NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Nutrition in Plants
Q1. Why do organisms take food?
Ans: Food is required by all living organisms mainly for four reasons or purposes:
- Food helps a living organism to grow. If enough food is not given or if, the food given is not of the right kind, the organism will not have proper growth.
- Another important function of food is to provide energy which is required for any living organism for movements and other activities.

Food
- Food is also needed by living organisms for the replacement and repairing of their damaged parts.
- Food provides us with the power to fight against infections and diseases.
Q2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
Ans: Q3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Q3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Ans: The presence of starch on leaves can be tested by the Iodine Test. Iodine turns starch solution blue.
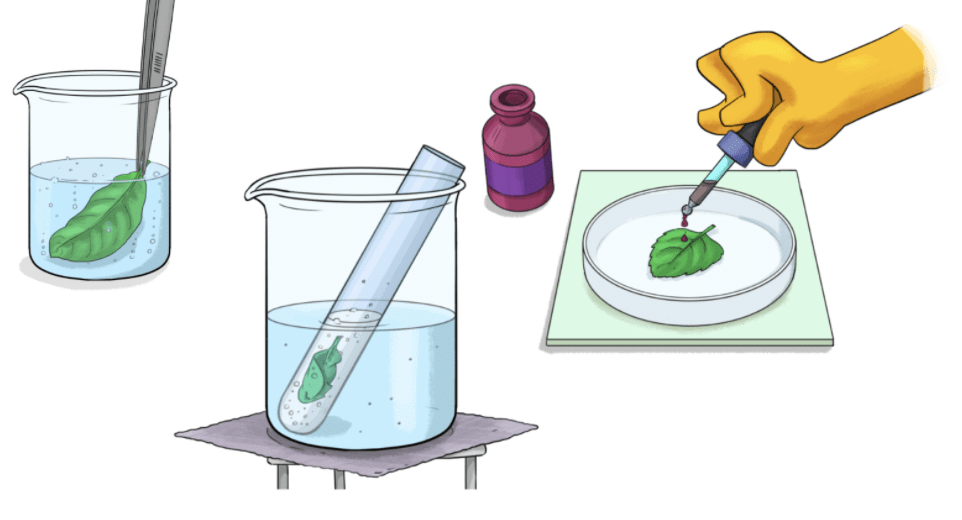
Iodine test:
- Set up one plant on a sunny windowsill and another in a dark room for 24 hours
- After 24 hours, fill a beaker with ethyl alcohol and place it in a saucepan full of water
- Continue heating the pan until ethyl alcohol starts boiling and then take it off from the heat
- With the help of tweezers, dip each of the leaves in hot water for a minute
- Now, dip the leaves in the beaker holding ethyl alcohol for 120 seconds or till they change their colour to almost white
- Place each of them in a shallow dish
- Cover these leaves with some drops of iodine solution and observe
Observation:
- Blue-black colour will be observed on the leaves of the plant kept in sunlight, which indicates the presence of starch.
- Blue-black colour will not be observed on the leaves of plant kept in the darkroom. This means starch is absent.
Q4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
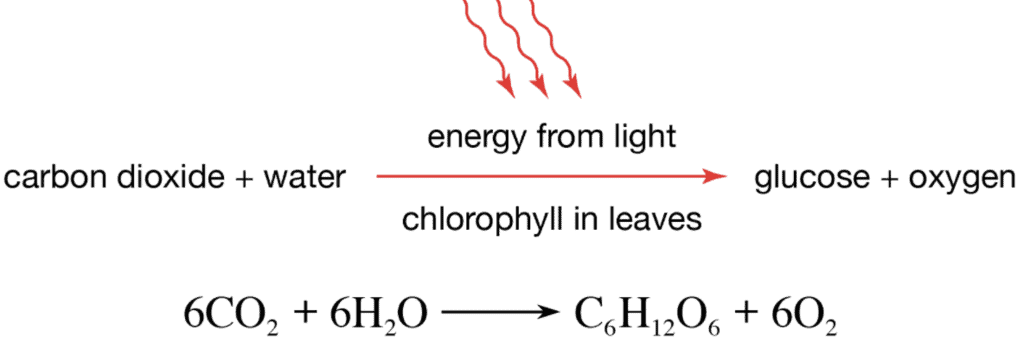
Ans: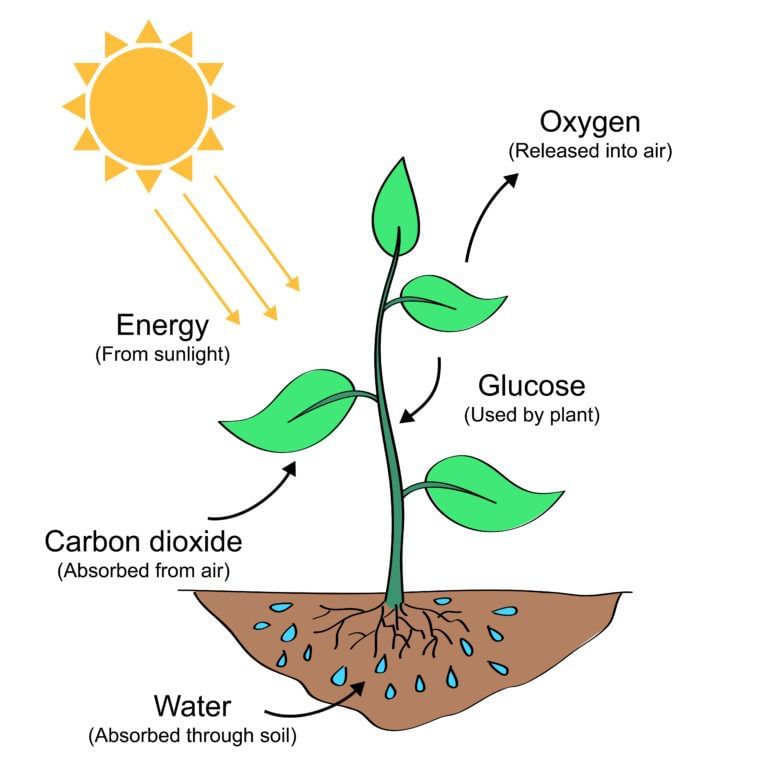 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
- Leaves have a green pigment called chlorophyll. In presence of sunlight, they use carbon dioxide and water to synthesize glucose.
- During this process, oxygen is released. The carbohydrates ultimately get converted into starch.
- Carbon dioxide from the air is taken through stomata.
- Water and minerals are absorbed by roots and transported to leaves.
Q5. Show with the help of a sketch that the plants are the ultimate source of food.
Ans: The food chain below shows that the plant is the ultimate producer.
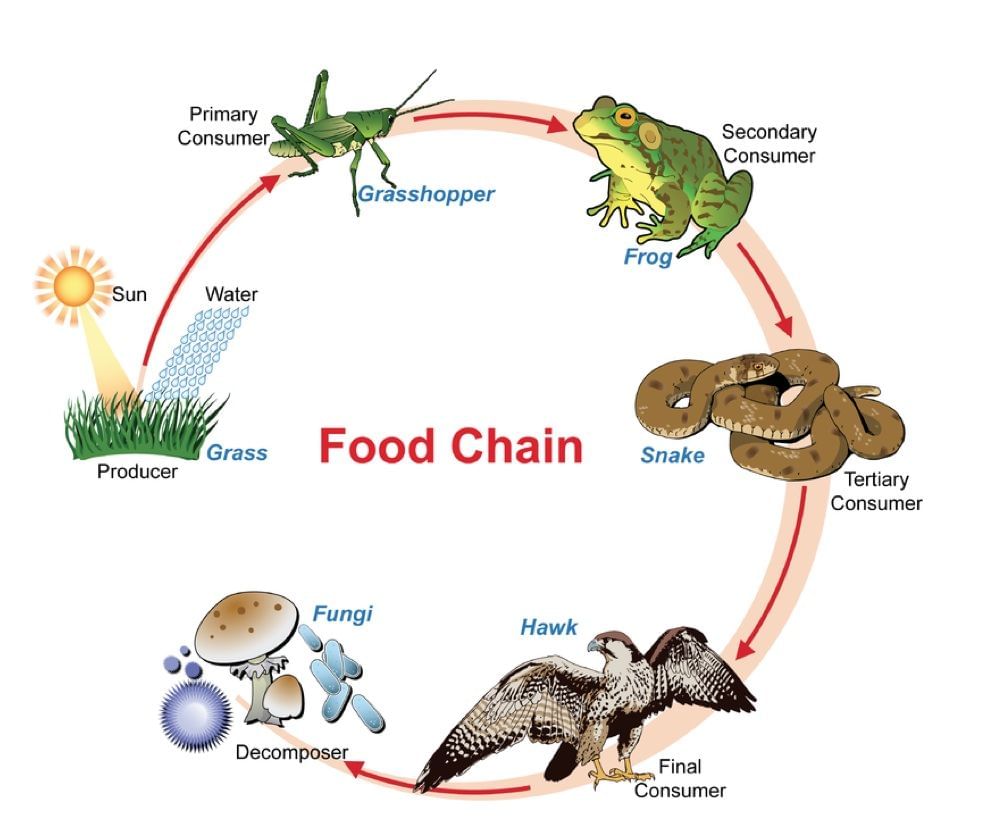 Food ChainQ.6. Fill in the blanks:
Food ChainQ.6. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Green plants are called __________ since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The foods synthesized by plants is stored as __________.
(c) In photosynthesis solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called _________.
(d) During photosynthesis plants take in _________ and release _________ gas.
Ans:
(a) Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesise their own food.
 View Answer
View Answer- Green plants are known as autotrophs because they have the ability to synthesize their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
- They use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen, making them self-sustaining organisms.
(b) The foods synthesized by plants is stored as starch.
 View Answer
View Answer- The glucose produced during photosynthesis is either used by the plant immediately for energy or stored in the form of starch.
- Starch serves as a reserve food material for the plant to use during periods when photosynthesis is not possible, such as at night.
(c) In photosynthesis solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called chlorophyll.
 View Answer
View Answer- Chlorophyll is the green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
- It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis by absorbing light energy from the sun, which is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
(d) Carbon dioxide, Oxygen
 View Answer
View AnswerDuring the process of photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata, and in turn, release oxygen as a by-product of converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Q.7. Name the following:
(i) A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and branched stem.
Ans: Cuscuta
 View Answer
View Answer- Cuscuta, also known as Amarbel, is a parasitic plant with a yellow, slender, and highly branched stem.
- It takes readymade food from the plant on which it is climbing. The plant on which it climbs is called the host.
 Cuscuta
Cuscuta
(ii) A plant that is partially autotrophic.
Ans: Insectivorous plants (Pitcher Plant)
 View Answer
View Answer- Insectivorous plants, like the Pitcher Plant, are partially autotrophic.
- They perform photosynthesis but also trap and digest insects to obtain nutrients, particularly nitrogen, from the animals to supplement their nutrition.
(iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Ans: Stomata
 View Answer
View Answer- Stomata are tiny openings or pores found mainly on the surface of leaves.
- They are responsible for the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the plant and the atmosphere and also play a key role in transpiration.
Q8. Tick the correct answer:
(a) Cuscuta is an example of:
(i) autotroph
(ii) parasite
(iii) saprotroph
(iv) host
Ans: (ii) Parasite
 View Answer
View AnswerCuscuta (also known as Amarbel) is a parasitic plant that does not perform photosynthesis and relies on a host plant to obtain its nutrients. It wraps itself around the host plant and absorbs water and nutrients directly from it, making it a parasite.
(b) The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) china rose
(iii) pitcher plant
(iv) rose
Ans: (iii) pitcher plant
 View Answer
View Answer- The pitcher plant is an insectivorous plant that traps and digests insects.
- It has a modified leaf shaped like a pitcher, which contains digestive enzymes to break down insects and obtain nutrients, especially nitrogen, from them.
- Plants like this use insects to supplement their nutrient intake, as they often grow in poor soil conditions.
 Pitcher PlantQ9. Match the items in column I with those in column II:
Pitcher PlantQ9. Match the items in column I with those in column II:
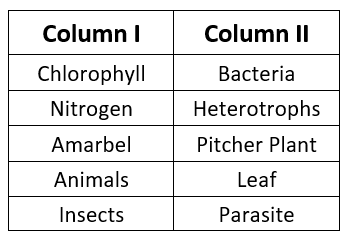 Ans:
Ans: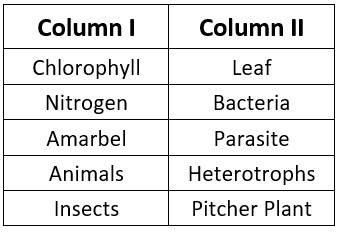
Chlorophyll - Leaf
Leaves contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll helps plants absorb light energy, enabling them to produce food.Nitrogen - Rhizobium
Plants cannot directly absorb nitrogen from the air. Instead, they rely on nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium that live symbiotically in the roots of leguminous plants. These bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plants.Cuscuta - Parasite
Cuscuta (also known as Amarbel) is an example of a parasitic plant. It attaches to host plants, deriving nutrients and support without making its own food, living off the host plant's resources.Animals - Heterotrophs
Animals cannot synthesize their own food, so they depend on other plants or animals for their nutrition. This mode of nutrition is called heterotrophic nutrition.Insects - Pitcher Plant
The Pitcher Plant is an insectivorous plant that traps and feeds on insects. It uses special adaptations to capture insects, which provide essential nutrients, especially nitrogen.
Q10. Mark “T” if the statement is true and “F” if it is false.
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer- During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants, not released.
- Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and convert it, along with water, into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen.
- The oxygen is then released as a byproduct.
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food are called saprotrophs.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer- Plants that synthesize their own food are called autotrophs, not saprotrophs.
- Autotrophs, such as green plants, make their food through photosynthesis.
- Saprotrophs, on the other hand, are organisms that feed on dead and decaying organic matter, like fungi and some bacteria.

(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer- The primary product of photosynthesis is glucose, which is a carbohydrate, not a protein.
- Glucose is used as an energy source or stored by plants, while proteins are made from amino acids through a different process that involves nitrogen.
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer- During photosynthesis, plants use the pigment chlorophyll to capture solar energy, which is then converted into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules.
- This stored energy can be used by the plant and other organisms that consume the plant.
Q11. Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(a) Root hair
(b) Stomata
(c) Leaf veins
(d) Petals
Correct Answer: Option (b)
 View Answer
View Answer- Stomata are holes made from spaces between special cells.
- These holes are where plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air. Once inside the leaf, the carbon dioxide can enter plant cells.
- Inside the plant, cells are special cell parts called chloroplasts, where photosynthesis takes place.
 Stomata
Stomata
Q12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(a) Roots
(b) Stem
(c) Flowers
(d) Leaves
Correct Answer: Option (d)
 View Answer
View Answer- Atmospheric carbon dioxide enters plants mainly through the pores in the leaves called stomata during photosynthesis.
- Stomata are the small opening on the surface of the leaves.
Q13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Ans. Fruits and vegetable crops are grown in large greenhouses because it protects crops from external climatic conditions and provides suitable temperature for the growth of crops.
Advantages to the farmers by growing fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses are:
- It provides optimum sunlight, temperature and water to the crop.
- It protects crops from adverse climatic conditions.
- It also protects crops from pests, rodents and different animals. Thus, preventing crops from several diseases.
|
111 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Nutrition in Plants
| 1. पौधों में पोषण की प्रक्रिया क्या होती है? |  |
| 2. पौधों के लिए मुख्य पोषण स्रोत क्या हैं? |  |
| 3. पौधों में किस प्रकार के पोषण होते हैं? |  |
| 4. प्रकाश संश्लेषण की प्रक्रिया में कितने चरण होते हैं? |  |
| 5. क्या सभी पौधे प्रकाश संश्लेषण कर सकते हैं? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|




















