NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur
Q1. Every village in India is surveyed once every ten years during the Census, and some of the details are presented in the following format. Fill up the following based on information on Palampur
(a) Location
(b) Total Area of The Village
(c) Land USE (in hectares) (d) Facilities
(d) Facilities Ans:
Ans:
(a) Location: Bulandshahar district, Western Uttar Pradesh
(b) Total Area of The Village: 226 hectares
(c) Land USE (in hectares):
(d) Facilities: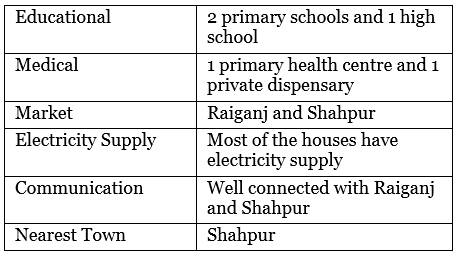
Q2. Modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industry. Do you agree?
Ans: Yes, it is correct to say that modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industries.
- Traditional farming uses seeds that don’t produce as much as modern ones but need less water. Farmers use cow dung and other natural fertilizers, which are easy for them to get. This means they don’t rely much on industrial products.
 Modern Farming Method
Modern Farming Method - Modern farming uses seeds that produce a lot of crops. These seeds need chemical fertilizers, pesticides, tractors, and electric tube wells to work well. All these things are made in factories.
Hence, it would be right to say that modern farming methods make use of a greater number of industrial outputs as compared to traditional farming methods.
Q3. How did the spread of electricity help farmers in Palampur?
Ans: The spread of electricity helped the farmers in Palampur in the following ways:
- Most of the houses have electricity connections.
- It is used to run tube wells in the field.
- It is used in various types of small businesses.
Q4. Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
Ans: It is important to increase the land under irrigation because:
- Farming is the primary income source for most people in India, but less than 40% of the land can be used for growing crops.
- Farmers rely on unpredictable monsoon rains, and when rainfall is low, they face significant losses.
- Improving irrigation for more land would improve production of crops, make more land suitable for farming, and encourage farmers to try new methods without the fear of losing money.
 Modern Irrigation Method
Modern Irrigation Method
Q5. Construct a table on the distribution of land among the 450 families of Palampur.
Ans: The distribution of land among 450 families of Palampur is as follows: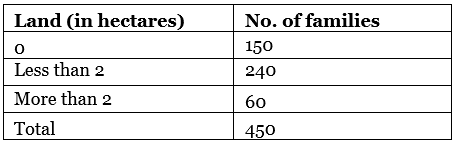
Q6. Why are farm labourers in Palampur's wages less than the minimum wage?
Ans: The wages for farm labourers in Palampur are less than the minimum wages because:
- There is heavy competition for work among the farmers.
- Employment is less, and farmers are more; therefore, farmers have to be content with what they are earning.
- The land is owned by landlords who desire to earn more and more profit by giving minimum wages.
- The farmers are illiterate and unaware of the amount of minimum wages set by the government.
Q7. In your region, talk to two labourers. Choose either farm labourers or labourers working at construction sites. What wages do they get? Are they paid in cash or kind? Do they get work regularly? Are they in debt?
Ans:
- There is a gym and a swimming pool under construction in our colony. On speaking with Masud and Rehman, two construction labourers, I understood that they get about 80-90 rupees per day for their labour.
- The two labourers belong to the Basti district of Uttar Pradesh and they had migrated to Delhi to work as labourers on daily wages. Their work is not permanent.
- They do not get regular work. They are always paid in cash by the contractor who hires them for work.
- Masud is in debt for taking a loan for his son's school and tuition fees.
Q8. What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Use examples to explain.
Ans: The land area under cultivation is practically fixed so in order to increase the production from the same piece of land, we can use the following methods:
(a) Multiple Cropping
- It is a common method to boost production on a piece of land by growing two or more crops in a year.
- For example, Indian farmers typically grow at least two main crops each year. In some places in India, like Palampur, farmers have even managed to grow a third crop over the past 20 years. There, they grow jowar and bajra as the main crops and add potatoes as the third crop.
(b) Modern Farming Methods
- Production on the same land can also be boosted by using modern farming techniques.
- The Green Revolution in India is a great example of this.
- Modern farming involves expanding the use of high-yielding seeds and better irrigation.
- Farmers should replace simple wooden ploughs with tractors, and using farm machinery like tractors, thrashers, and harvesters speeds up work and increases the amount of crops grown per hectare.
Q9. Describe the work of a farmer with 1 hectare of land.
Ans: A farmer who works on 1 hectare of land is called a small farmer.
He carries out the following activities:
- Ploughs the field by bullocks or tractors.
- Sow the seeds by simply sprinkling them with your hands.
- Waters the field with the help of the Persian wheel.
- Spray the insecticides with manual pumps.
- Cuts the crops with hand-operated tools.
Q10. How do the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming? How is it different from the small farmers?
Ans:
- Medium and large farmers retain a part of their produce and sell the surplus in the market.
- This provides them with the required capital for farming. Most of them even use these earnings to provide loans to small farmers.
- By charging high rates of interest on these loans, they succeed in furthering their earnings.
- Thus, medium and large farmers have ready capital with them from one agricultural season to the next.
- The situation of small farmers is in contrast. They begin an agricultural season with no working capital and end the season on more or less the same note.
- To begin working on their farms, they take loans at high rates of interest. Due to the small sizes of their farms, their total production is small.
- Their produce is kept for their needs or for repaying their lenders. As a result, they have no surplus to sell in the market and, thus, have limited savings.
Q11. On what terms did Savita get a loan from Tajpal Singh? Would Savita’s condition be different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest?
Ans: The terms of a loan of Savita taken from Tajpal Singh are:
- She took a loan of Rs. 3,000 at an interest rate of 24 per cent.
- She would have to repay the loan in four months.
- She also has to work in Tejpal’s field as a farm labourer during the harvesting season at Rs. 100 per day.
The bank could have provided her with a loan at a low rate of interest. In addition, she would have devoted more time to her own field of 1 hectare instead of working as a farm labourer for Tejpal Singh.
Q12. Talk to some old residents in your region and write a short report on the changes in irrigation and changes in production methods during the last 30 years.
Ans:
- On talking to two old residents, Ramlal and Dharam Singh, I learned about the irrigation methods that were traditionally used in our area.
- They told me that earlier, they were dependent on rainfall, and later on, they started to use the Persian wheel to draw water from the wells.
- With the development of technology, tube wells were used for better and more effective irrigation.
- In the farming methods, traditionally, they ploughed the field with ploughs drawn by bullocks, which were a very difficult and time-consuming process.
- They used ordinary seeds and cow dung manure for fertilization.
- However, with changes in technology, the farmers started using HYV seeds, chemical fertilizers, insecticides, pesticides and modern machinery like tractors and threshers.
- Which has led to an increase in yield per hectare and improved the lives of the farmers.
Q13. What are the non-farm production activities taking place in your region? Make a short list.
Ans:
- Dairy is a common activity in many families in our region.
- Some people are involved in small-scale manufacturing in their homes or in the field like the production of jaggery by Mishrilal.
- A few people are involved as shopkeepers and traders who buy various goods from the wholesale market in the cities and sell them in the villages.
- Some people near the bus stand have opened shops selling eatables.
- Some people are in the transportation sector, ferrying people and carrying goods from one place to another in different types of vehicles.
Q14. What can be done so that more non-farm production activities can be started in villages?
Ans: Three things that need to be done to encourage non-farm production activities in villages:
- The government should set up schemes whereby landless labourers and small farmers are able to get cheap loans to start small individual/community businesses.
- In addition to financial assistance, the government should set up rural workshops to enable the villagers to build on their skill levels.
 Rural Workshop
Rural Workshop - The government should also work towards improving the infrastructure of villages so that the rural parts of the country are well connected to the urban areas.
|
53 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur
| 1. What are the main features of the village Palampur as described in the chapter? |  |
| 2. How is agriculture important to the economy of Palampur? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of farming practices followed in Palampur? |  |
| 4. How does the village of Palampur utilize its resources for development? |  |
| 5. What role do small-scale industries play in the village economy of Palampur? |  |





















