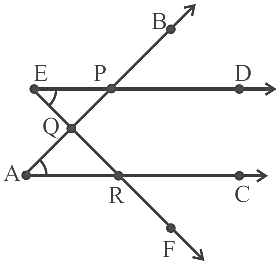
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. three.
From the given figure, the common points are P, Q and R.
Q30: The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. is ______.
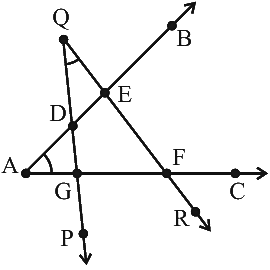
 View Answer
View Answer 
The number of common points in the two angles marked in Fig. is four.
From the given figure, the common points are D, E, F and G.
Q31: The common part between the two angles BAC and DAB in Fig. is ______.
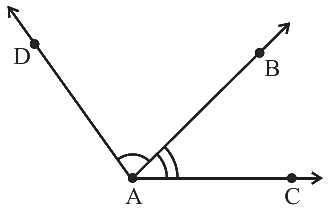
 View Answer
View Answer 
The common part between the two angles BAC and DAB in Fig. is ray AB.
State whether the statements given in questions 32 to 41 are true (T) or false (F):
Q32: A horizontal line and a vertical line always intersect at right angles.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Q33: If the arms of an angle on the paper are increased, the angle increases.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The angle is not affected, if the arms of an angle on the paper are increased or decreased.
Q34: If the arms of an angle on the paper are decreased, the angle decreases.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The angle is not affected, if the arms of an angle on the paper are increased or decreased.
Q35: If line PQ || line m, then line segment PQ || m.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
From the question, line PQ || line m.
Then, parts of those lines are also parallel.
Therefore, line segment PQ || m.
Q36: Two parallel lines meet each other at some point.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Parallel lines never meet each other.
Q37: Measures of ∠ABC and ∠CBA in Fig. are the same.
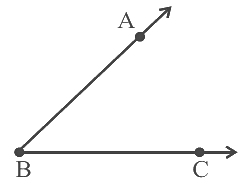
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
From the figure, both ∠ABC and ∠CBA contains common angle B.
Q38: Two line segments may intersect at two points.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Because, two line segments are intersecting at only one point.
Q39: Many lines can pass through two given points.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
only one line can pass through two given points.
Q40: Only one line can pass through a given point.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Infinite number of line can pass through a given point.
Q41: Two angles can have exactly five points in common.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Two angles can have either one or two five points in common.
Q42: Name all the line segments in given figure.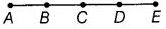
 View Answer
View Answer 
The line segments are AB, BC, CD, DE, AC, AD, AE, BD, BE and CE
Q43: Name the line segments shown m given figure.
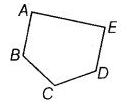
 View Answer
View Answer 
The line segments are
AB, BC, CD, DE and EA
Q44: State the mid points of all the sides of given figure.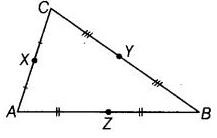
 View Answer
View Answer 
X is a mid-point of AC,
Y is a mid-point of BC and
Z is a mid-point of AB.
Q45: Name the vertices and the line segments in given figure.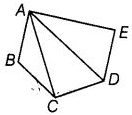
 View Answer
View Answer 
The vertices are : A, B, C, D and E.
The line segments are : AB, BC, CD, DE, EA, AC and AD.
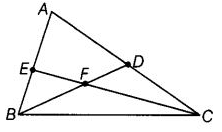
Q46: Write down fifteen angles (less than 180°) involved in given figure.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The names of fifteen angles (less than 180°) involved in figure are :
∠AEC, ∠ADB, ∠EAD, ∠EFD, ∠EFB, ∠DFC, ∠FBC, ∠FCB, ∠BFC, ∠ABC, ∠ACB, ∠DCF, ∠FDC, ∠EBF and ∠BEF.
Q47: Name the following angles of given figure, using three letters: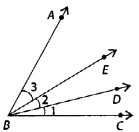
(a) ∠1
(b) ∠2
(c) ∠3
(d) ∠1 + ∠2
(e) ∠2 + ∠3
(f) ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3
(g) ∠CBA – ∠1
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) ∠1 = ∠CBD
(b) ∠2 = ∠DBE
(c) ∠3 = ∠EBA
(d) ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠CBD + ∠DBE = ∠CBE
(e) ∠2 + ∠3 = ∠DBE + ∠EBA = ∠DBA
(f) ∠l + ∠2 + ∠3 = ∠CBD + ∠DBE + ∠EBA
= ∠CBA
(g) ∠CBA – ∠1 = ∠CBA – ∠CBD = ∠DBA
Q48: Name the points and then the line segments in each of the following figures:
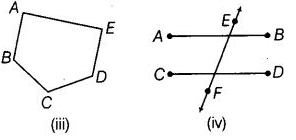
 View Answer
View Answer 
(i) Name of the points ➝ A, B and C. Name of the line segments ➝ AB, BC and CA.
(ii) Name of the points ➝ A, B, C and D. Name of the line segments ➝ AB, BC, CD and DA.
(iii) Name of the points ➝ A, B, C, D and E. Name of the line segments ➝ AB, BC, CD, DE and EA.
(iv) Name of the points ➝ A, B, C, D, E and F.
Name of the line segments ➝ AB, CD and EF.
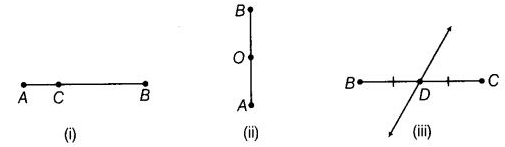
Q49: Which points in given figures, appear to be mid-points of the line segments? When you locate a mid-point, name the two equal line segments formed by it.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(i) The given figure shows there is no mid-point.
(ii) The given figure shows that O is the mid-point of ZB and the name of the two equal line segments are AC and OB.
(iii) The given figure shows that D is the mid-point of BC and the name of the two equal line segments are BD and DC.
Q50: Is it possible for the same
(a) line segment to have two different lengths?
(b) angle to have two different measures?
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) No, it is not possible for the same line segment to have two different lengths.
(b) No, it is not possible for the same angle to have two different measures.
Q51: Will the measure of ∠ABC and of ∠CBD make measure of ∠ABD in given figure?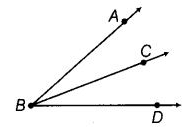
 View Answer
View Answer 
Yes, ∵ ∠ABD = ∠ABC + ∠CBD
⇒ ∠ABD is the sum of ∠ABC and ∠CBD
Q52: Will the lengths of line segment AB and line segment BC make the length of line segment AC in given figure?
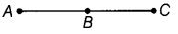
 View Answer
View Answer 
Yes, ∵ the length of line segment AC is the sum of the lengths of line segment AB and BC.
Q53: Draw two acute angles and one obtuse angle without using a protractor. Estimate the measures of the angles. Measure them with the help of a protractor and see how much accurate is your estimate.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Angles are measured in degrees. The symbol for degree is a little circle.
The full circle is 360° (360 degree). A half circle or a straight angle is 180°. A quarter circle or a right angle is 90°.
Place the mid-point of the protractor on the Vertex of the angle. Line up one side of the angle with the Zero line of the protractor (where you see the number 0).
Read the degrees here the other side crosses the number scale.
1. Measure the angles.
2. Measure the angles. Label each angle as acute or obtuse.
3. Tasha measured an acute angle, and got 146°. The teacher pointed out that she had read the wrong set of numbers on the protractor.
4. Measure the following angles using your own protractor. If you need to, make the sides of the angles longer with a ruler.
5. Draw four dots and connect them so that you get a quadrilateral.
Measure all the angles of your quadrilateral. Then add the angle measure.
Q54: Look at a given figure. Mark a point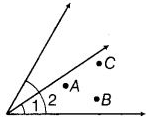
(a) A which is in the interior of both ∠1 and ∠2.
(b) B which is in the interior of only ∠1.
(c) Point C in the interior of ∠1.
Now, state whether points B and C lie in the interior of ∠2 also.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Yes, the given figure shows that the points B and C lie in the interior of ∠2 also.
Q55: Find out the incorrect statement, if any, in the following : An angle is formed when we have
(a) two rays with a common end-point
(b) two line segments with a common end-point
(c) a ray and a line segment with a common end-point
 View Answer
View Answer 
All the three statements (a), (b) and (c) are incorrect.
∵ The common initial point of two rays forms an angle.
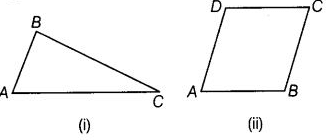
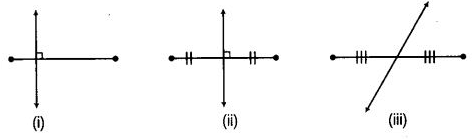
Q56: In which of the following figures,
(a) perpendicular bisector is shown?
(b) bisector is shown?
(c) only bisector is shown?
(d) only perpendicular is shown?
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Figure (ii) shows the perpendicular bisector
(b) Figure (ii) and (iii) shows the bisector.
(c) Figure (iii) shows only the bisector.
(d) Figure (i) shows only the perpendicular.
Q57: What is common in the following figures (i) and (ii)?
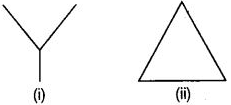
Is figure (i) that of triangle ? if not, why?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Both the figures (i) and (ii) have 3 line segments.
No, Fig. (i) is not a triangle since the three line segments does not form a closed figure.
Q58: If two rays intersect, will their point of intersection be the vertex of an angle of which the rays are the two sides?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Yes
Q59: In given figure,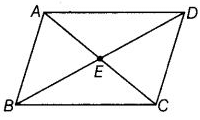
(a) name any four angles that appear to be acute angles.
(b) name any two angles that appear to be obtuse angles.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Acute angles : ∠ADE, ∠AEB, ∠ABE and ∠ECD.
(b) Obtuse angles : ∠BCD and ∠BAD.
Q60: In given figure,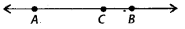
(a) is AC + CB = AB ?
(b) is AB + AC= CB ?
(c) is AB + BC = CA ?
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Yes, AC + CB = AB
(b) No, AB – AC = CB
(c) No, AB – BC = CA
Q61: In given figure
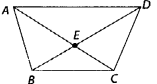
(a) What is AB + BC?
(b) What is AC – EC?
(c) What is BD – BE?
(d) What is BD – DE?
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) AE + EC = AC
(b) AC – EC = AE
(c) BD – BE = ED
(d) BD – DE = BE
Q62: Using the information given, name the right angles in each part of given figures.
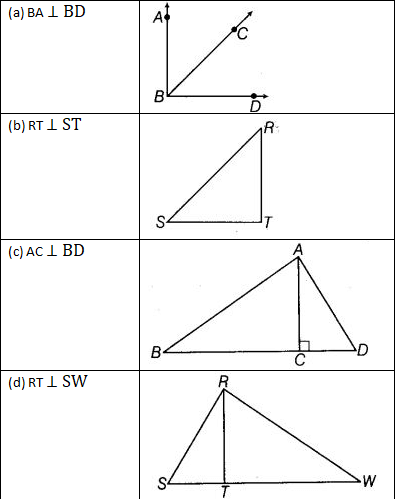
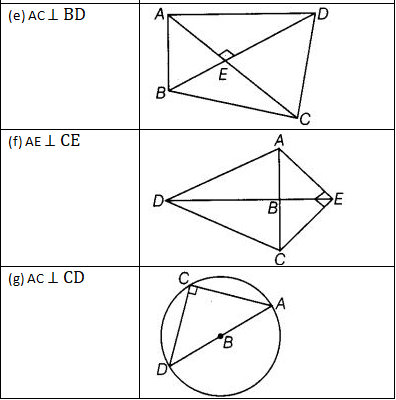
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) ∵ BA ⊥ BD,
∴ The right angle is ∠ABD
(b) ∵ RT ⊥ ST, ∴ The right angle is ∠RTS
(c) ∵ AC ⊥ BD,
∴ The right angles are ∠ACD and ∠ACB
(d) ∵ RS ⊥ RW,
∴ The right angle is ∠SRW
(e) ∵ AC ⊥ BD,
∴ The right angles are ∠AED, ∠AEB, ∠BEC and ∠CED
(f) ∵ AE ⊥ CE,
∴ The right angle is ∠AEC
(g) ∵ AC ⊥ CD,
∴ The right angle is ∠ACD
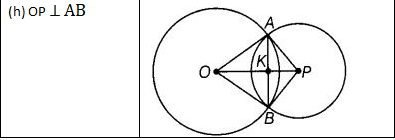
(h) ∵ OP ⊥ AB,
∴ The right angles are ∠AKO, ∠AKP, ∠BKO and ∠BKP.
Q63: What conclusion can be drawn from each part of given figures, if
(a) DB is the bisector of ∠ADC?
(b) BD bisects ∠ABC.
 (c) DC is the bisector of ∠ADB, CA ⊥ DA and CB ⊥ DB
(c) DC is the bisector of ∠ADB, CA ⊥ DA and CB ⊥ DB
 View Answer
View Answer 
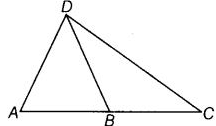
(a) ∵ DB is the bisector of ∠ADC.
∴ ∠ADB = ∠CDB
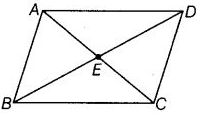
(b) ∵ BD bisects ∠ABC.
∴ ∠ABD = ∠CBD
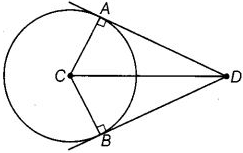
(c) ∵ DC is the bisector of ∠ADB, CA ⊥ DA and CB ⊥ DB
∠ADC = ∠BDC, ∠CAD = ∠CBD = 90°
Q64: An angle is said to be trisected, if it is divided into three equal parts. If in a given figure, ∠BAC = ∠CAD = ∠DAE, how many trisectors are there for ∠BAE ?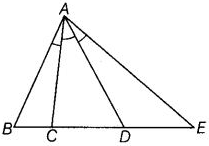
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have given, ∠BAC = ∠CAD = ∠DAE
∴ There are two trisectors namely, AC and AD.
Q65: How many points are marked in given figure?
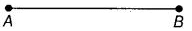
 View Answer
View Answer 
Two points A and B are marked.
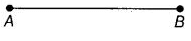
Q66: How many line segments are there in given figure?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Only one line segment, AB is there.
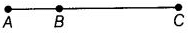
Q67: In given figure, how many points are marked? Name them.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Three points A, B and C are marked.
Q68: How many line segments are there in given figure? Name them.

 View Answer
View Answer 
Three line segments, namely AB, BC and AC are there.
Q69: In given figure, how many points are marked? Name them.

 View Answer
View Answer 
Four points A, B, C and D are marked.
Q70: In given figure how many line segments are there? Name them.
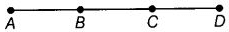
 View Answer
View Answer 
Six line segments, namely AB, AC, AD, BC, BD and CD.
Q71: In given figure, how many points are marked? Name them.
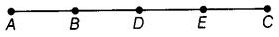
 View Answer
View Answer 
Five points are marked, namely A, B, D, E and C.
Q72: In given figure how many line segments are there? Name them.
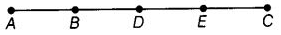
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ten line segments, namely AB, AD, AE, AC, BD, BE, BC, DE, DC and EC.
Q73: In given figure, O is the centre of the circle.
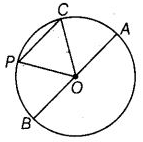
(a) Name all chords of the circle.
(b) Name all radii of the circle.
(c) Name a chord, which is not the diameter of the circle.
(d) Shade sectors OAC and OPB.
(e) Shade the smaller segment of the circle formed by CP.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Name of chords : PC and BA.
(b) Name of radii : PO, OC, OB and OA.
(c) PC is a chord which is not the diameter of the circle.
(d) Shaded sectors OAC and OPB are as:
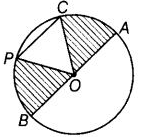 (e) Shade the smaller segment of the circle formed by CP.
(e) Shade the smaller segment of the circle formed by CP.
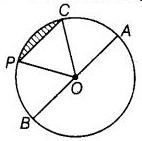
Q74: Can we have two acute angles whose sum is
(a) an acute angle? Why or why not?
(b) a right angle? Why or why not?
(c) an obtuse angle? Why or why not?
(d) a straight angle? Why or why not?
(e) a reflex angle? Why or why not?
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Yes, ∵ the sum of two acute angles can be the acute angle.
E.g., 30° and 40° are two acute angles and their sum = 30° + 40° = 70°, which is also an acute angle.
(b) Yes, ∵ the sum of two acute angles can be a right angle.
E.g., 30° and 60° are two acute angles and their sum = 30° + 60° = 90°, which is a right angle.
(c) Yes, ∵ the sum of two acute angles can be an obtuse angle.
E.g., 45° and 60° are two acute angles and their sum = 45° + 60° = 105°, which is an obtuse angle.
(d) No, ∵ the sum of two acute angles is always less than 180°.
(e) No, ∵ the sum of two acute angles is always less than 180°.
Q75: Can we have two obtuse angles whose sum is
(a) a reflex angle? Why or why not?
(b) a complete angle? Why or why not?
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Yes, ∵ the sum of two obtuse angles is always greater than 180°.E.g., 135° and 100° are two obtuse angles and their sum = 135° +
100° = 235°, which is greater than 180°.
(b) No, ∵ the sum of two obtuse angles is greater than 180° but less than 360°. In the above example, we can see that the sum of 135° and 100° i.e., 235° is greater than 180° but less than 360°.
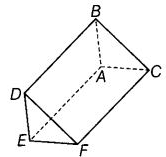
Q76: Write the name of
(a) vertices
(b) edges, and
(c) faces of the prism shown in given figure.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Vertices : A, B, C, D, E and F.
(b) Edges : AB, BC, AC, DF, FC, BD, EF, ED and AE.
(c) Faces : EACF, EDBA, ABC, DEF and DBCF.
Q77: How many edges, faces and vertices are there in a sphere?
 View Answer
View Answer 
In a sphere, edges – 0, faces – 0 and vertices – 0.
Q78: Draw all the diagonals of a pentagon ABCDE and name them.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The diagonals of a pentagon ABCDE are AC, AD, BE, BD and EC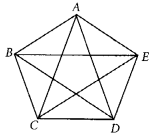
|
6 videos|117 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Geometry - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What are the key concepts covered in the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Geometry? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively use the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Geometry to prepare for my exams? |  |
| 3. Are the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Geometry aligned with the latest exam patterns? |  |
| 4. Can solving NCERT Exemplar problems help improve my geometry skills? |  |
| 5. Where can I find additional resources to supplement my study of geometry alongside the NCERT Exemplar Solutions? |  |
















