NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management
The Science Class 8 chapter, Crop Production & Management, is a fundamental topic in the field of agriculture that aims to teach students about the different agricultural practices used to cultivate crops. Let's have a look at the NCERT Solutions of the chapter.

Q1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
(float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation)
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called ______.
Ans: The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called the crop.
 View Answer
View Answer 
A crop refers to a large number of similar plants cultivated for agricultural purposes in a specific area. Examples:
- Food crops: Grown for people to eat, including wheat, rice, corn, apples, bananas, and dates.
- Cash crops: Grown for profit, such as cereals, oilseeds, coffee, cocoa, sugar cane, vegetables, fruits, peanuts, cotton, and tobacco.
(b) The first step before growing crops is ______ of the soil.
Ans: The first step before growing crops is the preparation of the soil.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Preparation of soil involves various activities such as plowing, leveling, and adding organic matter to the soil to create favorable conditions for plant growth.
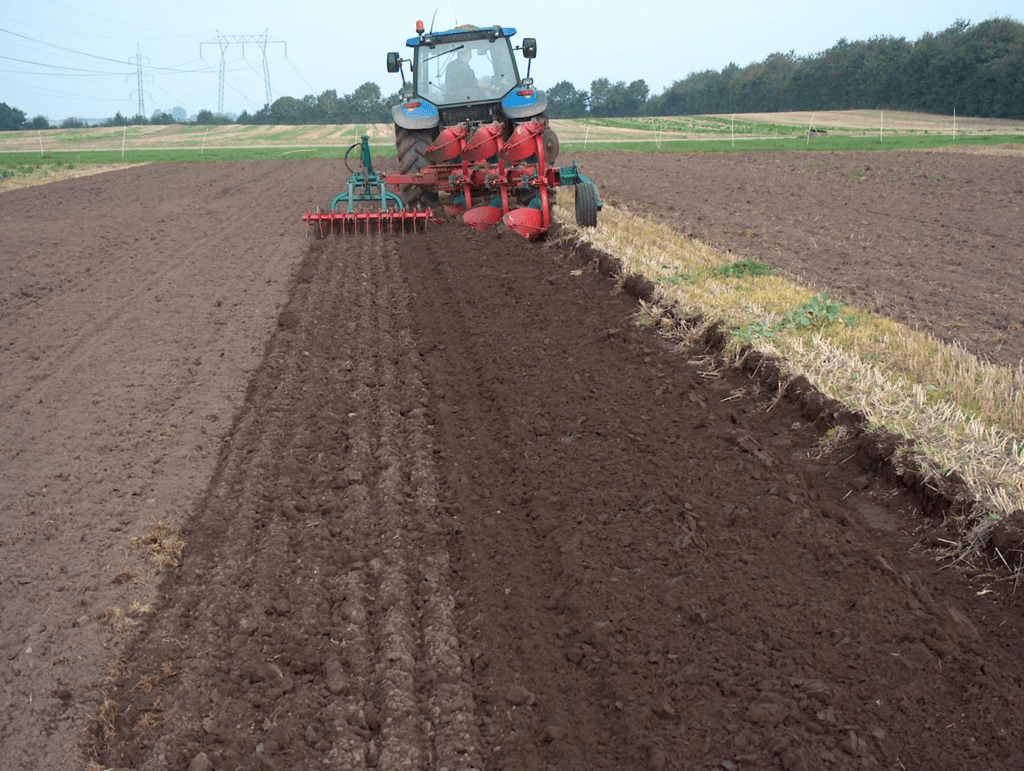 Preparation of Soil(c) Damaged seeds would ______ on top of water.
Preparation of Soil(c) Damaged seeds would ______ on top of water.
Ans: Damaged seeds would float on top of the water.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Damaged seeds would float on top of the water. Floating is a characteristic of damaged seeds, as damaged seeds have air pockets inside them that cause them to stay afloat when placed in water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and ______ and ______ from the soil are essential.
Ans: For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Sunlight provides energy for photosynthesis, while water and nutrients from the soil are necessary for the plant's growth, development, and overall health.
Q2. Match items in column A with those in column B. 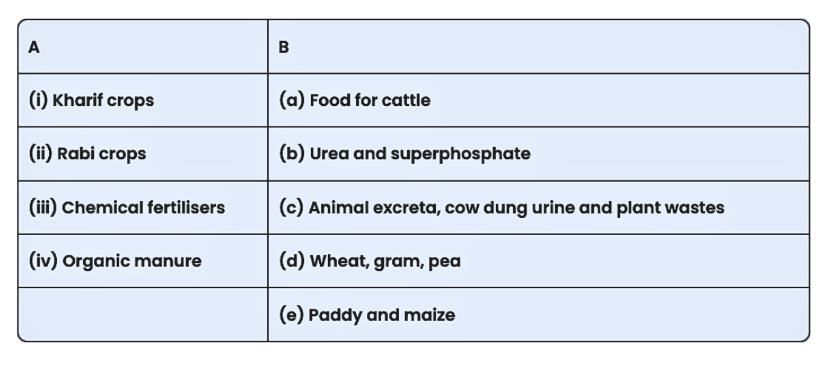 Ans:
Ans: 
 View Answer
View Answer 
(i) Kharif crops → (e) Paddy and maize
Kharif crops are sown in the rainy season (June–July) and harvested around September–October.
Examples: Paddy (rice), maize, jowar, bajra.
(ii) Rabi crops → (d) Wheat, gram, pea
Rabi crops are sown in the winter season (October–November) and harvested in spring (March–April).
Examples: Wheat, gram (chana), pea, mustard.
(iii) Chemical fertilisers → (b) Urea and superphosphate
These are man-made nutrients added to the soil to improve crop yield.
Urea and superphosphate are common chemical fertilisers rich in nitrogen and phosphorus.
(iv) Organic manure → (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant wastes
Organic manure is made from natural waste materials.
Examples include animal excreta (cow dung, urine) and decomposed plant matter.
It enriches the soil naturally and improves its fertility.
Q3. Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Ans:
(a) Paddy and maize (b) Wheat and gram
(b) Wheat and gram
Q4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following:
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Ans:
(a) Preparation of soil
- Preparation of soil is an important first step in farming. This process makes the soil ready for planting seeds.
- Farmers start by loosening the soil through plowing, which aerates it, improves air and water circulation, and breaks up compacted soil for better root growth.
- When the soil is turned over, it mixes in nutrients and organic matter that plants need to grow.
- Levelling the soil is also essential because it allows water to spread evenly when the crops are watered, preventing areas from becoming too wet or too dry.
- Good soil preparation is key to growing healthy plants and getting a good harvest.
(b) Sowing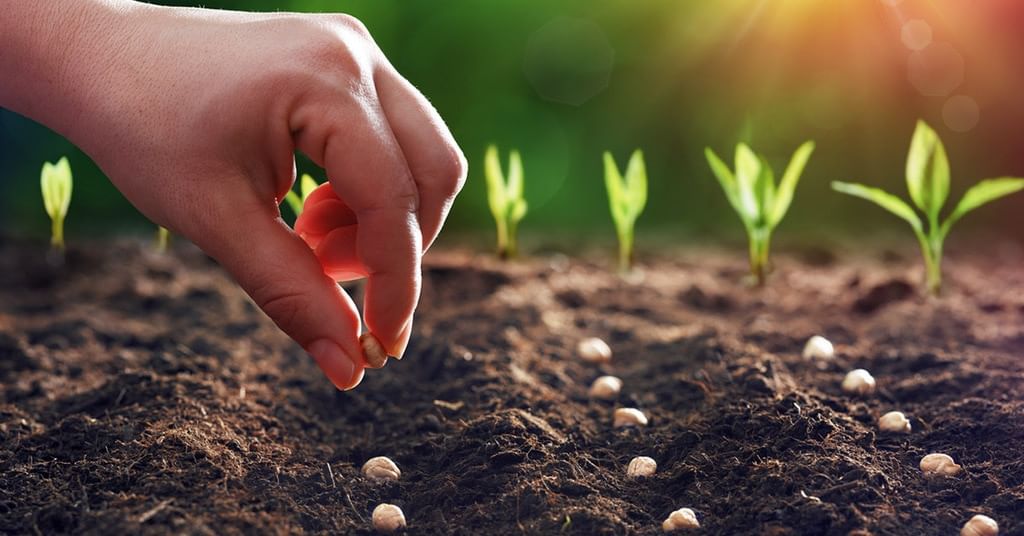 Sowing
Sowing
- Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the prepared soil, and it marks the beginning of crop growing.
- Farmers can sow seeds by hand, a method called broadcasting, where they sprinkle seeds over the soil.
- However, for larger fields, they often use machines called seed drills, which place the seeds at the right depth and distance apart.
- Timing is very important when sowing; it should be done when the weather is just right, with enough moisture and warmth in the soil to help the seeds sprout.
- Proper sowing leads to healthy plants and a better harvest.
(c) Weeding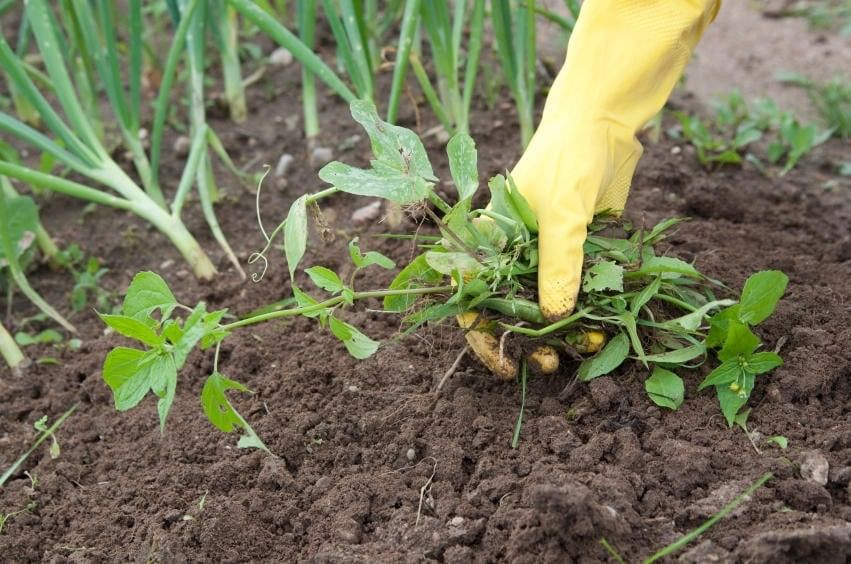 Weeding
Weeding
- Weeding is the act of removing unwanted plants, known as weeds, that grow alongside crops.
- Weeds can steal sunlight, water, and nutrients from the crops, making it hard for them to grow strong. Farmers usually remove weeds by hand or with tools like sickles.
- For larger fields, they might use special chemicals called weedicides to kill the weeds.
- Regular weeding is important because it helps the main crops get all the resources they need to grow well and produce a good yield.
(d) Threshing  Threshing
Threshing
- Threshing is the process of separating the grain from the straw after harvesting crops. Once the crops are cut, farmers need to get the edible grains out so they can use them for food or sell them.
- For small amounts, farmers can thresh by hand, but for larger amounts, they use machines that make the job faster.
- In some traditional methods, farmers may beat stalks against a surface, use tools like flails, or have animals like bullocks trample harvested plants to separate grains, though animal-based threshing is less common today due to mechanization.
- Threshing is an important step because it prepares the grains for storage and cooking, ensuring that farmers can make the most of their harvest.
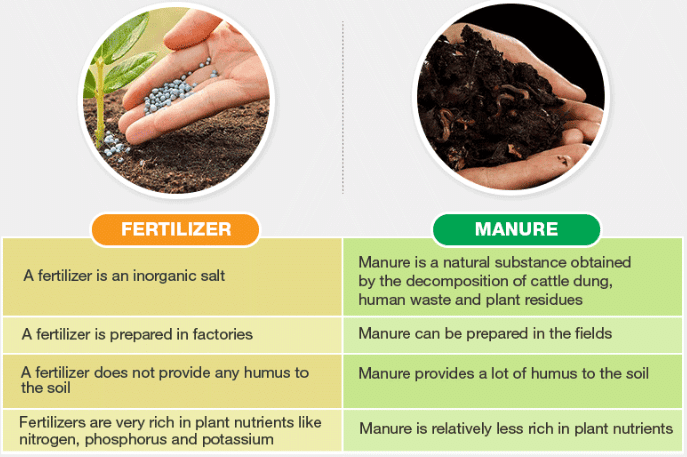
Q5. Explain how fertilizers are different from manure.
Ans: Here are the differences between fertilizers and manure.
Q6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation that conserve water.
Ans: Irrigation is the artificial application of water to soil or land to assist in the growing of crops and vegetation.
- It is an essential agricultural practice, especially in areas with inadequate rainfall, helping to ensure consistent water supply for crops, improve yields, and support food production.
- Efficient irrigation is crucial for conserving water resources and maintaining agricultural sustainability.
Two methods of irrigation that help in water conservation are as follows:
1. Drip Irrigation: Drip irrigation is a highly efficient method that delivers water directly to the base of plants through a network of tubes and emitters. This system allows water to drip slowly, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
 Drip Irrigation
Drip Irrigation
Benefits:
- Water Efficiency: Only the necessary amount of water is provided directly to the roots, significantly reducing water wastage.
- Reduced Weed Growth: Since water is applied only where needed, the surrounding areas remain dry, discouraging weed growth.
- Improved Plant Health: It reduces the risk of fungal diseases that can occur with overhead watering, as the foliage remains dry.
2. Sprinkler Irrigation: Sprinkler irrigation mimics natural rainfall by distributing water through a system of pipes and pumps that spray water onto the crops through a series of nozzles or sprinkler heads.
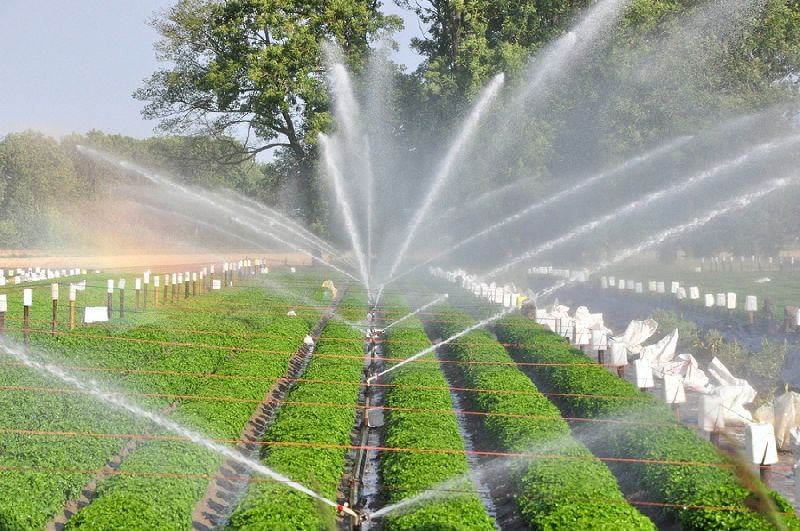 Sprinkler SystemBenefits:
Sprinkler SystemBenefits:
- Adjustability: Sprinkler systems can be modified to deliver different amounts of water based on crop needs and environmental conditions. However, they may lose water to evaporation or wind drift if not carefully managed.
- Reduced Water Loss: When properly designed and managed, modern sprinkler systems can minimize evaporation and drift, making them more efficient than traditional flood irrigation.
- Soil Moisture Control: This method allows for better control over soil moisture levels, promoting healthier crop growth.
7. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Ans:
- The crop of wheat needs mild to moderate temperatures and frost-free days; along with irrigation but no waterlogging. Winters are suitable for growing wheat.
- In the Kharif season, which coincides with the peak summer months in India, the temperature is at its peak, which is not suitable for wheat.
- Moreover, during the rainy season, a lot of water accumulates in fields, which can be harmful to the wheat crop. Hence, if wheat is sown in the Kharif season, the productivity would be minimum and would not be profitable for the farmers.
Q8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Ans: Continuous planting of the same crop can negatively affect soil health in several ways:
- Nutrient Depletion: When the same crop is grown year after year, it uses up important nutrients from the soil, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This means there are fewer nutrients left for future crops.
- Reduced Soil Fertility: As these nutrients become less available, the soil becomes less fertile. This leads to lower crop yields, meaning farmers will harvest less food and of poorer quality.
- Soil Structure Problems: Growing the same crop over and over can make the soil hard and compact. This makes it difficult for air and water to reach the roots of plants, which can harm their growth.
- More Pests and Diseases: Planting the same crop repeatedly can attract more pests and diseases that affect that specific crop. This often leads to farmers needing to use more pesticides, which can hurt helpful insects and soil organisms.
- Weed Growth: Some weeds can grow well when the same crop is planted all the time. These weeds compete with the main crop for sunlight, water, and nutrients, which can reduce the crop's growth.
- Crop Rotation as a Solution: To solve these problems, farmers practice crop rotation. This means changing the type of crop they plant each season. Crop rotation helps keep the soil healthy, restore nutrients, and reduce problems with pests and weeds.

Q9. What are the weeds? How can we control them?
Ans: Weeds are undesirable plants that grow naturally alongside crop plants in a field.
Farmers use various methods to control weeds and reduce their impact:
Tilling: Before sowing crops, tilling helps uproot and kill weeds, allowing them to dry up and mix with the soil.
Manual Removal: Manual weeding involves physically uprooting or cutting weeds close to the ground. Tools like a khurpi can be used for this purpose. It is best to remove weeds before they produce flowers and seeds.
Weedicides: Farmers also use chemicals known as weedicides, such as 2,4-D, to kill weeds without harming the crops, but safety precautions like wearing protective gear and following guidelines are essential to prevent harm to farmers, animals, and the environment.
Q10. Arrange the following boxes in the proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
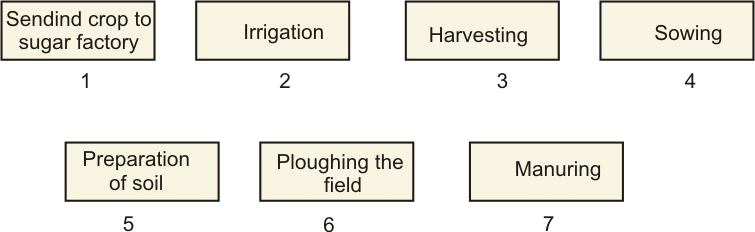 Ans: Preparation of soil → Ploughing the field → Sowing → Manuring → Irrigation → Harvesting → Sending crop to the sugar factory.
Ans: Preparation of soil → Ploughing the field → Sowing → Manuring → Irrigation → Harvesting → Sending crop to the sugar factory.
- Preparation of soil: Getting the soil ready for planting sugarcane.
- Ploughing the field: Breaking up the soil and creating a suitable seedbed.
- Sowing: Planting sugarcane seeds or setts into the prepared soil.
- Manuring: Adding fertilizers to provide nutrients to the plants.
- Irrigation: Providing water to the sugarcane plants at regular intervals.
- Harvesting: Cutting and removing mature sugarcane plants from the field.
- Sending crop to sugar factory: Transporting harvested sugarcane to a sugar factory for processing.
Q11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given:
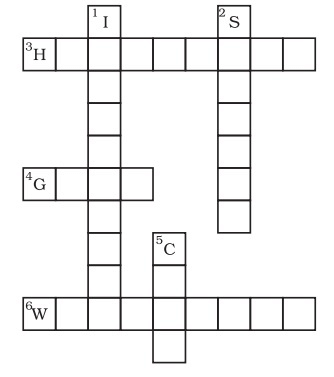 Down
Down
(a) Providing water to the crops.
(b) Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
(c) Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
(d) A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
(e) A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
(f) A process of separating the grain from the chaff.
Ans: 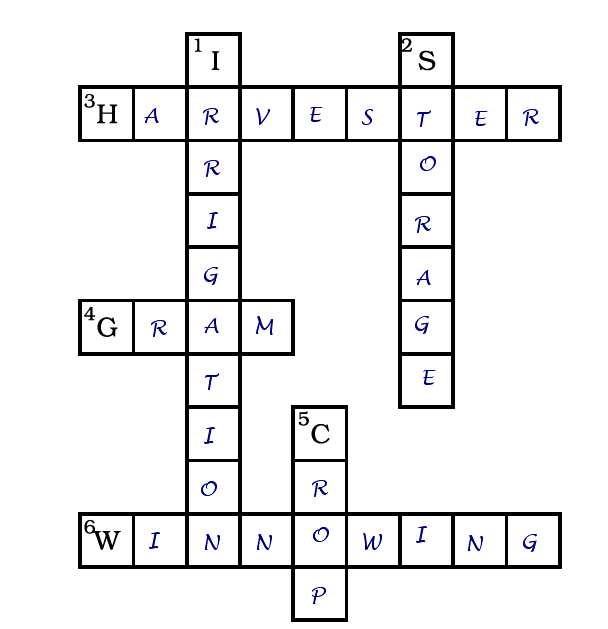
(a) Irrigation
(b) Storage
(c) Crop
(d) Harvester
(e) Gram
(f) Winnowing
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management
| 1. What are the main steps involved in crop production? |  |
| 2. How does irrigation impact crop production? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of sowing seeds? |  |
| 4. Why is pest control important in crop management? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of crop rotation? |  |

















