Landforms and Life NCERT Solutions | Social Studies (SST) Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Big Questions |

|
| Let's Explore (Page 42) |

|
| Think About It (Page 43) |

|
| Page 49 |

|
| Page 53 |

|
| Page 54 |

|
| Page 55 |

|
| Questions, Activities and Projects |

|
The Big Questions
1. What are the major types of landforms and their significance to life and culture?
Ans: The major types of landforms are:
- Mountains: Influence climate and weather. Provide habitats for diverse wildlife. Source of fresh water from melting snow. Hold cultural significance and attract tourism.
- Plateaus: Rich in minerals and have varied climates. Important for mining and agriculture, especially in volcanic regions. Home to beautiful waterfalls.
- Plains: Essential for agriculture due to fertile soils. Support large populations and human settlements. Provide favourable conditions for farming, transportation, and development.
2. What are the challenges and opportunities of life associated with each landform?
Ans: The challenges and opportunities of life associated with each landform are as follows:
- Mountains
Opportunities: Rich in minerals and forest resources; attract tourism.
Challenges: Harsh climate and difficult transportation. - Plains
Opportunities: Fertile soil for agriculture; ideal for building cities.
Challenges: Prone to flooding and overcrowding. - Plateaus
Opportunities: Abundant in minerals; supports cattle rearing.
Challenges: Scarcity of water and limited fertile soil. - Deserts
Opportunities: Rich in minerals and solar energy potential.
Challenges: Water scarcity and extreme temperatures.
Let's Explore (Page 42)
Q1. As a class activity, form groups of four or five students and observe the school's surroundings. What kind of landscape do you see? Will the landscape change a few kilometres away? Or within some 50 kilometres? Compare with other groups.
Ans: Observing the School's Surroundings: Group Observations
- Type of Landscape: Our school is located in an urban area with buildings, roads, parks, and some trees, but it lacks natural water bodies or hills.
- Nearby Changes: A few kilometres away, the landscape transitions to residential areas featuring more green spaces and parks, with fewer commercial buildings.
- Changes within 50 Kilometres: Beyond the urban area, we encounter suburban neighbourhoods with gardens and larger parks, eventually leading to rural landscapes with fields, farms, small forests, hills, and a river.
- Comparison with Other Groups: Other groups also observed urban landscapes, with one noting a nearby industrial area. Predictions about landscape changes were similar, anticipating greener spaces away from the school. One group mentioned a large lake 30 kilometres away that we had overlooked.
Class Discussion:
The area around our school is mainly urban, transitioning to residential spaces with greenery just a few kilometers away. Within 50 kilometers, we see a significant change to rural landscapes featuring farms and natural features. Factors influencing these changes include urban planning, natural geography, and human activities, with urban areas being densely built and rural areas offering more open spaces.
Q2. In the same groups, discuss a journey that any of you has made through a region of India. List the different landscapes seen on the way. Compare with other groups.
Ans: Journey Description: Priya's Trip from Delhi to Manali
- Delhi: Urban landscape with tall buildings, busy roads, crowded markets, parks, and historical monuments.
- Haryana: Suburban and rural landscape featuring residential areas, agricultural fields, and small villages, with flat terrain and occasional hills.
- Punjab: Rural landscape characterised by vast fields of wheat and rice, small villages, and canals, maintaining a flat landscape.
- Himachal Pradesh: Mountainous landscape with steep mountains, winding roads, dense pine and deodar forests, alongside rivers and streams.
- Manali: Alpine landscape showcasing snow-capped peaks, lush green valleys, and apple orchards, blending traditional wooden houses with modern buildings.
Comparison and Discussion
- Delhi to Haryana: A smooth transition from urban to suburban and rural landscapes, with increasing greenery.
- Haryana to Punjab: Similar rural landscapes, but Punjab features more extensive agriculture.
- Punjab to Himachal Pradesh: A significant shift to mountainous terrain with steep hills.
- Himachal Pradesh to Manali: Diverse terrains including forests, meadows, and snow-covered peaks.
Conclusion
Priya's journey from Delhi to Manali showcased a rich variety of landscapes, illustrating India's geographical diversity and the dramatic changes occurring over short distances.
Think About It (Page 43)
Q. What is snow? Unless you live in a Himalayan region (such as Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh), you may never have seen snow! In the rest of India, most precipitation is in the form of rain and hail. But at higher altitudes, if it is cold enough, snow will fall, covering the landscape in a soft and beautiful white blanket. Snow and hailstones are nothing but precipitation of water in a solid state.
Ans: Snow is a type of precipitation formed when water vapour in the air turns directly into ice crystals without becoming liquid. These ice crystals cluster together to create snowflakes, which fall to the ground when temperatures are low enough.
Key points about snow:
- Common in high-altitude areas like the Himalayas, including regions such as Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- In most of India, precipitation is mainly rain or hail due to warmer temperatures.
- In colder, high-altitude regions, the temperature is low enough for snow to form.
- Snow covers the ground in a beautiful white layer, creating a peaceful landscape.
- Both snow and hail are solid forms of water, illustrating how different types of precipitation occur based on temperature and altitude.
Page 49
Q. These images (Fig. 3.6 on page 50) depict a few challenges that people living in the mountains may face. Discuss them in groups in the class and write one paragraph on each. Also discuss why, despite many such challenges, people still choose to live in the mountains. 
Ans: Challenges of Living in the Mountains
- Avalanches: Sudden slides of snow, ice, and rocks can be deadly, destroying homes and blocking access. Residents must stay alert for emergencies, which creates stress.
- Landslides: Triggered by heavy rain, earthquakes, or human activity, landslides can damage infrastructure and hinder travel and farming. Precautions include building walls and avoiding construction on unstable ground.
- Heavy Snowfall: Large snow accumulations can isolate communities, disrupt travel, and damage buildings. Residents adapt by clearing snow and constructing sturdy homes.
- Flash Floods: Rapid floods from heavy rain or melting snow can wash away homes and livestock. Communities mitigate risks by building barriers and implementing early warning systems.
- Uncontrolled Tourism: While tourism boosts the economy, it can strain local resources and harm the environment through overcrowding and pollution. Balancing economic benefits with environmental protection is crucial.
Conclusion: Despite these challenges, living in the mountains offers natural beauty, fresh air, and strong community ties. Residents cherish cultural traditions and opportunities in tourism, farming, and crafts. The peaceful, independent lifestyle provides an appealing alternative to urban life, showcasing the resilience of mountain communities.
Page 53
Q. Use the colour code in Fig. 3.8 to add a landform to each name. For instance, 'Tibetan plateau', 'Rocky range', 'Nile plain'.
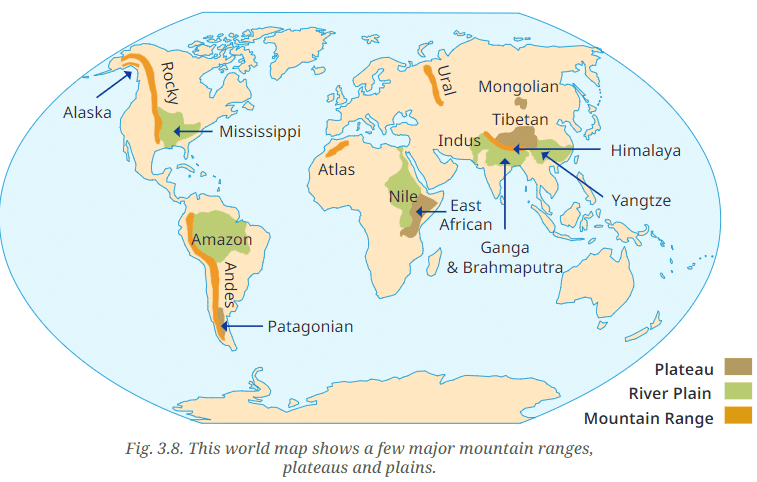
Ans:
Tibetan Plateau (Brown): The Tibetan Plateau, shown in brown, is the largest and highest plateau in the world.
Rocky Range (Orange): The Rocky Mountain Range, marked in orange, stretches along the western part of North America.
Nile Plain (Green): The Nile River Plain is depicted in green.
Additional Examples from the Map:
- Amazon Plain (Green): The Amazon river plain in South America, highlighted in green.
- Andes Range (Orange): The Andes mountain range in South America, marked in orange.
- East African Plateau (Brown): The East African plateau, shown in brown, located in eastern Africa.
- Mississippi Plain (Green): The Mississippi river plain, marked in green, located in the central United States.
- Atlas Range (Orange): The Atlas mountain range in North Africa, highlighted in orange.
- Patagonian Plateau (Brown): The Patagonian plateau in southern South America, shown in brown.
- Himalaya Range (Orange): The Himalayan mountain range in Asia, marked in orange.
- Yangtze Plain (Green): The Yangtze river plain in China, highlighted in green.
- Indus Plain (Green): The Indus river plain in South Asia, marked in green.
- Ural Range (Orange): The Ural mountain range in Russia, shown in orange.
- Ganga & Brahmaputra Plain (Green): The Ganga and Brahmaputra river plains in India and Bangladesh, highlighted in green.
- Mongolian Plateau (Brown): The Mongolian plateau in East Asia, marked in brown.
- Alaska Range (Orange): The Alaska mountain range in North America, highlighted in orange.
 |
Download the notes
NCERT Solutions: Landforms and Life
|
Download as PDF |
Page 54
Q. The picture in Fig. 3.9 has been taken from a satellite. It captures a portion of north India from a high altitude. Observe and discuss the image as a class activity.
→ Which colour is the Ganga plain?
→ What does the white expanse represent?
→ What does the brown expanse at the bottom left of the image represent?
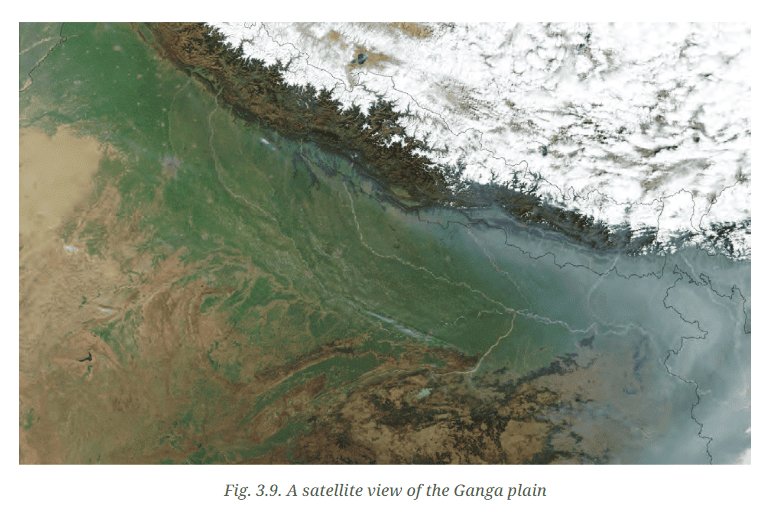
Ans:
→ The Ganga plain is depicted as a green expanse in the image, indicating its fertile and densely vegetated nature.
→ The white expanse at the top signifies the snow-covered Himalayan mountains, which remain permanently snowy due to their high altitude and cold temperatures.
→ The brown expanse at the bottom left represents the arid and semi-arid regions, likely including the Thar Desert. These areas have less vegetation, resulting in a brownish appearance from exposed soil and rock.
Page 55
Q1. Can you give examples of river sources or confluences from your region that are regarded sacred by any community?
Ans: Yes, there are several examples of river sources and confluences that are considered sacred by various communities:
- The Triveni Sangam at Prayagraj (Allahabad) is the confluence of the Ganga, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati rivers. It is regarded as a highly sacred site in Hinduism.
- The source of the Yamuna River at Yamunotri in Uttarakhand is also a revered pilgrimage site.
Q2. Visit a nearby river and observe all activities there, whether economic or cultural. Note them down and discuss with your classmates.
Ans: During my visit to the Yamuna River in Delhi, I observed a variety of activities:
- Economic Activities:
- People engaged in fishing.
- Boating activities were common.
- Vendors selling flowers and offerings.
- Washermen washing clothes by the riverbank.
- Cultural Activities:
- Rituals such as offering prayers.
- Floating diyas (lamps) during ceremonies.
- Immersing idols during festivals.
- Morning yoga and meditation by local communities.
These observations highlight the importance of the Yamuna River in supporting both economic and cultural practices, showcasing its significance in daily life.
Q3. Name some popular tourist destinations in India and identify the category of landform they are associated with.
Ans: Here is a list of some popular tourist destinations in India along with their geographical features:
- Agra (Taj Mahal): Located in the northern plains along the Yamuna River.
- Jaipur (Amber Fort): Situated in the Aravalli mountain range, known for its low hills and rocky terrain.
- Goa (Beaches): Found in the coastal plains along the Arabian Sea.
- Shimla (Hill Station): Located in the Himalayan mountain range, famous for its hilly terrain.
- Kerala (Backwaters): Positioned in the coastal plains, featuring a network of canals and lagoons along the Arabian Sea.
- Rajasthan (Thar Desert): A desert region characterised by arid and semi-arid landforms.
- Leh-Ladakh: Found in the high-altitude mountainous region of the Himalayas.
Questions, Activities and Projects
Q1. In what type of landform is your town/village/city located? Which features mentioned in this chapter do you see around you?
Ans: The landforms of your town, village, or city can differ significantly. Common types include:
- Plains: Flat areas ideal for agriculture.
- Mountains: Elevated regions with steep slopes.
- Plateaus: Raised flatlands often surrounded by steep cliffs.
Local features may include:
- Rivers: Flowing water bodies that may provide resources.
- Hills: Smaller elevations that can affect climate and vegetation.
- Agricultural land: Areas used for farming, often found in plains.
The specific characteristics depend on the local geography.
Q2. Let us go back to our initial trip from Chhota Nagpur to Prayagraj and Almora. Describe the three landforms you came across on the way.
Ans: On the journey from Chhota Nagpur to Prayagraj and Almora, three significant landforms are encountered:
- Chhota Nagpur: This is a plateau rich in mineral resources.
- Prayagraj: Situated in the fertile Ganga plain, it features extensive flat lands.
- Almora: A mountainous area that is part of the Himalayas.
Q3. List a few famous pilgrimage spots in India along with the landforms in which they are found.
Ans: Famous pilgrimage spots in India along with the landforms as follows:
- Varanasi: Situated in the plains along the Ganga river.
- Amarnath: Found in the mountainous region of the Himalayas.
- Tirupati: Located in the hilly area of the Eastern Ghats.
- Vaishno Devi: Nestled in the Trikuta Mountains of the Himalayas.
Q4. State whether true or false —
- The Himalayas are young mountains with rounded tops.
Ans: False - Plateaus usually rise sharply at least on one side.
Ans: True - Mountains and hills belong to the same type of landform.
Ans: True - Mountains, plateaus and rivers in India have the same types of flora and fauna.
Ans: False - Ganga is a tributary to the Yamuna.
Ans: False - Deserts have unique flora and fauna.
Ans: True - Melting snow feeds rivers.
Ans: True - Sediments from rivers deposited in the plains make the land fertile.
Ans: True - All deserts are hot.
Ans: False
Q5. Match words in pairs:
 Ans:
Ans:

|
69 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Landforms and Life NCERT Solutions - Social Studies (SST) Class 6
| 1. What are the major types of landforms found on Earth? |  |
| 2. How do landforms affect human life and activities? |  |
| 3. What processes lead to the formation of different landforms? |  |
| 4. How do landforms influence climate in a region? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of studying landforms in geography? |  |




























