NCERT Solution (Part - 3) - Accounting Ratios | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download

*Since the very first item is Inventory in the beginning, so this item should be Inventory at the end.
Answer :

Question 2 : A trading firm’s average inventory is Rs 20,000 (cost). If the inventory turnover ratio is 8 times and the firm sells goods at a profit of 20% on sale, ascertain the profit of the firm.
Answer :

Let Sale Price be Rs 100
Then Profit is Rs 20
Hence, the Cost of Revenue from Operations = Rs 100 − Rs 20 = Rs 80
If the Cost of Revenue from Operations is Rs 80, then Revenue from Operations = 100
If the Cost of Revenue from Operations is Rs 1, then Revenue from Operations = 100/80
Question 3 : You are able to collect the following information about a company for two years:
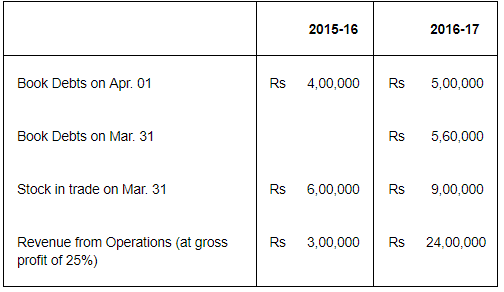
Calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio and Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio if in the year 2015-16 stock in trade increased by Rs 2,00,000.
Answer :

Note: It has been assumed that all sales are credit sales
Page no. 242
Numericals Questions
Question 1 : The following Balance Sheet and other information, calculate following ratios:
(i) Debt-Equity Ratio
(ii) Working Capital Turnover Ratio
(iii) Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio
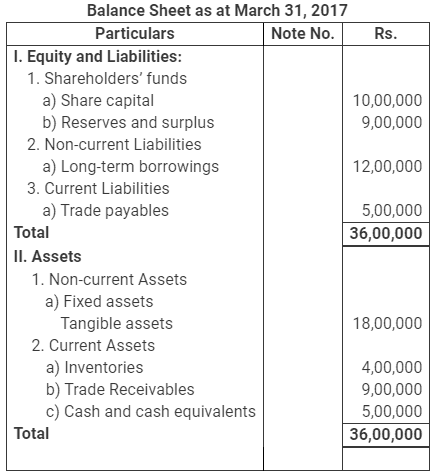
Additional Information: Revenue from Operations Rs. 18,00,000 Calculate:
i) Debt-Equity Ratio
ii) Working Capital Turnover Ratio
iii) Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio
(Debt-Equity Ratio 0.63:1; Working Capital Turnover Ratio 1.39 times; Trade
Receivables Turnover Ratio 2 times)
Answer : 1. Debt-Equity Ratio
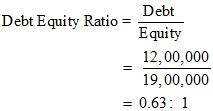
Debt = Long Term Borrowings = Rs 12,00,0000
Equity = Share Capital + Reserve and Surplus
= 10,00,000 + 9,00,000
= Rs 19,00,000
2. Working Capital Turnover Ratio
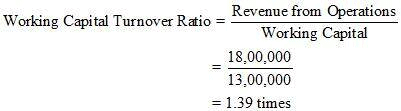
Revenue from Operations = Rs 18, 00,000
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 18,00,000 – 5,00,000
= Rs 13,00,000
3. Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio
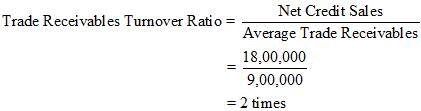
Net Credit Sales = Rs 18,00,000
Average Trade Receivables = Rs 9,00,000
Notes:
1. Revenue from Operations are assumed to be revenue generated from credit sales.
2. The amount of trade receivables given in the Balance Sheet is assumed to be Average Trade Receivables.
Question 2 : From the following information, calculate the following ratios:
i) Quick Ratio
ii) Inventory Turnover Ratio
iii) Return on Investment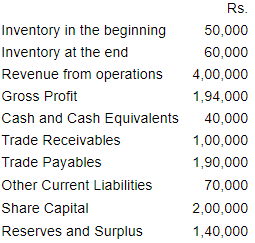
(Balance in the Statement of Profit & Loss A/c)
Answer :
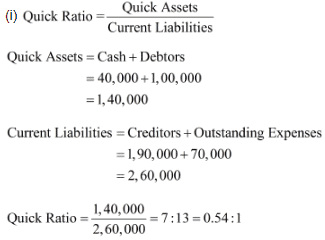
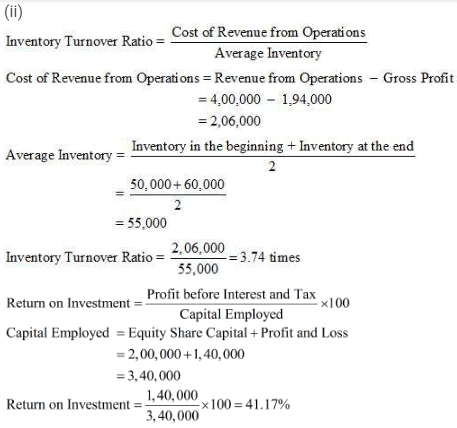
Page no. 243
Numerical Questions :
Question 3 : From the following, calculate
(a) Debt Equity Ratio (b) Total Assets to Debt Ratio (c) Proprietary Ratio.
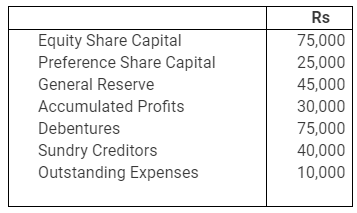
Answer :

Question 4 : Cost of Revenue from Operations is Rs 1,50,000. Operating expenses are Rs 60,000. Revenue from Operations is Rs 2,50,000. Calculate Operating Ratio.
Answer :

Question 5 : The following is the summerised transactions and Statement of Profit and Loss Account for the year ending March 31, 2007 and the Balance Sheet as on the basis of following information, calculate:
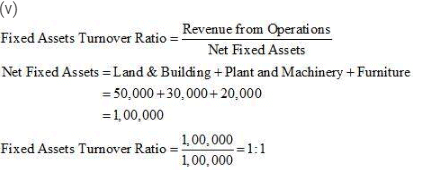
(i) Gross Profit Ratio (ii) Current Ratio (iii) Acid Test Ratio (iv) Inventory Turnover Ratio (v) Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio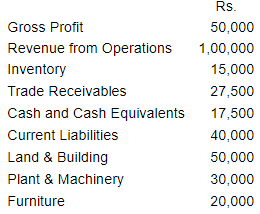
Answer :


Average Inventory = 15,000*
*Note: Since values for inventory in the beginning and inventory at the end is not given, the amount of inventory is assumed to be average inventory.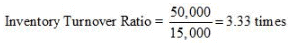
Question 6 : From the following information calculate Gross Profit Ratio, Inventory Turnover Ratio and Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio. 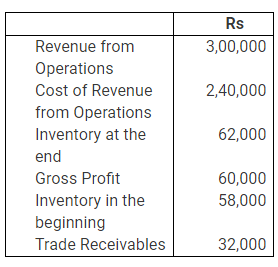
Answer :
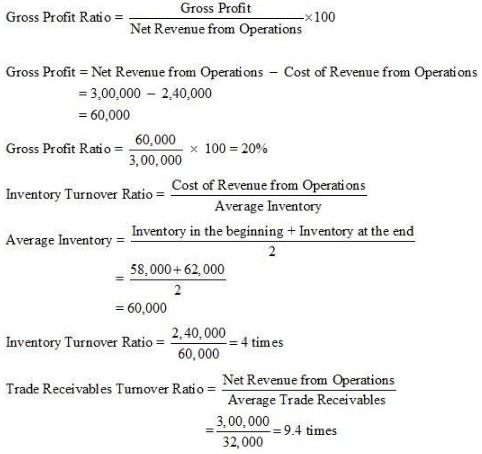
Note: In the solution, Trade Receivables are assumed as the Average Trade Receivables.
|
4 videos|168 docs
|
FAQs on NCERT Solution (Part - 3) - Accounting Ratios - Additional Study Material for Commerce
| 1. What are accounting ratios and why are they important in commerce? |  |
| 2. How are accounting ratios calculated? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of profitability ratios in analyzing a company's financial performance? |  |
| 4. How do liquidity ratios help in assessing a company's short-term financial position? |  |
| 5. What is the role of solvency ratios in determining a company's long-term financial stability? |  |






















