NCERT Solution - Recording of Transactions-II | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Short Question Answers
Q1: Briefly state how the cash book is both journal and a ledger.
Ans: The preparation of the journal entries when the journal entry is sent directly from sources to the cashbook. The ledger also has a bank column to balance the cash column. This then serves as the basis for a ledger account and where separate money and bank account do not need to be maintained; that is why a book of books is a magazine and a magazine in this way.
Q2: What is the purpose of contra entry?
Ans: A contra entry is an entry during the place where the deposit was made or the withdrawal occurs at the same time is done when the debit and credit transaction is bank and cash. eg When a deposit is made or money is withdrawn, the input is claimed to be contrary to entry. During the double-column book letter Contra entry is entered on each side of the account with the letter "C" in the LF column. This suggests that the conflicting account involved in this transaction is on the other side of the account. And Contra entry does not affect the record in any way because to take advantage of the reduction of cash and Cash in bank overruns or vice versa.
Q3: What are special purpose books?
Ans: Books for special purpose are considered as sections of the Journal. Any business has a large number of transactions throughout the year. This transaction is natural and possible always. The inclusion of the magazine in all such transactions must be forwarded as this happens. Therefore special purpose books such as Purchase Books and ₹Sales Books are prepared and stored to record this transaction directly without making any entries. This thus saves time and effort on the business of installing such duplicate entries.
Q4: What is petty cash book? How is it prepared?
Ans: Every business has got to undergo petty expenses such postage, telephone, stationery etc. rather than making the journal entries for these petty transactions as they occur whenever, the petty cashbook is maintained by the entities which directly record such transactions. There are two sorts of petty cash books:
i. Original System: during this system a specific amount of sum is given to the cashier so as to undergo such petty transactions. The cashier makes petty expenses out of this amount and records them as they're spent. After when the whole amount is spent, the report is handed over to the cashier for such expenses.
ii. Imprest system: during this system, a specific fixed amount of sum is provided to the petty cashier within the beginning of any accounting period. After the passage of the certain interval of your time, the petty cash book is checked and therefore the petty cashier is given the quantity spent to offer the petty cashier the fixed amount of sum during a necessitated manner. This fixed amount of sum is named Imprest cash.
Q5: Explain the meaning of posting of journal entries?
Ans: The transfer of recorded transactions from magazine entries to the ledger is understandable because the submission of magazine entries. Magazine submissions are designed to record a large number of business transactions at regular intervals. The process of sending the magazine to the logger accounts is stated due to the division of funds.
Q6: Define the purpose of maintaining a subsidiary journal.
Ans: The purpose of the auxiliary journal is to reduce the burden and difficulty of recording the dynamic transactions of the natural environment when they are sent directly to unsolicited letters rather than to the corresponding journal entry at any time in the books of accounts. Business transactions such as day-to-day purchases and sales are therefore incorporated directly into the manual. This continues to allow the business to quickly review such transactions and verify according to the need of the business. The purpose of keeping the following documents is as follows:
- Provides an opportunity for business to differentiate between organizational employees who benefit exclusively in their field.
- This allows the business to save a lot of their time and therefore even attempts where the entries are sent directly to the books of account rather than a different contribution at any time such as the journal entry.
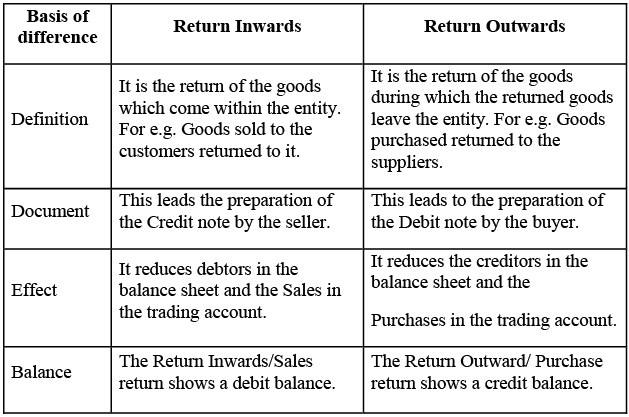
Q7: Write the difference between return inwards and return outwards.
Ans: The difference between return inwards and return outwards are as follows:
Q8: What do you understand about ledger folio?
Ans: The Ledger folio (L.F.) number is mentioned because the reference number which denotes the pagination of the corresponding ledger account. This hence allows a private to see the first entry posted within the Ledger Account, allowing the due tracking and therefore the examination of the transaction. This reduces the complexity to travel through the massive number of the transactions within the day to day which is posted within the day to day basis so as to seem after the special transaction.
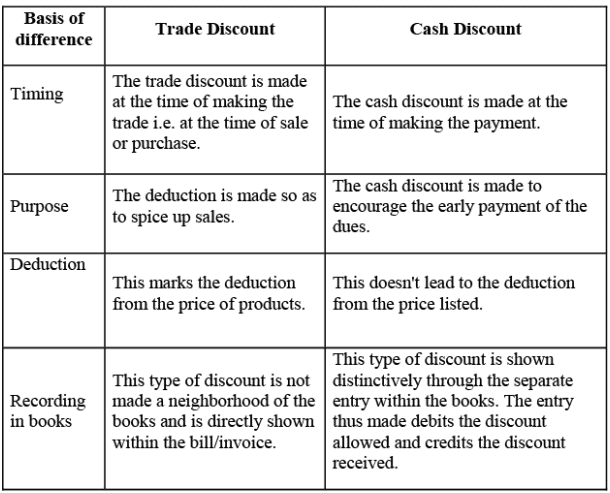
Q9: What is the difference between a trade discount and a cash discount?
Ans: The difference between trade discount and cash discount are as follows:
Q10: Write the process of preparing ledger from a journal.
Ans: The process for preparing a ledger from a magazine is:
- Recording transactions for magazine submissions and identifying loan and credit transactions for them.
- Adjusting the ledger account on time by keeping in mind the format of the ledger. The ledger columns should therefore include the following columns: Date, details, JF and number on each side of the sheet.
- The left side of the account is that accounting must therefore contain a date which is why the account will be debited within the data column. Journal Folio number and therefore Value must be specified accordingly.
- The right side of the account should include the credit entries and should have a date so it is mainly to say that the account will be credited, as well as the amount.
Q11: What do you understand by the Imprest amount in a petty cash book?
Ans: Imprest amount is that the fixed amount of sum which is given to the petty cashier to form petty expenses for the required period of your time. The petty cash book is checked at regular intervals and therefore the petty cashier is given the reimbursement to take care of the fixed amount or Imprest amount. This amount is provided within the beginning of the accounting period which is to be searched for the whole accounting year.
Long Question Answers
Q1: Explain the need for drawing up the special purpose books.
Ans: The following is a requirement for keeping books for a specific purpose:
- Specialized purpose books help the business decide to respond within the organization because the person assigned to keep the specific purpose book must keep his or her own book which is why he or she is responsible for the true accuracy of the business.
- The keeping of special-purpose books allows the organization to see the benefits of quick-made recording that accompanies a special-purpose book within the books because the entries are made in a very simple way.
- It helps to achieve the efficiency of accountants once they have acquired the technology within the domain of their special purpose book.
- It is helpful for a business to make it easier when recurring transactions such as purchases and therefore the sale is sent directly within special purpose letters rather than made in magazine entries. v. Bookkeeping for special purposes continues to provide an opportunity for a business to track transactions if it is not required to check magazine entries for a book transaction.
Q2: What is a cash book? Explain the types of cash book.
Ans: Accounting is often referred to as a special book for cash savings purposes and therefore a business transaction in a business where within accounting records transactions. Within the calculation of a transaction, a transaction that carries a deposit amount to the bank and therefore cash receipts are recorded and therefore financial records are payments made by the bank and cash made by the business. It is considered an authentic logbook that sends directly to the source from source documents. It is also considered to be a Ledger as one can directly cash in and therefore the business bank balances of any of your time. The ledger is usually kept monthly. There are four types of books
- Simple Cash Book: this sort of money book records only the cash transactions incurred by the business where within the accounting receipts and within the accounting the payments are recorded.
- Double column Cash book: this sort of money book records the cash and therefore the bank transaction made by the business. It thus has two columns on all sides of the cash book. These sorts of cash books record the contra entries during which both the cash and therefore the bank side is debited and credited.
- Triple column cash book: this sort of money book records the discount allowed and received by the business and thus comprises the extra column for an equivalent.
- Fund Book: The fund Book is maintained for the aim of recording the petty expenses made by the business like postage charges, telephone and stationery bills etc.
Q3: What is contra entry? How can you deal with this entry while preparing the double column cash book?
Ans: The Contra entry is made when the deposit or withdrawal made in the bank through the cash happens in a simultaneous manner. Thus the effect of the contra entry happens on both sides of the cash book – debit and credit. It is denoted by the letter “C” in the Ledger Folio column. It is important to note that the contra entries do not affect the balance of the balance sheet because as with the loss in Cash in Hand there is a rise in the balance of the bank and vice versa.
The following is an example when cash is withdrawn from Bank: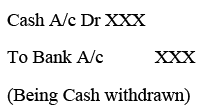
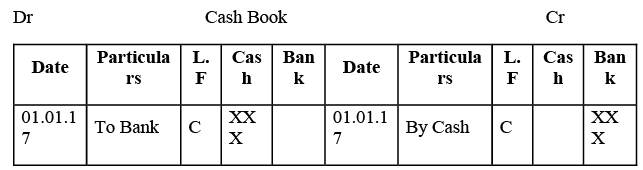
This entry is illustrated in the cash book below:
Q4: What is a petty cash book? Write the advantages of a petty cash book?
Ans: The fund book is the cash book which records the petty expenses made by the business like postage charges, stationery, electricity bill etc. The one that handles and maintains the fund book is named petty cashier.
The fund book is maintained in two ways.
Original System: Under this technique a specific amount of sum is given to the cashier who spends it on the petty expenses and records an equivalent within the petty cash book. The petty cashier reports the small print of an equivalent when the quantity held by him/her is spent.
Imprest system: Under this technique the petty cashier is given the actual fixed amount of sum at the start of every accounting period of which he/she is required to form expenses. After every certain duration of your time the fund book is checked and therefore the amount spent on the petty expenses is given such that the fixed balance of the determined cash for the petty expenses is held by the petty cashier. This fixed amount of sum is mentioned as Imprest cash.
The benefits of bookkeeping are as follows:
- There is a small cost to the business so bookkeeping makes it easier and easier to record what is being done instead of making magazine entries equal.
- Minor expenses are usually controlled by the entity by providing a minimum amount of cash to the person responsible for using it wisely and continuing to report costs to the recipient.
- The booklet helps the business to see the division of labor when the burden of keeping accounts is only a small cashier.
This, in turn, allows the chief financial officer to ensure the effectiveness of the small-scale recording system.
Q5: Describe the advantages of subdividing the Journal.
Ans: The benefits of classifying the magazine are as follows:
- The division of magazines makes it incumbent on the business to transfer responsibility to the people responsible for their work books of account. This, in turn, enables them to justify their accuracy and, as a result, their accuracy. It, therefore, serves as a check on the illegal participation of employees of the organization.
- Magazine division creates staff divisions where roles are therefore assigned to individuals within the organization to maintain their proper book. This reduces the difficulty of having an accounting job. · Separate book production of different types of transactions saves business time when such transactions are often recorded directly in the books rather than making magazine entries equivalent.
- Separation of magazine entries allows the company to see the company to see effective results when everyone gives the responsibility to keep their books running smoothly. So they got the technology.
- Recording different transactions in different books make it easier for a business to track transactions of different types by browsing their books. For example, in order to determine a credit purchase made by an organization on any given day it can be viewed directly by browsing the receipts rather than looking at magazine entries that contain large transactions.
Q6: What do you understand by the balancing of accounts?
Ans: The balancing of the account means making the quantities accounting adequate to the amount within the accounting. This is often done on regular basis from time to time by the business. The following is that the steps in balancing of account:
Step 1: Total the debit and therefore the accounting of the account and determine which amount is higher by tallying both of them.
Step2: the entire of the sides comprising the upper amount either on the credit or on the accounting of the account has got to be written because the grand total amount.
Step 3: Determine the difference of the quantity of the lower side with the grand total to work out the balancing figure. The balancing figure has got to be written as Balance c/d.
Step 4: the quantity of the balance c/d are going to be posted within the side whichever sides features a lower total
Step 5: This amount of Balance c/d has got to brought down within the subsequent accounting period and treated as Balance b/d.
Numerical Question Answers
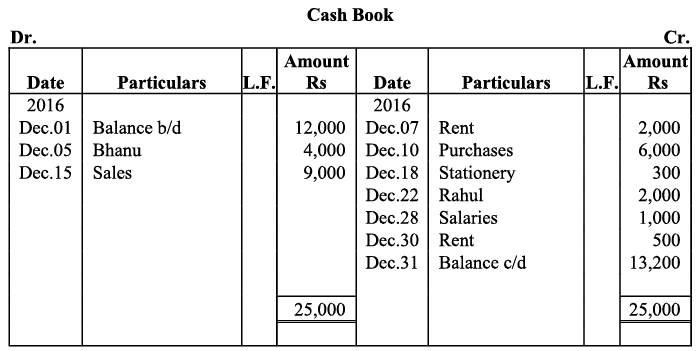
Q1: Enter the following transactions in a simple cash book for December 2016:
 Ans:
Ans:
Q2: Record the following transaction in simple cash book for November 2016.
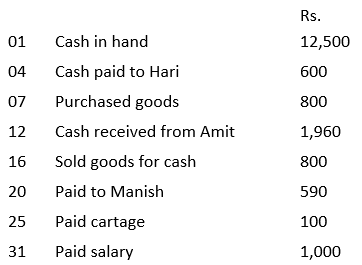
Ans:
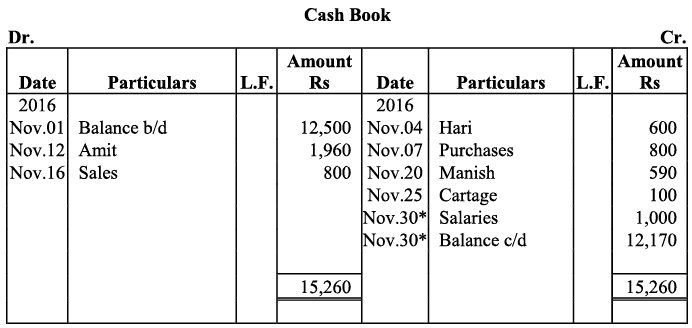
Q3: Enter the following transaction in Simple cash book for December 2017
 Ans:
Ans:
Q4: Record the following transactions in a bank column cash book for December 2016:
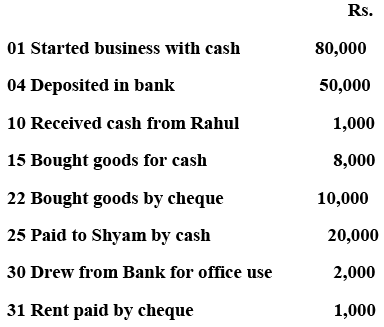
Ans:
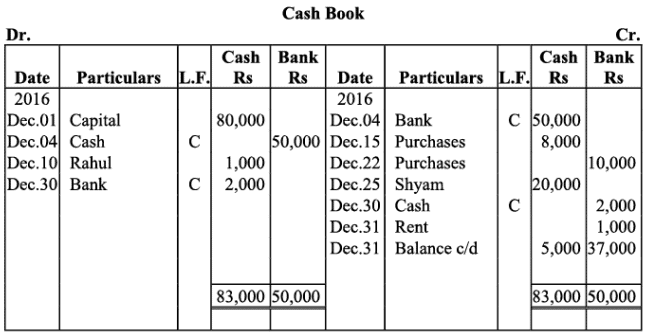
Q5: Prepare a double column cash book with the help of following information for December 2016:

Ans: 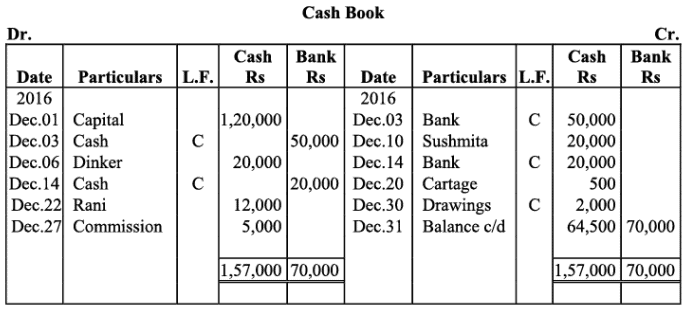
Q6: Enter the following transactions in double column cash book of M/s Ambica Traders for July 2017:
 Ans: Books of M/s. Ambika Traders
Ans: Books of M/s. Ambika Traders
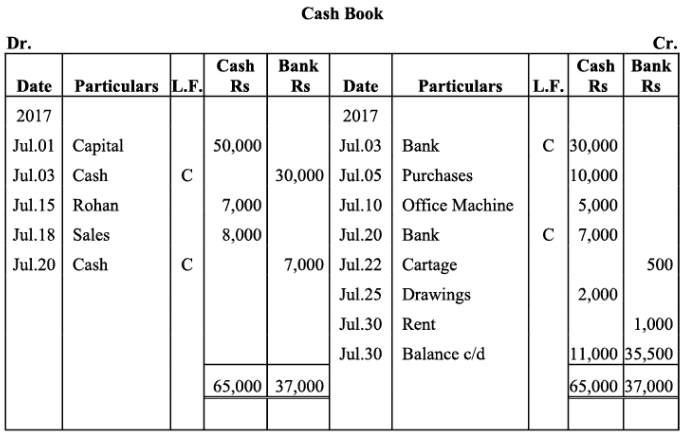
Q7: Prepare double column cash book from the following information for July 2017:
 Ans: Books of M/s. Ruchi Trader
Ans: Books of M/s. Ruchi Trader
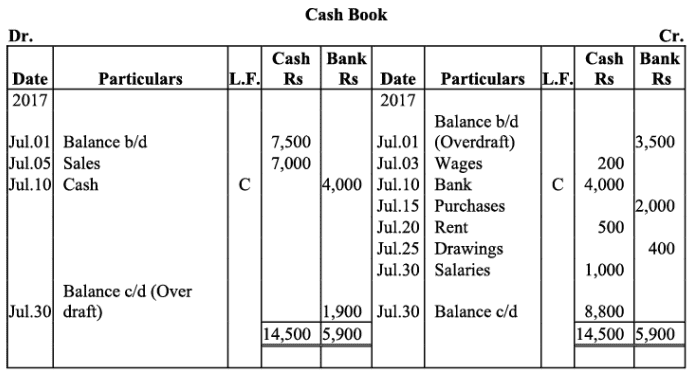
Q8: Enter the following transaction in a double column cash book of M/s.Mohit Traders for January 2017:

Ans: Books of M/s. Mohit Traders
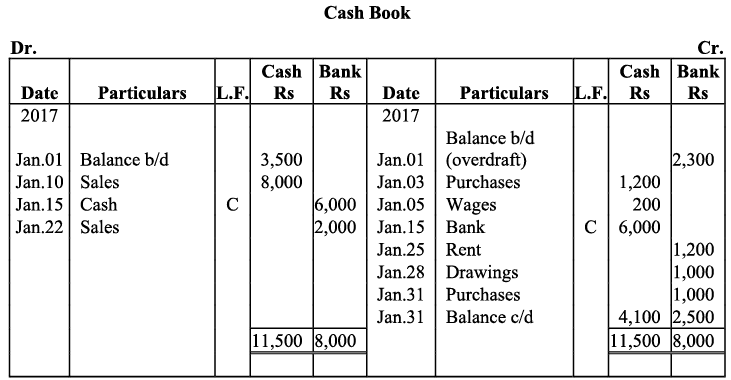
Q9: Prepare double column cash book from the following transactions for the year August 2017: Ans:
Ans:
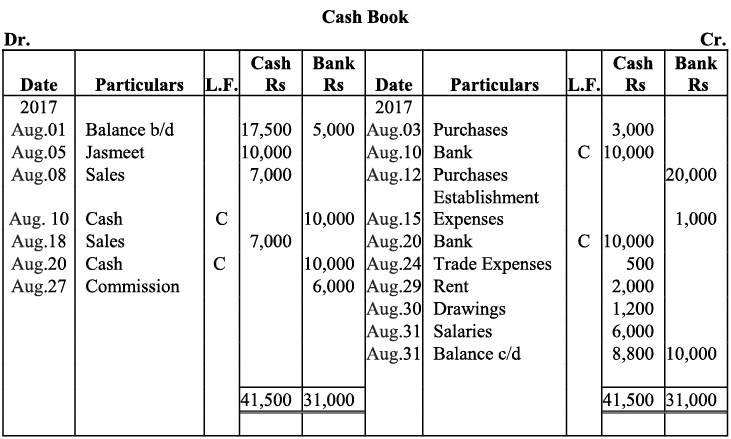
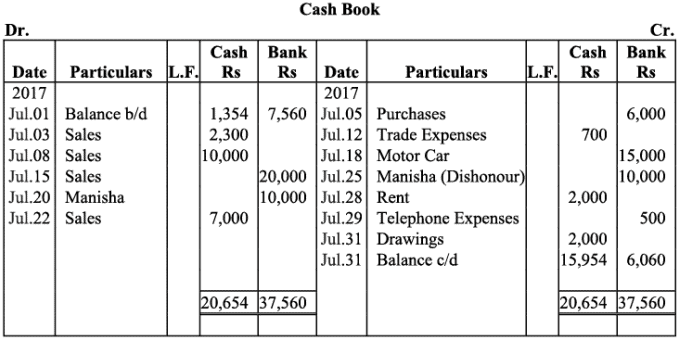
Q10: M/s Ruchi trader started their cash book with the following balances on July 2017: cash in hand ₹1,354 and balance in bank current account ₹7,560. He had the following transaction in the month of July 2017: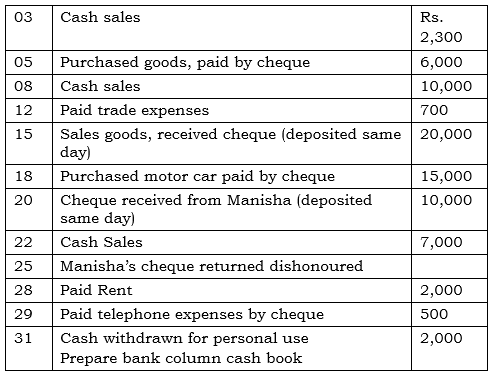
Ans: Books of M/s. Ruchi Trader
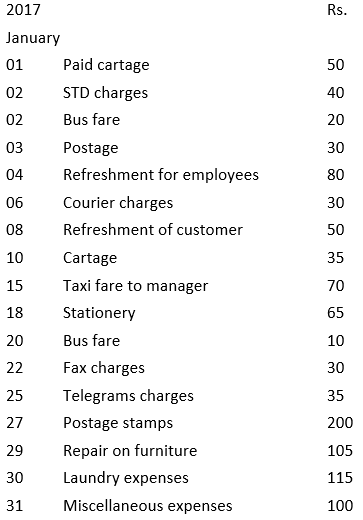
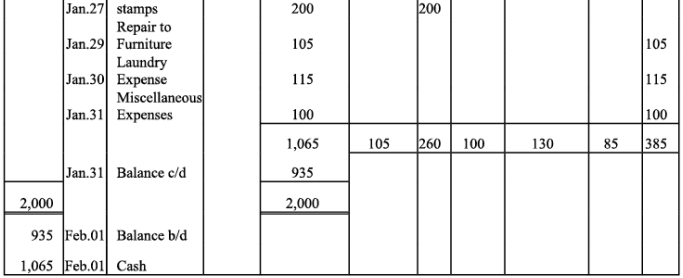
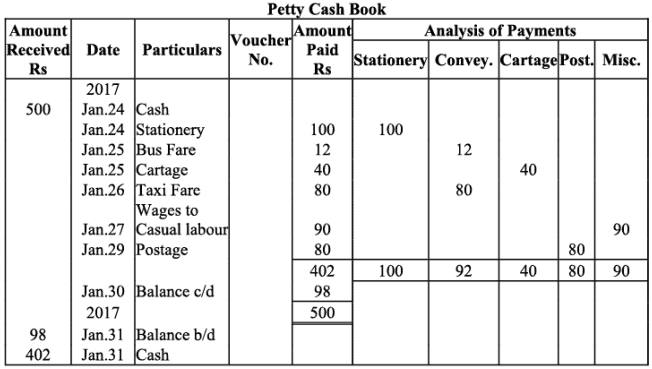
Q11: Prepare petty cash book from the following transactions. The imprest amount is ₹2,000.
Ans: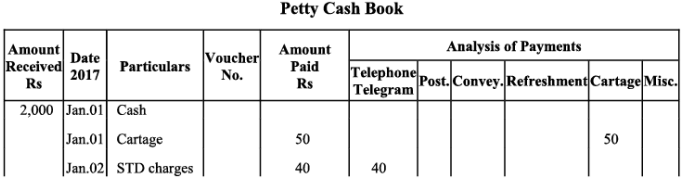

Q12: Record the following transactions during the week ending Dec.30, 2014 with a weekly imprest ₹ 500.
 Ans:
Ans:
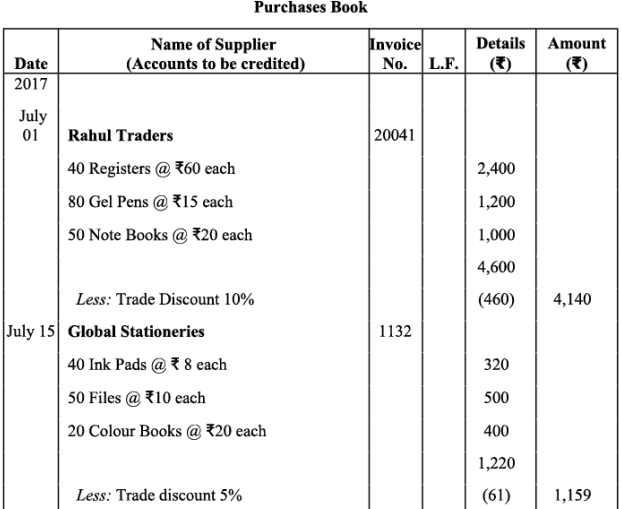
Q13: Enter the following transactions in the Purchase Journal (Book) of M/s Gupta Traders of July 2017:

Ans: Books of M/s. Gupta Traders

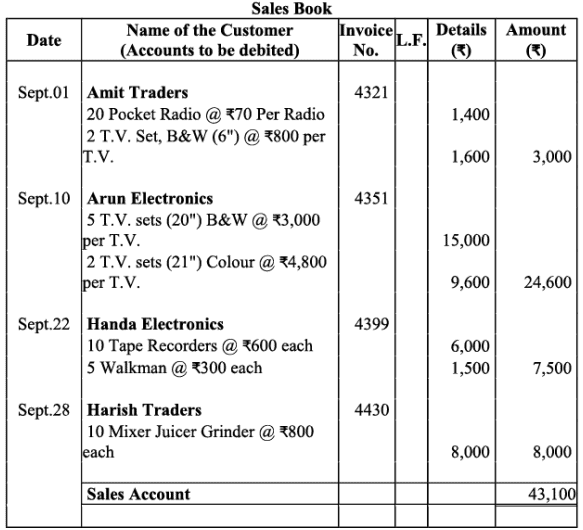
Q14: Enter the following transactions in sales (journal) book of M/s. Bansal electronics:
 Ans: Books of M/s. Bansal Electronics
Ans: Books of M/s. Bansal Electronics
Q15: Prepare a purchases return (journal) book from the following transactions for April 2017.
 Ans:
Ans: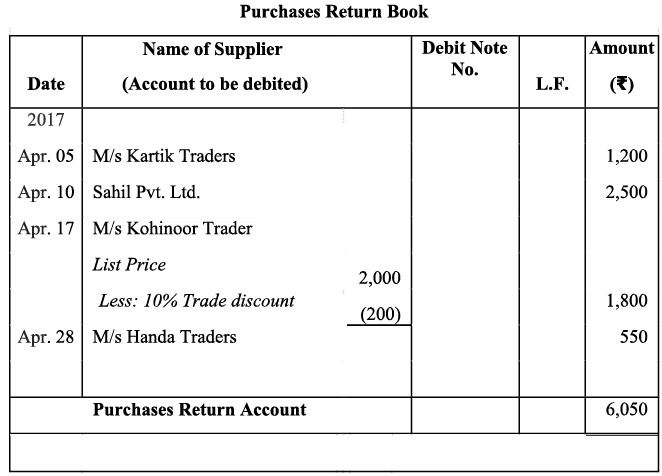
Q16: Prepare Return Inward Journal (Book) from the following transactions of M/s Bansal Electronics for July 2017:

Ans: Books of M/s. Bansal electronics
Sales Returns Book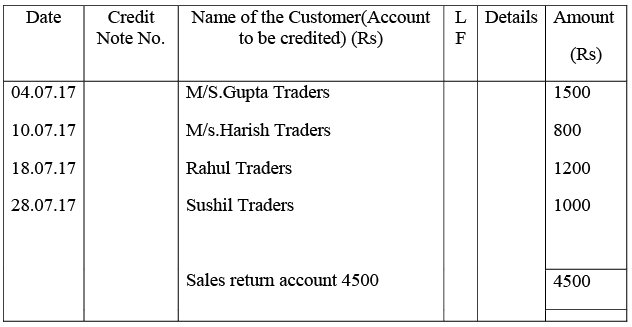
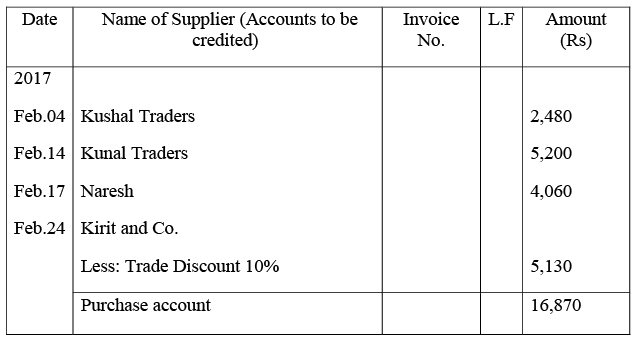
Q17: Prepare proper subsidiary books and post them to the ledger from the following transactions for the month of February 2017:
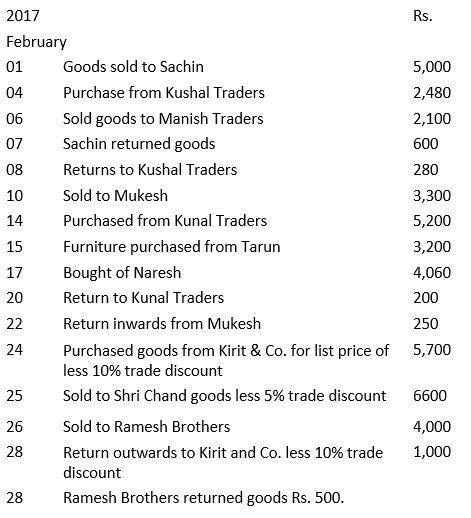 Ans: Journal
Ans: Journal
Purchases Book
Sales Book
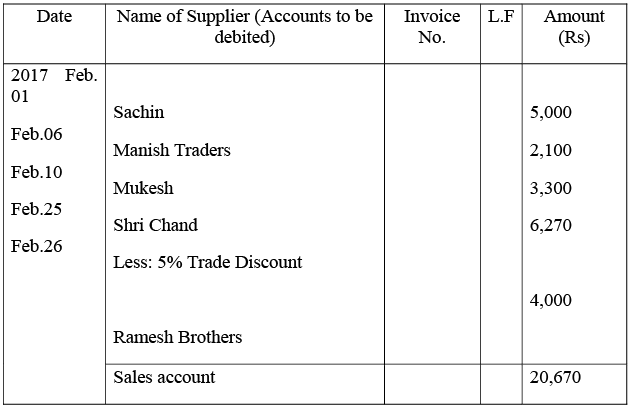 Sales Return Book
Sales Return Book
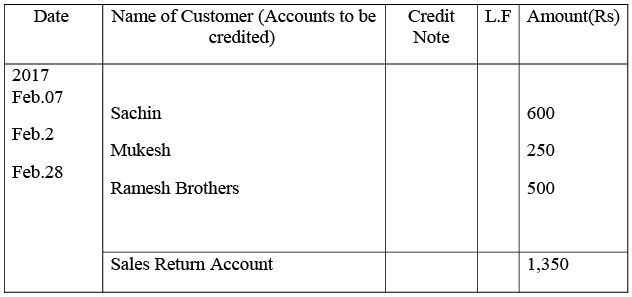
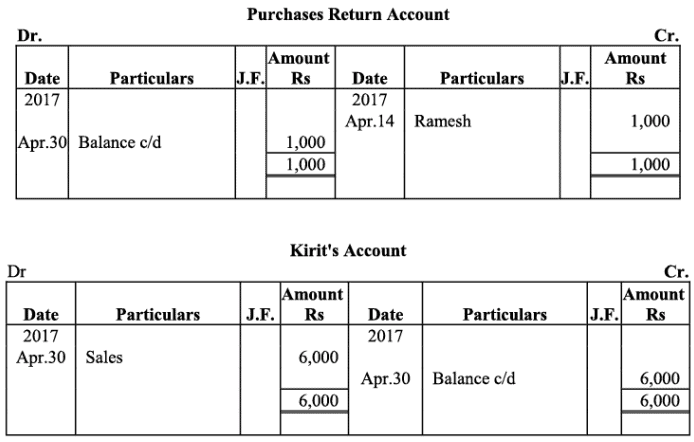
Purchases Return Book
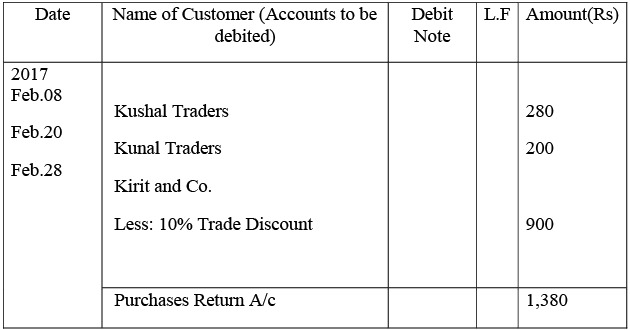
Journal Proper
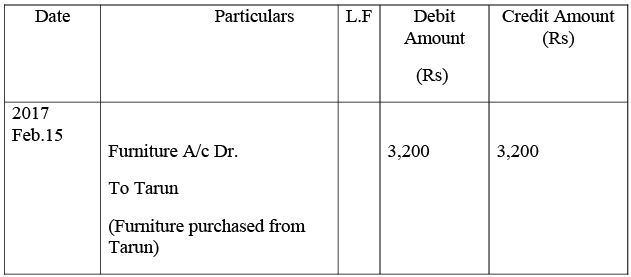
Ledger
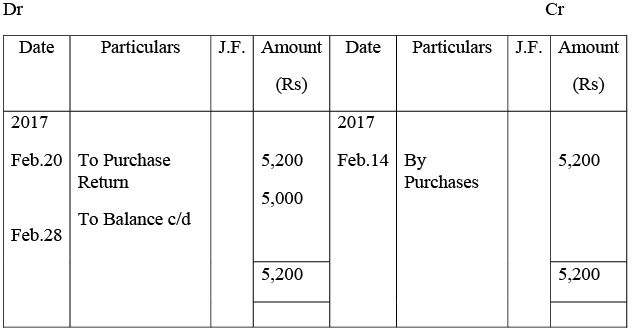
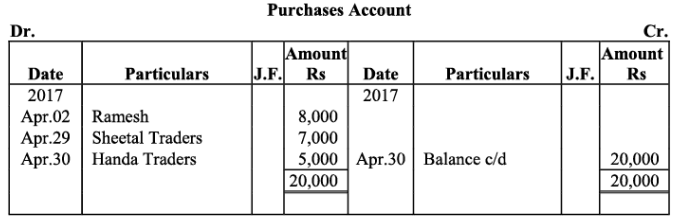
Purchases Account
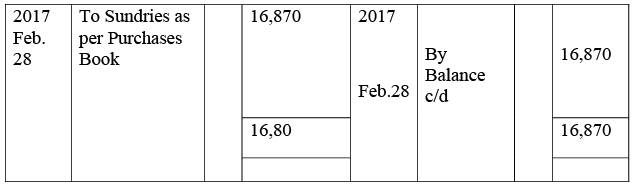
Sales Account
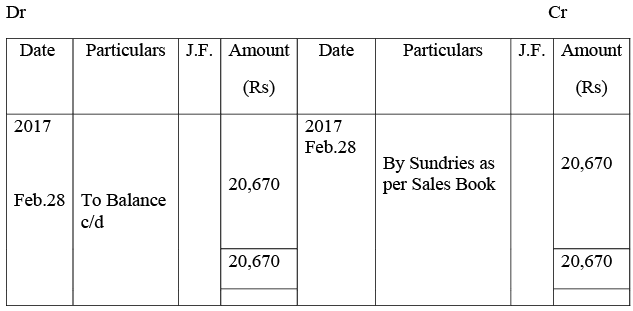
Sales Return Account
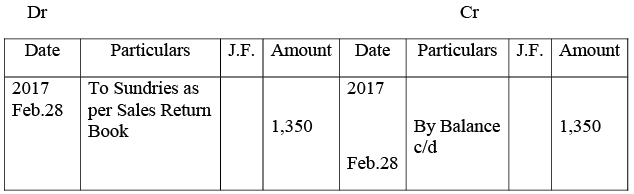

Purchases Return Account
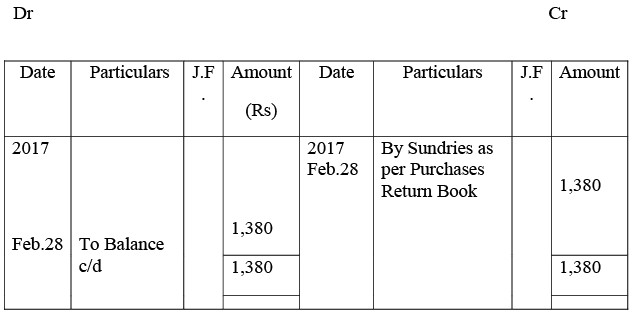
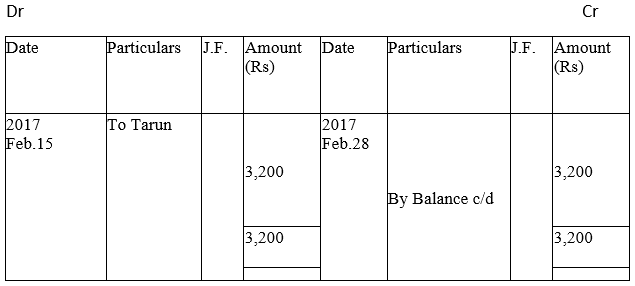
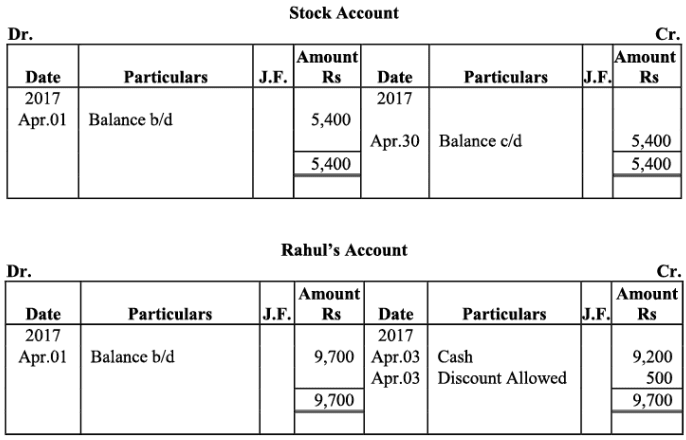
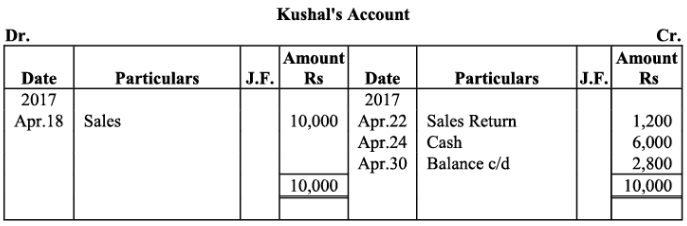
Sachin’s Account
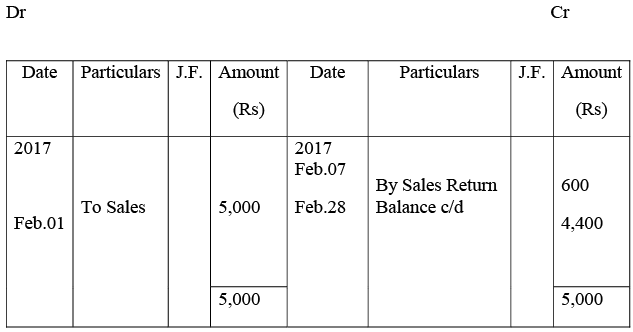
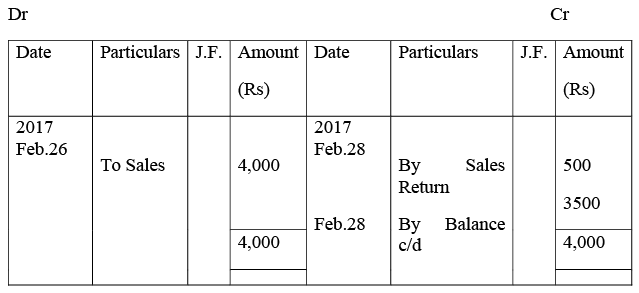
Kushal Traders’ Account
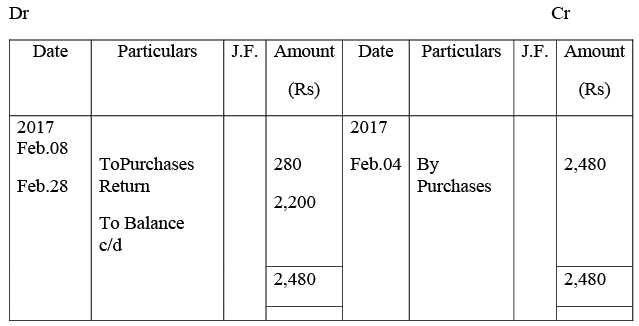
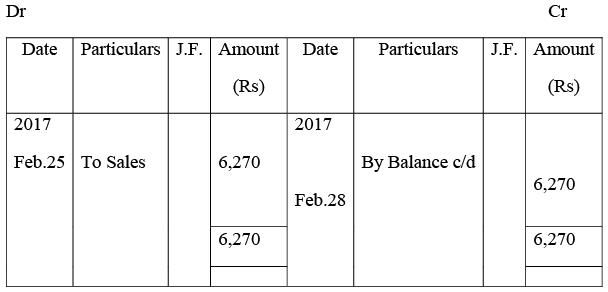
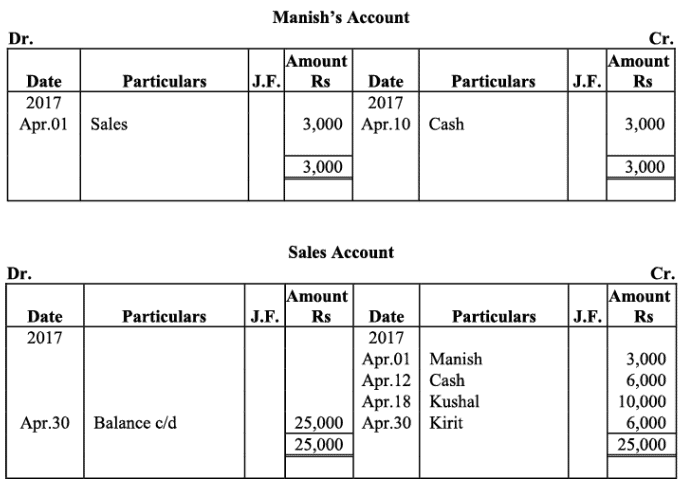
Manish Traders’ Account
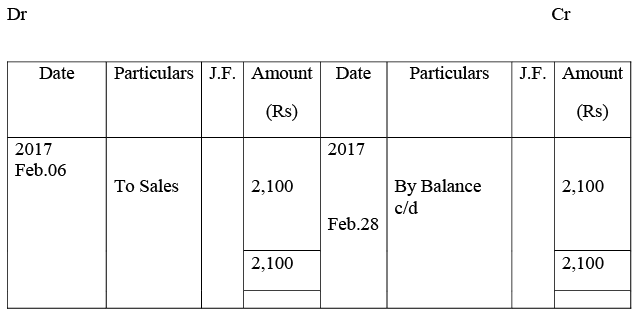
Mukesh’s Account
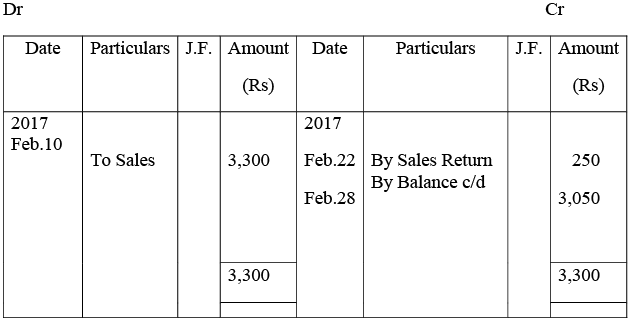
Kunal Traders’ Account
 Furniture Account
Furniture Account
 Tarun’s Account
Tarun’s Account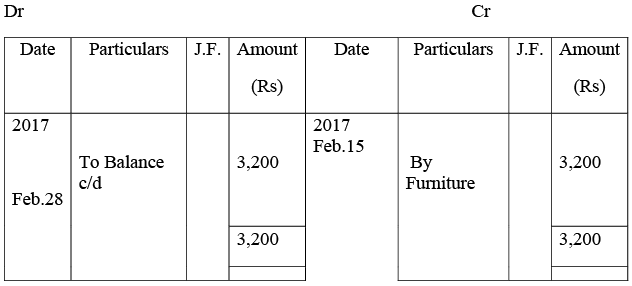
Naresh’s Account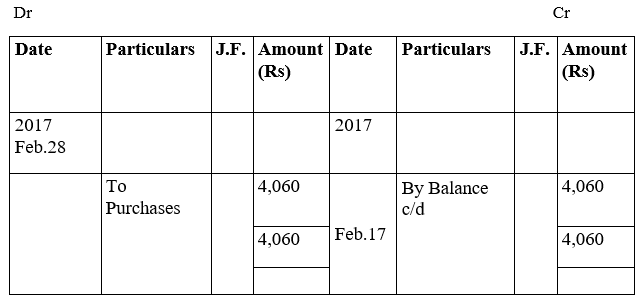
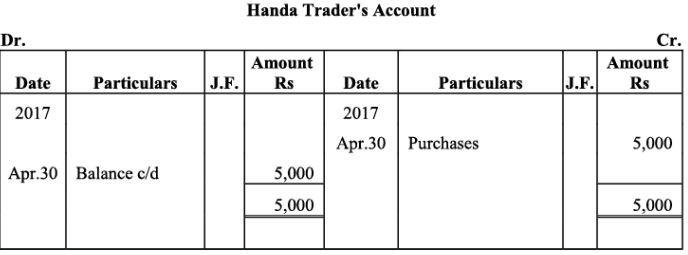
Kirit & Co. Account
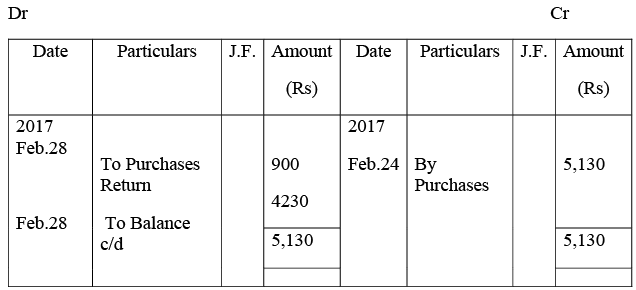
Shri Chand & Co. Account
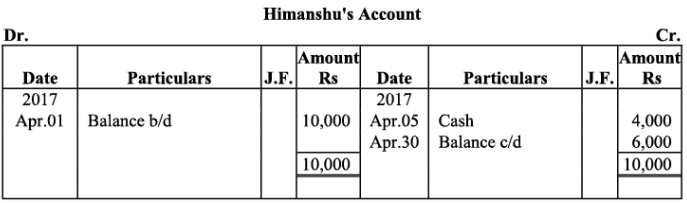
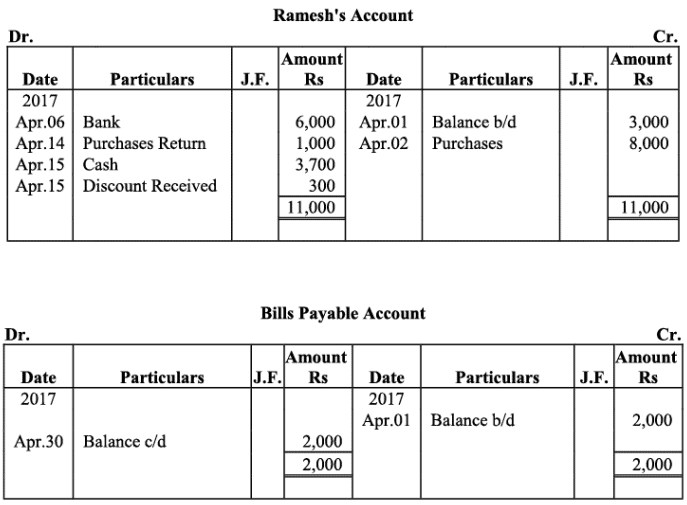
Ramesh’s Account
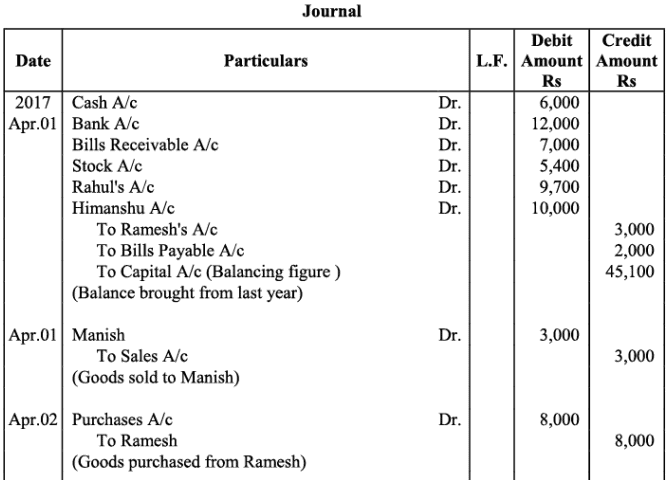
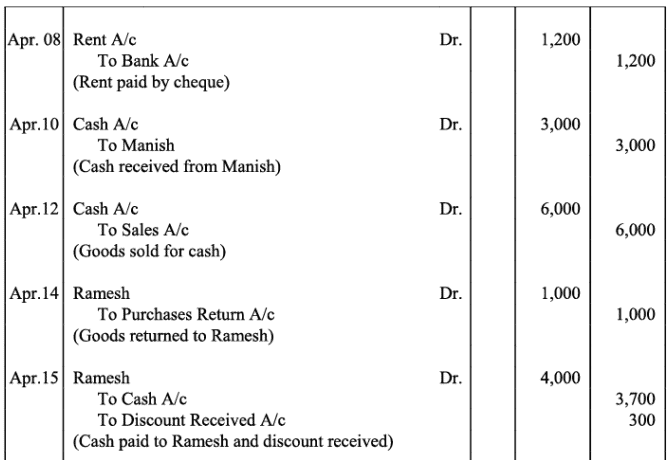
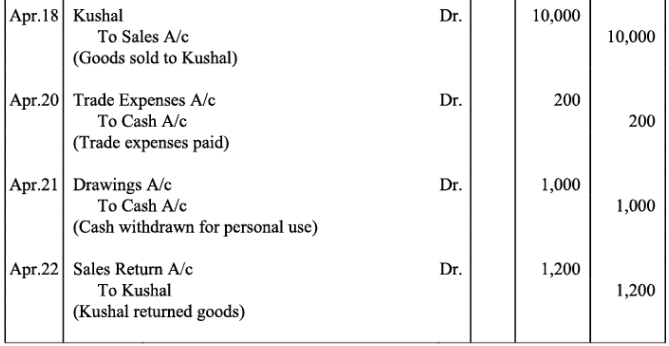
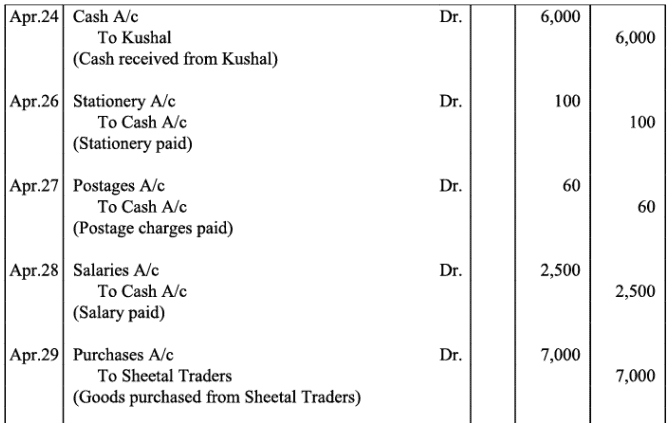
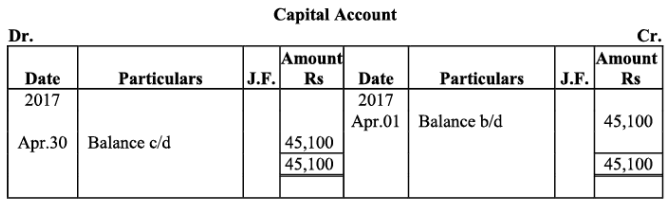
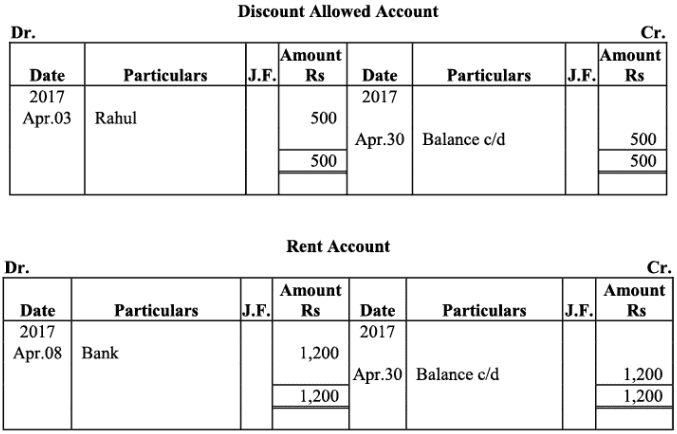
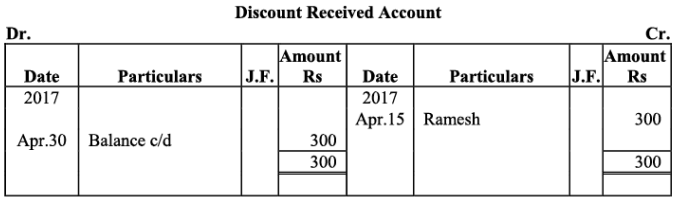
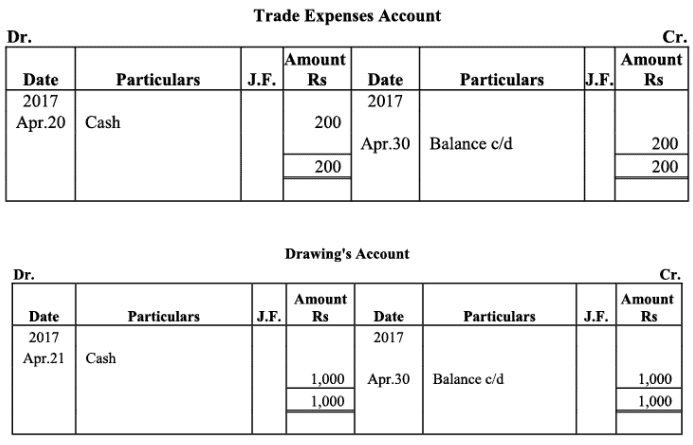
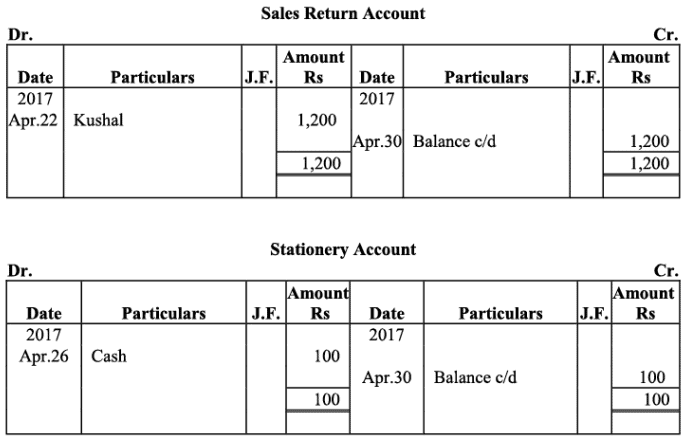
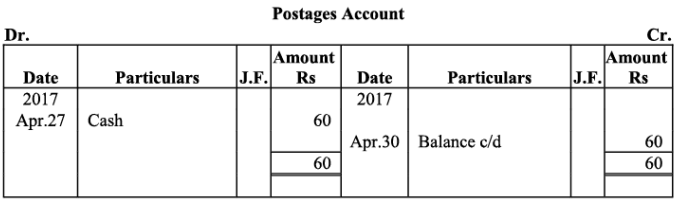
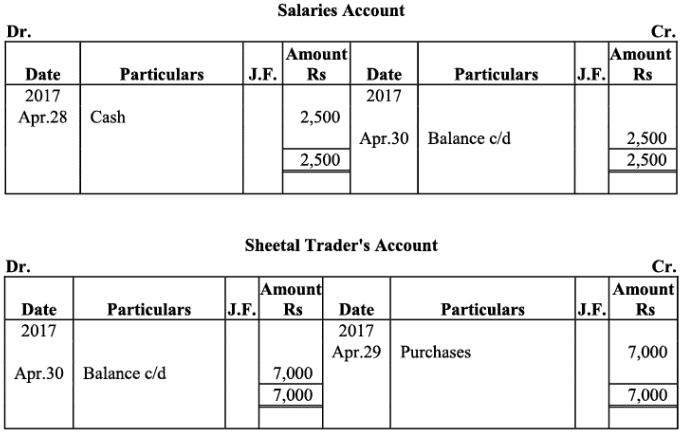
Q18: The following balances of ledger of M/s Marble Traders on April 01, 2017
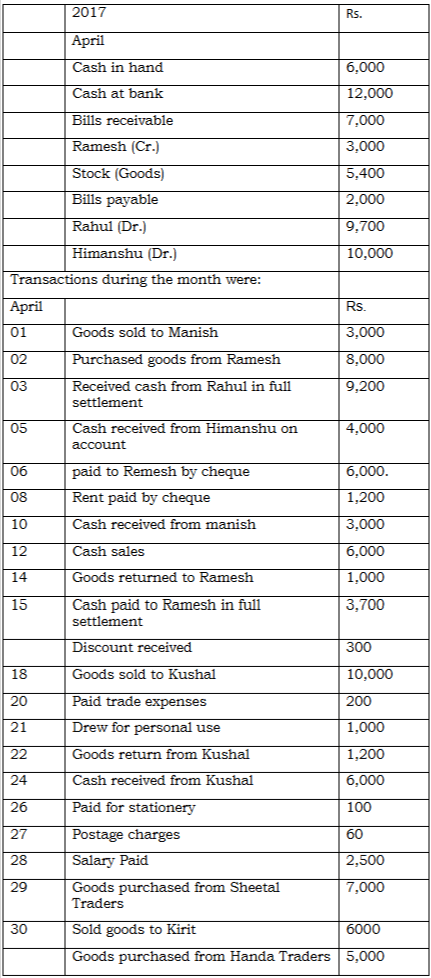
Journlise the above transactions and post them to the ledger.
Ans:

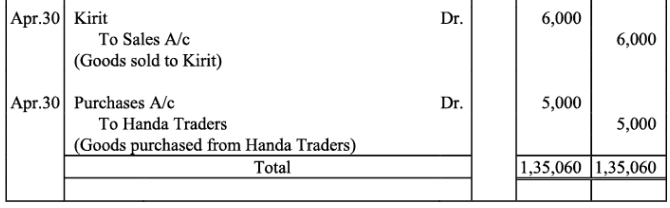
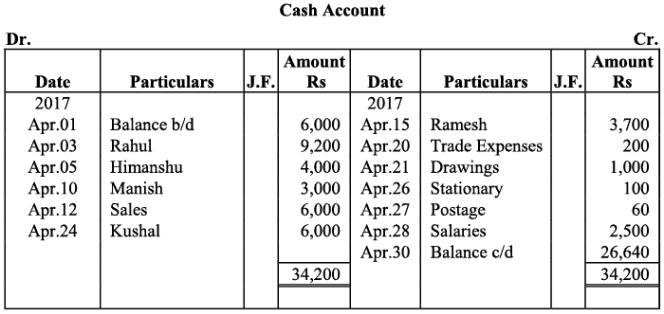
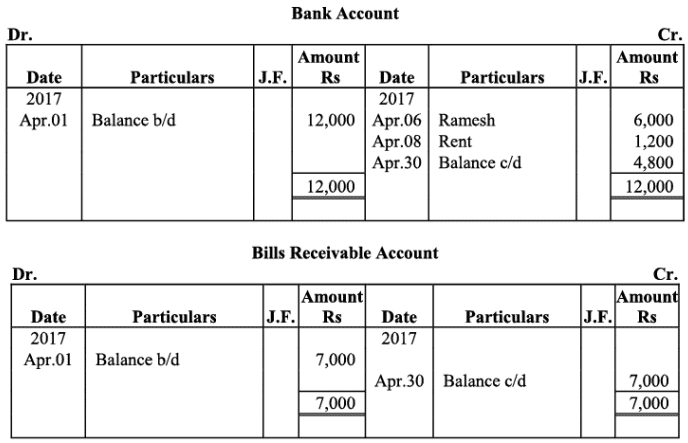
Ledger
|
64 videos|152 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solution - Recording of Transactions-II - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the main types of transactions recorded in accounting? |  |
| 2. How do journal entries play a role in recording transactions? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of double-entry bookkeeping in recording transactions? |  |
| 4. What are the basic components of a ledger in accounting? |  |
| 5. How do financial statements relate to recorded transactions? |  |























