NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths - (Ex: 14.4 to 14.6): Practical Geometry
Exercise 14.4
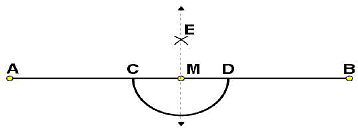
Question 1: Draw any line segment  . Mark any point M on it. Through M, draw a perpendicular to
. Mark any point M on it. Through M, draw a perpendicular to  . (Use ruler and compasses)
. (Use ruler and compasses)
Answer 1:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line segment and mark a point M on it.
and mark a point M on it.
(ii) Taking M as centre and a convenient radius, construct an arc intersecting the line segment  at points C and D respectively.
at points C and D respectively.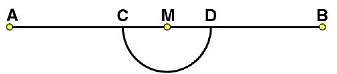 (iii) By taking centres as C and D and radius greater than CM, construct two arcs such that they intersect each other at point E.
(iii) By taking centres as C and D and radius greater than CM, construct two arcs such that they intersect each other at point E.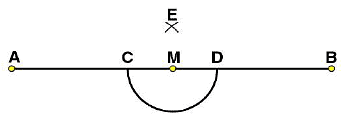
(iv) Join EM. Now 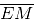 is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to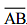
Question 2: Draw any line segment 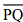 . Take any point R not on it. Through R, draw a perpendicular to
. Take any point R not on it. Through R, draw a perpendicular to 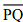 . (Use ruler and set-square)
. (Use ruler and set-square)
Answer 2:
(i) Draw a given line segment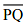 and mark a point R outside the line segment
and mark a point R outside the line segment 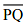

(ii) Place a set square on 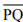 such that one of its right angles arm aligns along
such that one of its right angles arm aligns along 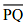
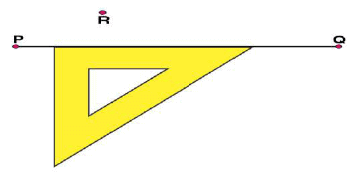 (iii) Now, place the ruler along the edge opposite to right angle of set square.
(iii) Now, place the ruler along the edge opposite to right angle of set square.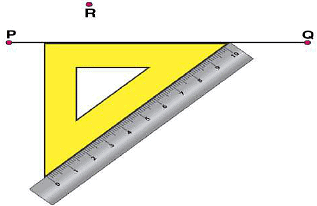 (iv) Hold the ruler fixed. Slide the set square along the ruler such that the point R touches the other arm of set square.
(iv) Hold the ruler fixed. Slide the set square along the ruler such that the point R touches the other arm of set square. (v) Draw a line along this edge of set square which passes through point R. Now, it is the required line perpendicular to
(v) Draw a line along this edge of set square which passes through point R. Now, it is the required line perpendicular to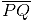
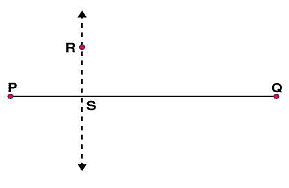
Question 3: Draw a line l and a point X on it. Through X, draw a line segment  perpendicular to l. Now draw a perpendicular to
perpendicular to l. Now draw a perpendicular to  to Y. (use ruler and compasses)
to Y. (use ruler and compasses)
Answer 3:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line l and mark a point X on it. (ii) By taking X as centre and with a convenient radius, draw an arc intersecting the line l at points A and B respectively.
(ii) By taking X as centre and with a convenient radius, draw an arc intersecting the line l at points A and B respectively.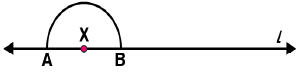 (iii) With A and B as centres and a radius more than AX, construct two arcs such that they intersect each other at point Y.
(iii) With A and B as centres and a radius more than AX, construct two arcs such that they intersect each other at point Y.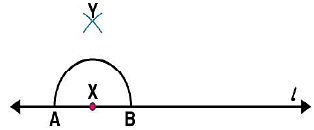 (iv) Join XY. Here
(iv) Join XY. Here 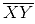 is perpendicular to l
is perpendicular to l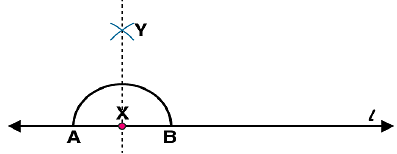 Similarly, by taking C and D as centres and radius more than CY, construct two arcs intersecting at point Z. Join ZY. The line
Similarly, by taking C and D as centres and radius more than CY, construct two arcs intersecting at point Z. Join ZY. The line 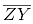 is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to 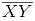 at Y
at Y
Exercise 14.5
Question 1: Draw  of length 7.3 cm and find its axis of symmetry.
of length 7.3 cm and find its axis of symmetry.
Answer 1: Axis of symmetry of line segment  will be the perpendicular bisector of
will be the perpendicular bisector of  . So, draw the perpendicular bisector of
. So, draw the perpendicular bisector of  .
.
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line segment  = 7.3 cm
= 7.3 cm
(ii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C and D.
(iii) Join CD. Then CD is the axis of symmetry of the line segment AB.
Question 2:
Draw a line segment of length 9.5 cm and construct its perpendicular bisector.
Answer 2:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line segment  = 9.5 cm
= 9.5 cm
(ii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C and D.
(iii) Join CD. Then CD is the perpendicular bisector of  .
.

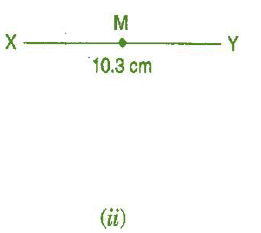
Question 3: Draw the perpendicular bisector of  whose length is 10.3 cm.
whose length is 10.3 cm.
(a) Take any point P on the bisector drawn.
Examine whether PX = PY.
(b) If M is the mid-point of  , what can you say about the lengths MX and XY?
, what can you say about the lengths MX and XY?
Answer 3:
Steps of construction:
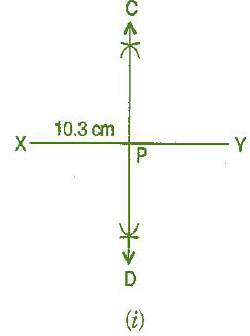
 (i) Draw a line segment
(i) Draw a line segment  = 10.3 cm
= 10.3 cm
(ii) Taking X and Y as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C and D.
(iii) Join CD. Then CD is the required perpendicular bisector of  .
.
Now:
(a) Take any point P on the bisector drawn. With the help of divider we can check that 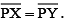
(b) If M is the mid-point of 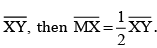
Question 4:
Draw a line segment of length 12.8 cm. Using compasses, divide it into four equal parts. Verify by actual measurement.
Answer 4:
Steps of construction: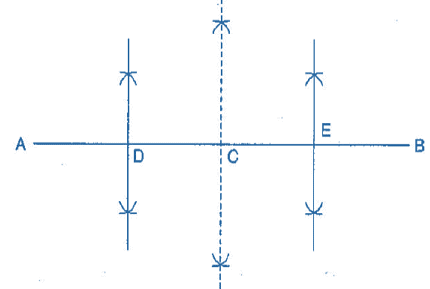 (i) Draw a line segment AB = 12.8 cm
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 12.8 cm
(ii) Draw the perpendicular bisector of  which cuts it at C. Thus, C is the midpoint of
which cuts it at C. Thus, C is the midpoint of  .
.
(iii) Draw the perpendicular bisector of 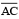 which cuts it at D. Thus D is the midpoint of.
which cuts it at D. Thus D is the midpoint of.
(iv) Again, draw the perpendicular bisector of 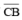 which cuts it at E. Thus, E is the mid-point of
which cuts it at E. Thus, E is the mid-point of 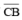 .
.
(v) Now, point C, D and E divide the line segment  in the four equal parts.
in the four equal parts.
(vi) By actual measurement, we find that 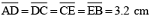
Question 5:
With  of length 6.1 cm as diameter, draw a circle.
of length 6.1 cm as diameter, draw a circle.
Answer 5:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line segment  = 6.1 cm.
= 6.1 cm.
(ii) Draw the perpendicular bisector of PQ which cuts, it at O. Thus O is the mid-point of  .
.
(iii) Taking O as centre and OP or OQ as radius draw a circle where diameter is the line segment  .
.
Question 6:
Draw a circle with centre C and radius 3.4 cm. Draw any chord  . Construct the perpendicular bisector
. Construct the perpendicular bisector  and examine if it passes through C.
and examine if it passes through C.
Answer 6:
Steps of construction:
(i) Mark any point C on the sheet
(ii) Adjust the compasses up to 3.4 cm and by putting the pointer of compasses at point C, turn compasses slowly to draw the circle. This is the required circle of 3.4 cm radius.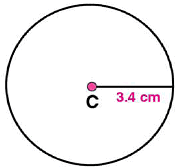
(iii) Mark any chord 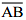 in the circle
in the circle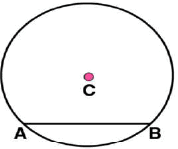 (iv) Now, taking A and B as centres, draw arcs on both sides of
(iv) Now, taking A and B as centres, draw arcs on both sides of 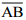 . Let these intersect each other at points D and E.
. Let these intersect each other at points D and E.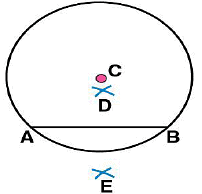 (v) Join DE. Now DE is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
(v) Join DE. Now DE is the perpendicular bisector of AB.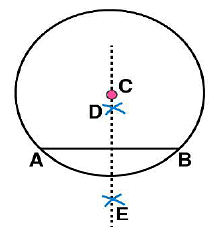
If 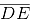 is extended, it will pass through point C.
is extended, it will pass through point C.
Question 7: Repeat Question 6, if  happens to be a diameter.
happens to be a diameter.
Answer 7:
Steps of construction:
(i) Mark any point C on the sheet.
(ii) Adjust the compasses up to 3.4 cm and by putting the pointer of compasses at point C, Turn the compasses slowly to draw the circle. This is the required circle of 3.4 cm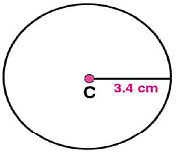 (iii) Now mark any diameter
(iii) Now mark any diameter  in the circle.
in the circle. (iv) Now taking A and B as centres, draw arcs on both sides of
(iv) Now taking A and B as centres, draw arcs on both sides of 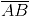 with radius more than
with radius more than 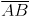 . Let these intersect each other at points D and E.
. Let these intersect each other at points D and E. (v) Join DE, which is perpendicular bisector of AB.
(v) Join DE, which is perpendicular bisector of AB.
Now, we may observe that  is passing through the centre C of the circle.
is passing through the centre C of the circle.
Question 8:
Draw a circle of radius 4 cm. Draw any two of its chords. Construct the perpendicular bisectors of these chords. Where do they meet?
Answer 8:
Steps of construction:
(i) Mark any point C on the sheet. Now adjust the compasses up to 4 cm and by placing the pointer of compasses at point C, turn the compasses slowly to draw the circle. This is the required circle of 4 cm radius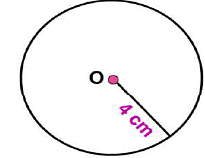 (ii) Take any two chords
(ii) Take any two chords 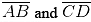 in the circle
in the circle (iii) By taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of
(iii) By taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of  draw arcs on both sides of AB. The arcs are intersecting each other at point E and F. Join EF which is perpendicular bisector of AB.
draw arcs on both sides of AB. The arcs are intersecting each other at point E and F. Join EF which is perpendicular bisector of AB.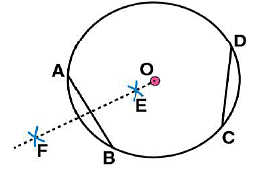 (iv) Again take C and D as centres and radius more than half of
(iv) Again take C and D as centres and radius more than half of 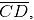 draw arcs on both sides of CD such that they are intersecting each other at points G, H. Join GH which is perpendicular bisector of CD
draw arcs on both sides of CD such that they are intersecting each other at points G, H. Join GH which is perpendicular bisector of CD
We may observe that when EF and GH are extended they meet at the point O, which is the centre of circle
Question 9:
Draw any angle with vertex O. Take a point A on one of its arms and B on another such that OA = OB. Draw the perpendicular bisectors of  and
and  . Let them meet at P. Is PA = PB?
. Let them meet at P. Is PA = PB?
Answer 9:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw any angle with vertex as O.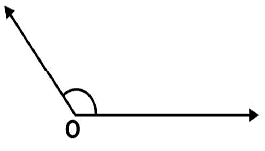 (ii) By taking O as centre and with convenient radius, draw arcs on both rays of this angle. Let these points are A and B
(ii) By taking O as centre and with convenient radius, draw arcs on both rays of this angle. Let these points are A and B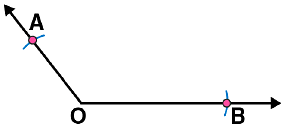 (iii) Now take O and A as centres and with radius more than half of OA, draw arcs on both sides of OA. Let these intersects at points C and D respectively. Join CD
(iii) Now take O and A as centres and with radius more than half of OA, draw arcs on both sides of OA. Let these intersects at points C and D respectively. Join CD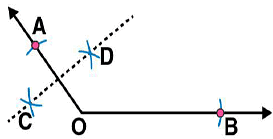 (iv) Similarly we may find
(iv) Similarly we may find  which is perpendicular bisector of
which is perpendicular bisector of  . These perpendicular bisectors
. These perpendicular bisectors  intersects each other at point P. Now measure PA and PB. They are equal in length.
intersects each other at point P. Now measure PA and PB. They are equal in length.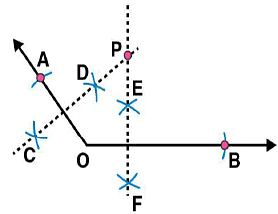
Exercise 14.6
Question 1:
Draw ∠ POQ of measure 75° and find its line of symmetry.
Answer 1:
Steps of construction: (i) Draw a line l and mark a point O on it.
(i) Draw a line l and mark a point O on it.
(ii) Place the pointer of the compasses at O and draw an arc of any radius which intersects the line l at A.
(iii) Taking same radius, with centre A, cut the previous arc at B.
(iv) Join OB, then ∠ BOA = 60 .
(v) Taking same radius, with centre B, cut the previous arc at C.
(vi) Draw bisector of ∠BOC. The angle is of 90 . Mark it at D. Thus, ∠DOA = 90o
(vii) Draw 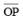 as bisector of ∠DOB. Thus, ∠POA = 75o.
as bisector of ∠DOB. Thus, ∠POA = 75o.
Question 2: Draw an angle of measure 147o and construct its bisector.
Answer 2:
Steps of construction:
Following steps are followed to construct an angle of measure 1470 and its bisector
(i) Draw a line l and mark point O on it. Place the centre of protractor at point O and the zero edge along line l
(ii) Mark a point A at an angle of measure 1470. Join OA. Now OA is the required ray making 1470 with line l
(iii) By taking point O as centre, draw an arc of convenient radius. Let this intersect both rays of angle 1470 at points A and B.
(iv) By taking A and B as centres draw arcs of radius more than 1 / 2 AB in the interior angle of 1470. Let these intersect each other at point C. Join OC.
OC is the required bisector of 1470 angle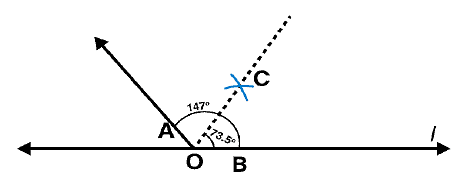
Question 3:
Draw a right angle and construct its bisector.
Answer 3:
Steps of construction: (i) Draw a line PQ and take a point O on it.
(i) Draw a line PQ and take a point O on it.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, draw an arc which intersects PQ at A and B.
(iii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C.
(iv) Join OC. Thus, ∠COQ is the required right angle.
(v) Taking B and E as centre and radius more than half of BE, draw two arcs which intersect each other at the point D.
(vi) Join OD. Thus,  is the required bisector of ∠COQ.
is the required bisector of ∠COQ.
Question 4:
Draw an angle of measure 153o and divide it into four equal parts.
Answer 4:
Steps of construction:
Following steps are followed to construct an angle of measure 1530 and its bisector
(i) Draw a line l and mark a point O on it. Place the centre of protractor at point O and the zero edge along line l
(ii) Mark a point A at the measure of angle 1530. Join OA. Now OA is the required ray making 1530 with line l
(iii) Draw an arc of convenient radius by taking point O as centre. Let this intersects both rays of angle 1530 at points A and B.
(iv) Take A and B as centres and draw arcs of radius more than 1 / 2 AB in the interior of angle of 1530. Let these intersect each other at C. Join OC
(v) Let OC intersect major arc at point D. Draw arcs of radius more than 1 / 2 AD with A and D as centres and also D and B as centres. Let these are intersecting each other at points E and F respectively. Now join OE and OF
OF, OC, OE are the rays dividing 1530 angle into four equal parts.
Question 5:
Construct with ruler and compasses, angles of following measures:
(a) 60°
(b) 30°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
(e) 45°
(f) 135°
Answer 5:
Steps of construction:
(a) 60°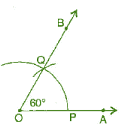 (i) Draw a ray
(i) Draw a ray  .
.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc, which intersects  at P.
at P.
(iii) Taking P as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Q.
(iv) Join OQ.
Thus, ∠BOA is required angle of 60° .
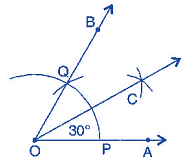
(b) 30o
 (i) Draw a ray
(i) Draw a ray  .
.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc, which intersects  at P.
at P.
(iii) Taking P as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Q.
(iv) Join OQ. Thus, ∠BOA is required angle of 60o.
(v) Put the pointer on P and mark an arc.
(vi) Put the pointer on Q and with same radius, cut the previous arc at C. Thus, ∠COA is required angle of 30o.
(c) 90°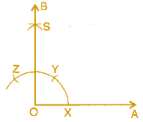 (i) Draw a ray
(i) Draw a ray  .
.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc, which intersects  at X.
at X.
(iii) Taking X as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Y.
(iv) Taking Y as centre and same radius, draw another arc intersecting the same arc at Z.
(v) Taking Y and Z as centres and same radius, draw two arcs intersecting each other at S.
(vi) Join OS and produce it to form a ray OB.
Thus, ∠BOA is required angle of 900.
(d) 120°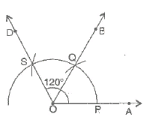 (i) Draw a ray
(i) Draw a ray 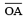 .
.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc, which intersects 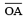 at P.
at P.
(iii) Taking P as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Q.
(iv) Taking Q as centre and same radius cut the arc at S.
(v) Join OS.
Thus, ∠AOD is required angle of 120°.
(e) 45o  (i) Draw a ray
(i) Draw a ray  .
.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc, which intersects  at X.
at X.
(iii) Taking X as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Y.
(iv) Taking Y as centre and same radius, draw another arc intersecting the same arc at Z.
(v) Taking Y and Z as centres and same radius, draw two arcs intersecting each other at S.
(vi) Join OS and produce it to form a ray OB. Thus, ∠BOA is required angle of 90°.
(vii) Draw the bisector of ∠BOA.
Thus, ∠MOA is required angle of 45°.
(f) 135°
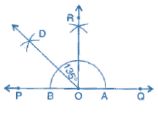
(i) Draw a line PQ and take a point O on it.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc, which intersects PQ at A and B.
(iii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs intersecting each other at R.
(iv) Join OR. Thus, ∠QOR = ∠POQ = 90°.
(v) Draw 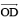 the bisector of ∠POR.
the bisector of ∠POR.
Thus, ∠QOD is required angle of 135°.
Question 6:
Draw an angle of measure 45o and bisect it.
Answer 6:
Steps of construction:
Following steps are followed to construct an angle of measure 450 and its bisector.
(i) Using the protractor ∠POQ of 450 measure may be formed on a line l
(ii) Draw an arc of convenient radius with centre as O. Let this intersects both rays of angle 450 at points A and B
(iii) Take A and B as centres, draw arcs of radius more than 1 / 2 AB in the interior of angle of 450. Let these intersect each other at C. Join OC
OC is the required bisector of 450 angle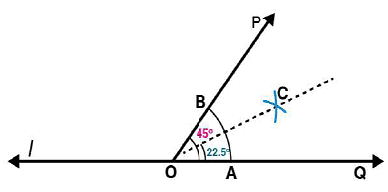
Question 7:
Draw an angle of measure 135o and bisect it.
Answer 7:
Steps of construction:
Following steps are followed to construct an angle of measure 1350 and its bisector.
(i) By using a protractor ∠POQ of 1350 measure may be formed on a line l
(ii) Draw an arc of convenient radius by taking O as centre. Let this intersect both rays of angle 1350 at points A and B respectively.
(iii) Take A and B as centres, draw arcs of radius more than 1 / 2 AB in the interior of angle of 1350.
Let these intersect each other at C. Join OC.
OC is the required bisector of 1350 angle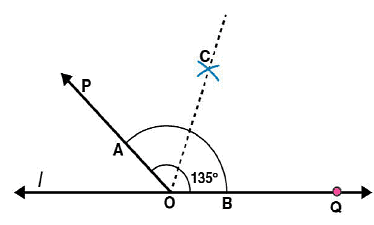
Question 8:
Draw an angle of 70o. Make a copy of it using only a straight edge and compasses.
Answer 8:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw an angle 70o with protractor, i.e., ∠POQ = 70o
(ii) Draw a ray 
(iii) Place the compasses at O and draw an arc to cut the rays of ∠POQ at L and M.
(iv) Use the same compasses, setting to draw an arc with A as centre, cutting AB at X.
(v) Set your compasses setting to the length LM with the same radius.
(vi) Place the compasses pointer at X and draw the arc to cut the arc drawn earlier at Y.
(vii) Join AY. Thus, ∠YAX = 70o
Question 9:
Draw an angle of 40o. Copy its supplementary angle.
Answer 9:
Steps of construction: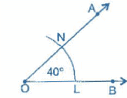
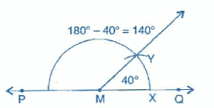 (i) Draw an angle of 40° with the help of protractor, naming ∠AOB.
(i) Draw an angle of 40° with the help of protractor, naming ∠AOB.
(ii) Draw a line PQ.
(iii) Take any point M on PQ.
(iv) Place the compasses at O and draw an arc to cut the rays of ∠AOB at L and N.
(v) Use the same compasses setting to draw an arc O as centre, cutting MQ at X.
(vi) Set your compasses to length LN with the same radius.
(vii) Place the compasses at X and draw the arc to cut the arc drawn earlier Y.
(viii) Join MY.
Thus, ∠QMY = 40° and ∠PMY is supplementary of it.
|
5 videos|378 docs|164 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths - (Ex: 14.4 to 14.6): Practical Geometry
| 1. What are the basic tools required for practical geometry? |  |
| 2. How can we construct an angle bisector using a compass and ruler? |  |
| 3. Can we construct a triangle if we know the lengths of its three sides? |  |
| 4. How can we construct a perpendicular bisector of a line segment? |  |
| 5. Can we construct a square if we know the length of its diagonal? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|


















