NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 - Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Q1: Fill in the blanks
(a) Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of, _______,______and ______.
Ans: Acids, Bases and Salts
Explanation: Electricity can be conducted through a liquid when it contains charged particles, called ions, that are capable of moving and carrying the electric current. Acids, bases, and salts are types of compounds that ionize in water, creating ions that allow for the conduction of electricity.
- Acids are substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
- Bases, also known as alkaline substances, release hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
- Salts are compounds formed from the reaction between an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of a neutral salt and water.
(b) The passage of an electric current through a solution causes ______________ effects.
Ans: Chemical
Explanation: When an electric current is passed through a solution, it leads to the movement of ions towards their respective electrodes, resulting in the process called electrolysis. 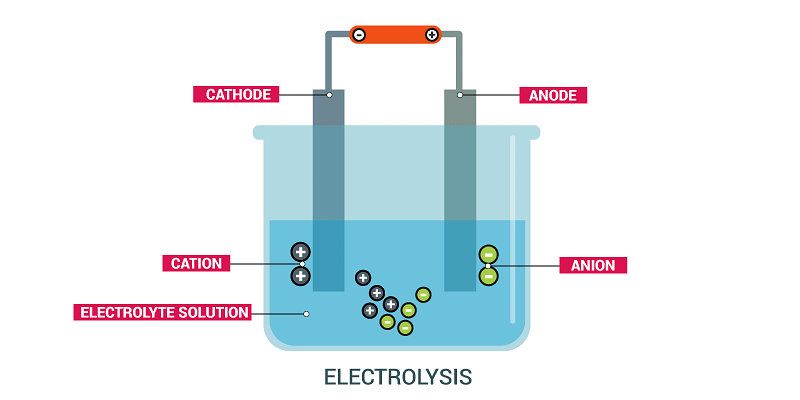 During electrolysis, chemical reactions occur at the electrodes, causing the decomposition of the compound in the solution. This process leads to the production of new substances, such as elemental forms of the ions or new compounds.
During electrolysis, chemical reactions occur at the electrodes, causing the decomposition of the compound in the solution. This process leads to the production of new substances, such as elemental forms of the ions or new compounds.
(c) If you pass current through copper sulphate solution, copper gets deposited on the plate connected to the ___________ terminal of the battery.
Ans: Negative
Explanation: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution undergoes electrolysis when an electric current is passed through it.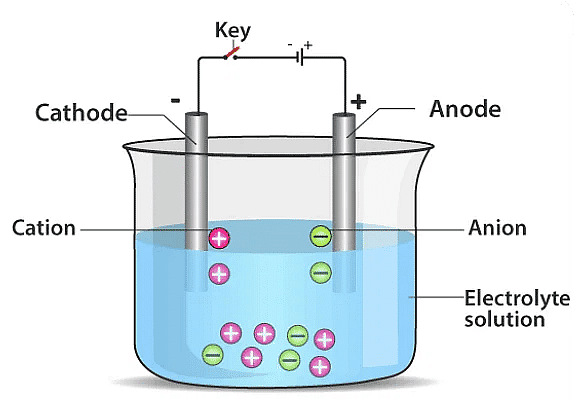 Electrolysis of CuSO4
Electrolysis of CuSO4
- During electrolysis, CuSO4 dissociates into Cu2+ (copper ions) and SO4 2- (sulphate ions).
- The copper ions (Cu2+) are attracted to the cathode, which is the negative terminal of the battery.
- At the cathode, Cu2+ ions gain electrons and undergo reduction, transforming into solid copper (Cu) atoms.
- These copper atoms deposit on the surface of the cathode, forming a layer of copper.
- The deposition of copper on the cathode is due to the reduction of Cu2+ ions, which occurs at the negative terminal of the battery.
(d) The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material by means of electricity is called _________.
Ans: Electroplating
Explanation: Electroplating is a process that uses an electric current to reduce dissolved metal cations so that they form a thin, coherent metal coating on an electrode. In simpler terms, it is a metal finishing technique in which a thin layer of one metal is deposited onto the surface of another metal, usually to improve its appearance, prevent corrosion, or increase durability.
Q2: When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution, the magnetic needle shows deflection. Can you explain the reason?
Ans: When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution and the magnetic needle shows deflection, it indicates the presence of an electric current in the solution. This happens because the electric current in the solution creates a magnetic field around the tester's wires, including the needle. The interaction between the magnetic fields of the current and the needle causes the needle to deflect. This deflection is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the movement of charged particles (ions) in the solution generates the electric current.
Q3: Name three liquids, which when tested in the manner shown in the figure, may cause the magnetic needle to deflect.

Ans: Saltwater, Vinegar, Sodium hydroxide solution
Explanation: The three liquids that may cause the magnetic needle to deflect when tested are:
- Saltwater: Saltwater is a solution that contains ions (sodium and chloride ions) which can conduct electricity. When the tester is dipped into saltwater, the flow of electric current through the solution will cause the magnetic needle to deflect.
- Vinegar: Vinegar is an acidic solution that contains acetic acid. Acids can ionize in water, producing ions that can conduct electricity. When the tester is dipped into vinegar, the presence of ions allows for the flow of electric current, resulting in the deflection of the magnetic needle.
- Sodium hydroxide solution: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a strong base that can dissociate in water to form hydroxide ions (OH-). When the tester is dipped into a solution of sodium hydroxide, the presence of hydroxide ions allows for the conduction of electricity. As a result, the electric current flows through the solution, leading to the deflection of the magnetic needle.
These three liquids exhibit conductivity due to the presence of ions, allowing them to complete an electric circuit and produce deflection in the magnetic needle when tested with the method shown in the figure.
Q4: The bulb does not glow in the setup shown in the figure. List the possible reasons. Explain your answer.

Ans: The lists of possible reasons for the bulb not glowing are:
(i) The circuit might be incomplete.
(ii) The bulb might be fused.
(iii) Liquid in the beaker might be non-conducting.
(iv) Insufficient charge of battery which might be responsible for bulb not glowing.
Q5: A tester is used to check the conduction of electricity through two liquids, labeled A and B. It is found that the bulb of the tester glows brightly for liquid A while it glows very dimly for liquid B. You would conclude that
(i) liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.
(ii) liquid B is a better conductor than liquid A.
(iii) both liquids are equally conducting.
(iv) conducting properties of liquid cannot be compared in this manner.
Ans: (i) liquid A is better conductor than liquid B.
Q6: Does pure water conduct electricity? If not, what can we do to make it conducting
Ans: Pure water is a poor conductor of electricity. To make it conducting, we can add substances such as salt, acids, or bases. These substances ionize in water, creating charged particles that enable the flow of electric current. For example, adding salt produces ions from the salt, while adding an acid introduces hydrogen ions, and adding a base generates hydroxide ions. These added substances make the water conductive, but it's important to note that the resulting solution is no longer pure water and contains ions from the added compound.
Q7: In case of a fire, before the firemen use the water hoses, they shut off the main electrical supply for the area. Explain why they do this.
Ans: Firefighters shut off the main electrical supply before using water hoses in a fire to prevent electrical accidents. Water conducts electricity, so it can cause electric shocks if it comes into contact with live wires. By cutting off the power, they reduce the risk of shocks and prevent short circuits that could start new fires. This helps keep firefighters and people nearby safe. Additionally, it allows the water hoses to be used more effectively to put out the fire without worrying about electricity causing more problems.
Q8: A child staying in a coastal region tests the drinking water and also the seawater with his tester. He finds that the compass needle deflects more in the case of seawater. Can you explain the reason?
Ans: Since seawater contains more salts dissolved in it, thus in the case of seawater, the compass needle of the tester deflects more than the drinking water.
Q9: Is it safe for the electrician to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during heavy downpours? Explain.
Ans: No, it is not safe for the electrician to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during heavy downpours because the rainwater contains dissolved salts. This makes rainwater a good conductor of electricity; hence, it might cause electrical shock to electricians.
Q10: Paheli had heard that rainwater is as good as distilled water. So she collected some rainwater in a clean glass tumbler and tested it using a tester. To her surprise, she found that the compass needle showed deflection. What could be the reasons?
Ans: Many impurities get dissolved in the rainwater when it comes to the ground. Due to the presence of these impurities, rainwater conducts electricity. This explains Paheli’s observation.
Q11: Prepare a list of objects around you that are electroplated.
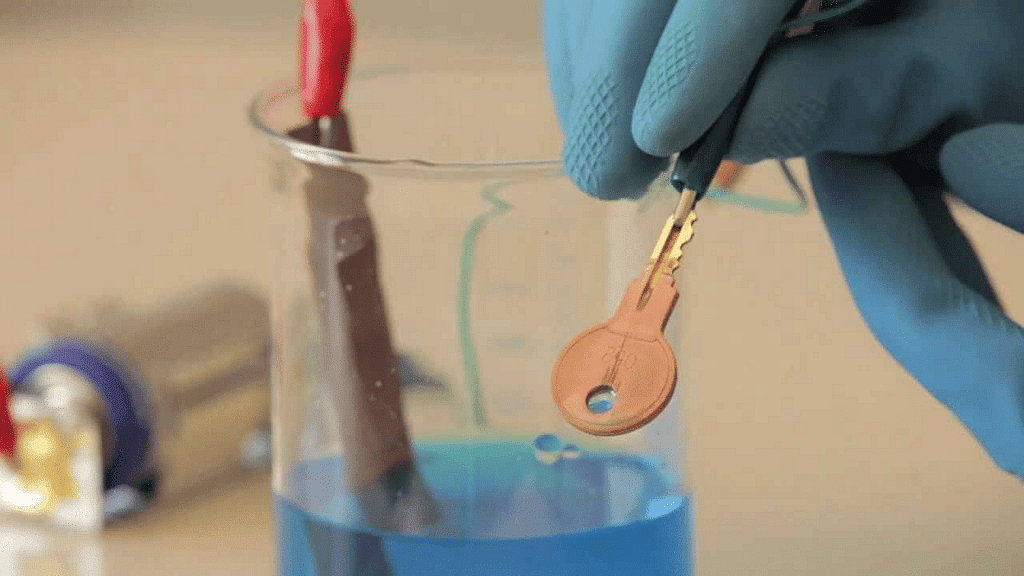 Electroplated Key
Electroplated Key
Ans: The following is a list of objects around me which are electroplated:
(i) Cars, buses, etc. are electroplated with chromium to give them a shiny appearance.
(ii) Artificial jewelry items are either silver or gold plated.
(iii) Door handles, metal items, etc. are zinc plated.
(iv) Cans are tin-plated.
(v) Iron used in building constructions is coated with zinc to prevent corrosion and rusting of iron.
Q12: The process that you saw in Activity 14.7 is used for the purification of copper. A thin plate of pure copper and a thick rod of impure copper are used as electrodes. Copper from the impure rod is sought to be transferred to the thin copper plate. Which electrode should be attached to the positive terminal of the battery and why?
Ans: The electrode of impure copper is connected with the positive terminal. Pure copper metal, which is positively charged, from the positive terminal is deposited over the negative terminal of thin copper after dissolving in the solution.
|
90 videos|273 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 - Chemical Effects of Electric Current
| 1. What are the chemical effects of electric current? |  |
| 2. How does electrolysis work? |  |
| 3. What is electroplating and how does it work? |  |
| 4. What is the role of an electrolyte in an electrochemical cell? |  |
| 5. How can the chemical effects of electric current be harmful? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|


















