NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Exercises
Q1. Answer the following questions.
(i) Which are the two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation?
Ans: The two primary climatic elements driving soil formation are temperature and rainfall. Temperature affects the rate of chemical reactions involved in weathering, while rainfall determines the moisture levels contributing to both weathering and organic matter decomposition, thereby impacting humus formation.
(ii) Write any two reasons for land degradation today.
Ans: Land degradation today is primarily driven by deforestation, which removes vegetation cover, leading to soil erosion and loss of fertility. Additionally, excessive use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture disrupts the natural soil composition, causing nutrient depletion and land degradation.
(iii) Why is land considered an important resource?
Ans: Land is considered an important resource as it provides habitation to a wide variety of flora and fauna. Also used by Human beings for various purposes such as agriculture, forestry, mining, building houses and roads, and setting up industries.
(iv) Name any two steps that the government has taken to conserve plants and animals.
Ans: Two steps that the government has taken to conserve plants and animals:
- Government has set up national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves for protecting natural vegetation and wildlife; for example, the Kaziranga National Park in Assam.
- The killing of lions, tigers, deer, Great Indian Bustards and peacocks is banned. It has also prohibited the trade of the species of plants and animals protected under the international agreement CITES.
(v) Suggest three ways to conserve water.
Ans: Three ways to conserve water:
- Rain-water harvesting.
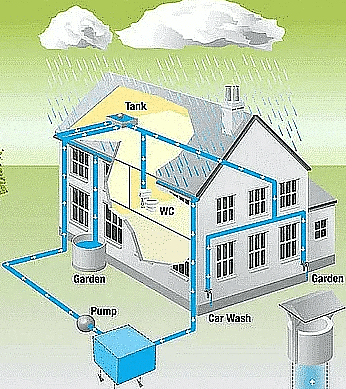 Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater Harvesting
- Lining irrigation canals to avoid seepage of water.
 Lining Irrigation
Lining Irrigation
- Replenishing groundwater by promoting afforestation.
 Afforestation
Afforestation
Q2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which one of the following is not a factor of soil formation?
(a) Time
(b) Soil texture
(c) Organic matter
Ans: (b) Soil texture
The factors of soil formation are parent material (the original rock matter), climate (weathering processes), living organisms (contribute to the breakdown of parent material), topography (the physical and geometric configuration of the surface), and time (for the above factors to interact and evolve). Soil texture (sand, silt, clay) is a characteristic of soil, not a factor of its formation.
(ii) Which one of the following methods is most appropriate to check soil erosion on steep slopes?
(a) Shelterbelts
(b) Mulching
(c) Terrace cultivation
Ans: (c) Terrace cultivation
Steep slopes are vulnerable to soil erosion as gravity pulls water, and the soil it carries, downhill. Terrace cultivation helps to slow down this process. Terraces are essentially steps cut into the slope, acting as individual level plots of farmland. This reduces the speed of water runoff, allowing more time for it to seep into the ground, thus preserving the topsoil.
(iii) Which one of the following is not in favour of the conservation of nature?
(a) Switch off the bulb when not in use
(b) Close the tap immediately after using
(c) Dispose poly packs after shopping
Ans: (c) Dispose poly packs after shopping
Conservation of nature involves practices that protect, preserve, and sustainably manage natural resources. Switching off bulbs when not in use and closing the tap immediately after using are examples of conservation as they save energy and water respectively. However, disposing of poly packs after shopping is not in favour of conservation. These packs are often non-biodegradable, cause pollution, and take up landfill space. A better practice would be to reuse or recycle them, or use alternatives like cloth bags.
Q3. Match the following.
| (i) Land Use | (a) Prevent soil erosion |
| (ii) Humus | (b) Land suitable for agriculture |
| (iii) Rock dams | (c) Productive use of land |
| (iv) Arable land | (d) Organic matter deposited on top soil |
| (e) contour ploughing |
Ans:
| (i) Land Use | (c) Productive use of land |
| (ii) Humus | (d) Organic matter deposited on top soil |
| (iii) Rock dams | (a) Prevent soil erosion |
| (iv) Arable land | (b) Land suitable for agriculture |
Q4. State whether the given statements are true or false. If true, write the reasons.
(i) Ganga-Brahmaputra plain of India is an overpopulated region.
(ii) Water availability per person in India is declining.
(iii) Rows of trees planted in the coastal areas to check the wind movement is called intercropping.
(iv) Human interference and changes of climate can maintain the ecosystem.
Ans:
(i) This statement is true. Plains and river valleys offer suitable land for agriculture.
Hence, these are densely-populated areas of the world.
(ii) This statement is true. Though water is present in abundance, freshwater is a scarce resource. Water availability is a serious problem in many regions of the world. Due to the wastage of water, deforestation, and pollution and depletion of freshwater reserves (such as rivers and groundwater), the availability of water is fast declining.
(iii) This statement is false. because intercropping is an agricultural practice that involves growing two or more crops together in close proximity.
 Intercropping
Intercropping
The described process is called shelterbelts. Intercropping is the process in which different crops are grown in alternate rows, and are sown at different times to protect the soil from rain wash.
(iv) This statement is false. Human interference and climatic changes for the most part adversely affect the balance of the ecosystem.
Soil formation, a complex process, is significantly influenced by two primary climatic factors - temperature and rainfall. These two elements play a crucial role in determining the characteristics and fertility of the soil.
|
63 videos|424 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
| 1. What is the importance of soil conservation? |  |
| 2. How does deforestation affect natural vegetation and wildlife resources? |  |
| 3. What are the effects of water pollution on aquatic life? |  |
| 4. How does urbanisation affect natural resources? |  |
| 5. What are the effects of climate change on natural resources? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|



















