NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Economics - Theory of Consumer Behaviour
Q1: What do you mean by the budget set of a consumer?
Ans: The collection of all bundles of goods and services that the consumer can buy with their income at the prevailing market prices is called the budget set of a consumer.
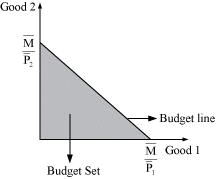
In the figure, the whole shaded area represents all the quantities of Good 1 and Good 2 that the consumer can attain within his budget.
Q2: What is a budget line?Ans:A budget line represents the different combinations of two goods that are affordable and are available to a consumer; while being aware of his/her income level and market prices of both goods.
Let x1 be the amount of good 1
x2 be the amount of good 2
P1 is the price of good 1
P2 is the price of good 2
P1x1 = Total money spent on good 1
P1x2 = Total money spent on good 2
Then, the budget line will be:
P1x1 + P2x2 = M
All the consumption bundles on the budget line cost the consumer exactly the equivalent of his/her income.
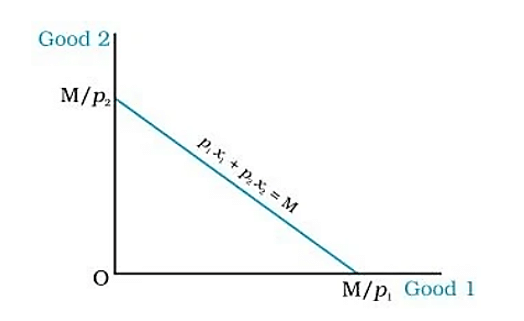
Ans:The budget line is downward-sloping because to increase the consumption of Good 1, the consumer must decrease the consumption of Good 2 to be on the same budget line (i.e., having a fixed amount of income). For example, if a person's budget is Rs 100, for every extra snack bought at ₹10, you must give up 2 drinks at ₹5 each to stay within the budget.
The slope of the budget line, which denotes the rate of exchange at which Good 1 can be substituted for Good 2, can be represented as:
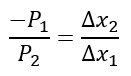
(i) Write down the equation of the budget line.
(ii) How much of good 1 can the consumer consume if he/she spends his/her entire income on that good?
(iii) How much of good 2 can be consumed if he/she spends his/her entire income on that good?
(iv) What is the slope of the budget line?
Ans: (i) P1 = Rs 4
P2 = Rs 5
M = Rs 20
Equation of the budget line = P1x1 + P2x2 = M
4x1 + 5x2=20
(ii) Total income = Rs 20
Price of Good 1 per unit = Rs 4
Amount of Good 1 consumer can purchase by spending entire income = 20/4 = 5 units.
This can also be found out with the help of the budget line. If the entire amount is spent on Good 1, the amount spent on Good 2 would be zero (x2-0).
4x1 + 5(0) = 20
4x1=20
x1=5 units
(iii) Total income = Rs 20
Price of Good 2 per unit = Rs 5
Amount of Good 1 consumer can purchase by spending entire income = 20/5 = 4 units.
(iv) Slope of the budget lines = -Price of good 1/Price of good 2
-P1/P2 = -4/5 = -0.8
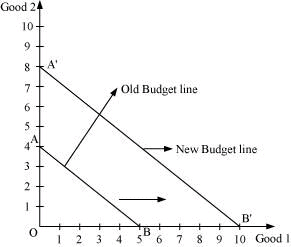
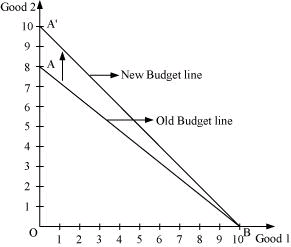
Q5: How does the budget line change if the consumer’s income increases to Rs 40 but the prices remain unchanged?
Ans:
M2 = Rs 40
P1 = Rs 4
P2 = Rs 5
Initial equation of the budget line:
4x1 + 5x2 = 20
A new equation of the budget line:
4x1 + 5x2 = 40
As M has increased, the consumer can now purchase more of both the goods and the budget line will shift parallelly outwards to A’B’ from AB.
- Calculating horizontal intercept: To be on the x-axis, the consumer must spend all of his income on Good 1 and purchase zero units of Good 2. We can get this by dividing the price of Good 1 by the total income.
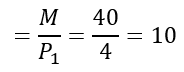
- Calculating the vertical intercept: It will be
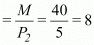
The slope of the new budget line will be the same as that of the old budget line because it is dependent on the prices of the goods.
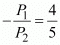
Q6: How does the budget line change if the price of good 2 decreases by a rupee but the price of good 1 and the consumer’s income remain unchanged?
Ans:P1 = Rs 4
P2 = Rs 5
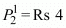
M = Rs 20
Since the income and the price of good 1 are unchanged, the decrease in the price of good 2 will increase the vertical intercept of the budget line. The new budget line will also pivot outwards around the same horizontal intercept.
Horizontal intercept
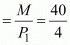 =10
=10Vertical intercept 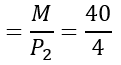 =10
=10
Slope 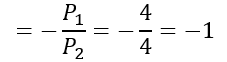
The slope of the new budget line will be higher, and it will be steeper than the previous one.
Q7: What happens to the budget set if the prices as well as the income double?
Ans: If the prices and the income are doubled, the budget line will remain unchanged.
For example:
M1 = Rs 20 | M2 = Rs 40 |
P1 = Rs 4 |
|
P2 = Rs 5 |
|
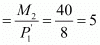
Vertical intercept 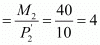
Slope 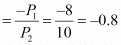
Hence, the vertical intercept, the horizontal intercept, and the slope of the budget line will remain the same. The new budget line will be the same as the old budget line but associated with higher income and higher prices for both goods.
Q8: Suppose a consumer can afford to buy 6 units of good 1 and 8 units of good 2 if he/she spends her entire income. The prices of the two goods are Rs 6 and Rs 8. How much is the consumer’s income?
Ans: We can find the consumer's income with the help of the budget line.
P1 = Rs 6
P2 = Rs 8
x1 = 6
x2 = 8
Budget line = M = P1x1 + P2x2
M = 6 × 6 + 8 × 8
M = 36 + 64
M = 100
Thus, the consumer’s income is Rs 100.
Q9: Suppose a consumer wants to consume two goods that are available only in integer units. The two goods are equally priced at Rs 10 and the consumer’s income is Rs 40.
(i) Write down all the bundles that are available to the consumer.
(ii) Among the bundles that are available to a consumer, identify those that cost will him/her exactly Rs 40.
Ans: (i) P1 = Rs 10
P2 = Rs 10
M = Rs 40
Budget set ⇒ P1x1 + P2x2 ≤ M
10x1 + 10x2 ≤ 40
The bundles that are available to the consumer should cost less than or equal to Rs 40.
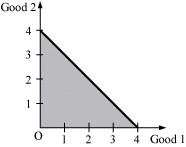
Horizontal intercept 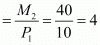
Vertical intercept 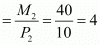
Slope 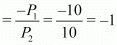
The bundles in the shaded region (ΔAOB) are all available to the consumer, including the bundles lying on line AB.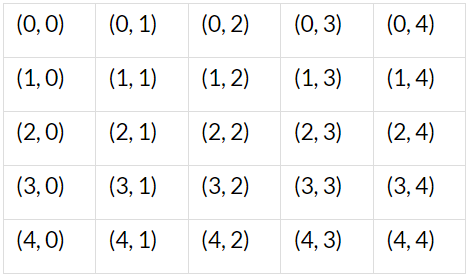
(0, 4), (1, 3), (2, 2), (3, 1), (4, 0)
These combinations of goods cost the consumer exactly Rs 40.
Q10: What do you mean by monotonic preferences?
Ans: It means that a rational consumer would always prefer to have more of a commodity because it gives him a higher level of satisfaction. If a consumer's preferences are monotonic between two bundles of goods, he would prefer a bundle that would have more of one or more goods than a bundle that has less.
For example, if bundle A (3, 5) and bundle B (3, 2) are available to the consumer, then he will prefer bundle A over bundle B because bundle A consists of more units of good 2 than bundle B.
Q11: If the consumer has monotonic preferences, then can he/she be indifferent towards bundles (10, 8) and (8, 6)?
Ans: No, he/she cannot be indifferent towards these two bundles as bundle I consist of more of both goods as compared to bundle II. He/she will prefer bundle I over bundle II as it contains 10 units of good 1 and 8 units of good 2 as compared to 8 units and 6 units of good 1 and good 2 respectively in bundle II.
Q12: Suppose a consumer’s preferences are monotonic. What can you say about his/her preference ranking over the bundles (10, 10), (10, 9), and (9, 9)?
Ans:
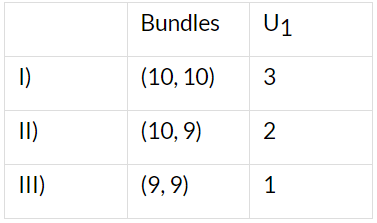 As the consumer’s preferences are monotonic, more is better and he will prefer bundle I over the rest of the bundles. This means that bundle I will be assigned a higher utility number i.e., three (rank = three) out of the available three bundles, followed by bundle II and finally bundle I.
As the consumer’s preferences are monotonic, more is better and he will prefer bundle I over the rest of the bundles. This means that bundle I will be assigned a higher utility number i.e., three (rank = three) out of the available three bundles, followed by bundle II and finally bundle I.
Q13: Suppose your friend is indifferent to the bundles (5, 6) and (6, 6). Are the preferences of your friend monotonic?
Ans: It is given that my friend is indifferent towards the bundles (5, 6) and (6, 6). This implies that his/her preferences are not monotonic. If he/she is indifferent towards both bundles, then it means that he/she derives the same level of satisfaction and assigns them the same rank. However, the second bundle consists of more of both goods. Thus, according to the monotonicity assumption, he/she must prefer the second bundle over the first.
Q14: Suppose there are two consumers in the market for a good and their demand functions are as follows:
d1(p) = 20 − p for any price less than or equal to 20 and d1(p) = 0 at any price greater than 20.
d2(p) = 30 − 2p for any price less than or equal to 15 and d1(p) = 0 at any price greater than 15.
Find out the market demand function.
Ans:
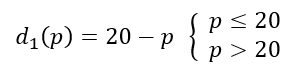
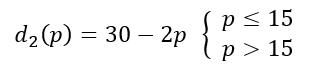
For a price less than Rs 15 (p ≤ 15)
Market demand for a good = d1 (p) + d2 (p)
= 20 − p + 30 − 2p
= 50 − 3p
For prices more than Rs 15 but less than Rs 20 (15 <p≤20)
Market demand = d1(p) + d2 (p)
= 20 − p + 0 ( for p > 15, d2 (p) = 0)
for p > 15, d2 (p) = 0)
= 20 − p
For prices more than Rs 20 (p> 20)
Market demand = d1(p) + d2 (p)
= 0 + 0 (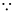 for p > 10, d1 (p) = 0, d2 (p) = 0)
for p > 10, d1 (p) = 0, d2 (p) = 0)
= 0
Thus, market demand
= 50 − 3p if p ≤ 15
=20 − p if 15 < p ≤ 20
= 0 if p > 20
Q15: Suppose there are 20 consumers for a good and they have identical demand functions:
D(p) = 10 − 3p for any price less than or equal to 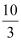 and d1(p) = 0 at any price greater than
and d1(p) = 0 at any price greater than 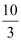 .
.
What is the market demand function?
Ans: d(p) = 10 − 3p if p ≤ 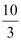
d1 (p) = 0 if p > 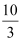
Market demand = Summation of demand of all the consumers in the market
- For price ≤
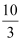
Market demand = 20 ∑d (p) ( Since consumers have identical demand curve)
Since consumers have identical demand curve)
= 20 × (10 − 3p)
= 200 − 60p
- For price >
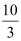
Market demand = 20 × d1(p)
= 20 × 0
= 0
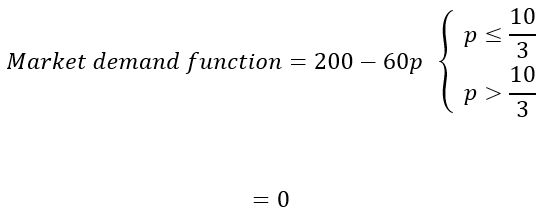
Q16: Consider a market where there are just two consumers and suppose their demands for the good are given as follows:
Calculate the market demand for the goods.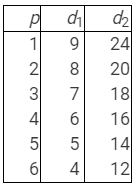 Ans:
Ans: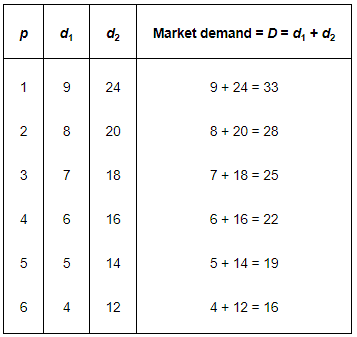
Q17: What do you mean by a normal good?
Ans: Those goods that share a positive relationship with income but a negative relationship with price are called normal goods. In other words, if the income of a consumer increases, then the demand for a normal good also increases. However, the demand will fall with the rise in the price of that good.
That is,
If the price of a good (Px) increases, then the demand for a good (Dx) decreases.
If a consumer’s income (M) increases, then the demand for good Dx increases.
Q18: What do you mean by an ‘inferior good’? Give some examples.
Ans: Inferior goods are those goods that share an inverse relationship with their prices and with the income of a consumer. That is, if the income of the consumer falls, then the demand for an inferior good will rise. Inversely, if the income of the consumer increases, he will consume less of the inferior good.
Examples: Coarse cereals, bidis, etc.
Q19: What do you mean by substitutes? Give examples of two goods that are complements of each other.
Ans: Those goods that can be consumed in place of other goods are called substitute goods. Example: Tea and coffee are goods that can be substituted for each other. If the price of tea increases, then the demand for tea will decrease and people will substitute coffee for tea, which will increase the demand for coffee.
The demand for goods moves in the same direction as the price of its substitutes.
Price of tea (PT) increases →Demand for tea (DT) decreases →Demand for coffee(DC) increases.
Q20: What do you mean by complements? Give examples of two goods that are complements of each other.
Ans: Those goods that are consumed together are called complementary goods. Example: Tea and sugar. If the price of sugar increases, then it will lead to a decrease in the demand for tea. If the price of tea increases, then it will reduce the demand for sugar. The demand for goods moves in the opposite direction of the price of its complementary goods. That is, If the price of tea (PT) increases, then the demand for sugar (DS) decreases. If the price of sugar (PS) increases, then the demand for tea (DT) decreases.
Q21: Explain the price elasticity of demand.
Ans: Price elasticity of demand is the measure of the degree of responsiveness of the demand for a good to the changes in its price. It is defined as the percentage change in the demand for a good divided by the percentage change in its price.
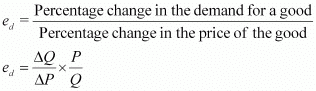 Where,
Where,
ΔQ = Q2 − Q1, change in demand
ΔP = P2 −P1, change in demand
P = Initial price
Q = Initial quantity
Q22: Consider the demand for a good. At a price of Rs 4, the demand for the good is 25 units. Suppose the price of the good increases to Rs 5, and as a result, the demand for the good falls to 20 units. Calculate the price elasticity.
Ans:
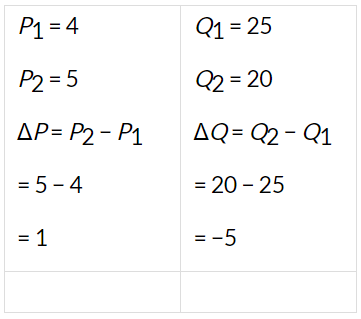
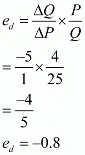
Q23: Consider the demand curve D(p) = 10 − 3p. What is the elasticity at price 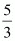 ?
?
Ans: D(p) = 10 − 3p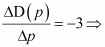 Change in demand per unit change in price
Change in demand per unit change in price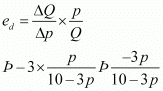
At price p =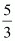 ,
,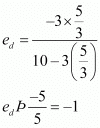
i.e., the elasticity of demand at price p =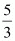 is unitary elastic.
is unitary elastic.
Q24: Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a good is −0.2. If there is a 5% increase in the price of the good, then by what percentage will the demand for the good go down?
Ans: ed = −0.2 [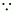 Note that ed = −2. Hence, we need not prefix ed to (−2)]
Note that ed = −2. Hence, we need not prefix ed to (−2)]
Percentage change in price = 5%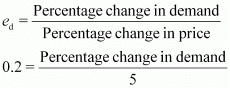
1.0 ⇒ Percentage change in demand
= 1%
Q25: Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a good is −0.2. How will the expenditure on the good be affected if there is a 10% increase in its price?
Ans: Price elasticity of demand = −0.2
Percentage increase in price = 10%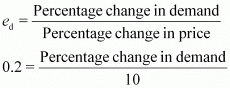
−2 = Percentage change in demand
Thus, the percentage decrease in demand is less than the percentage increase in price. This means that when the price increases and ed < 1, the demand is inelastic and hence, the expenditure will increase.
Q26: Suppose there was a 4% decrease in the price of a good, and as a result, the expenditure on the good increased by 2%. What can you say about the elasticity of demand?
Ans: Percentage decrease in price = 4%
Increase in expenditure = 2%
ΔE= ΔP {q + (1 + ed)}
Since the price has decreased, the expenditure on the good will increase. This implies that the percentage of change in demand has increased more than the percentage decrease in price.
Thus, elasticity = 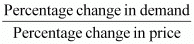
The numerator is more than the denominator. This means that elasticity is more than 1. We can say that the small change in price has led to a bigger change in demand, and as a result, the demand is elastic.
|
138 videos|431 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Economics - Theory of Consumer Behaviour
| 1. What is the theory of consumer behaviour? |  |
| 2. What are the main assumptions of consumer behaviour theory? |  |
| 3. How does the concept of utility relate to consumer behaviour? |  |
| 4. What role do budget constraints play in consumer behaviour? |  |
| 5. How do changes in income affect consumer behaviour? |  |

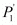 = Rs 8
= Rs 8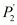 = Rs 10
= Rs 10















