Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics NCERT Solutions | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Let us enhance our learning
Q1. List the similarities and differences in life cycles of plants and animals.Ans:
Similarities:
- Both plants and animals grow and develop over time.
- They undergo different stages in their life cycles, such as seed to plant or egg to adult.
- Both reproduce to ensure the continuity of their kind.
Differences:
- Plants grow continuously throughout their life, while animals have a fixed growth period.
- Animals can move from one place to another, whereas most plants are stationary.
- The life cycle stages of animals often involve significant physical changes, like from larva to adult, while plants mainly change in size and structure.
Q2. The table on the next page shows some data. Study the data and try to find out examples appropriate for the conditions given in the second and third columns. If you think that an example for any of the conditions given below is not possible, explain why.
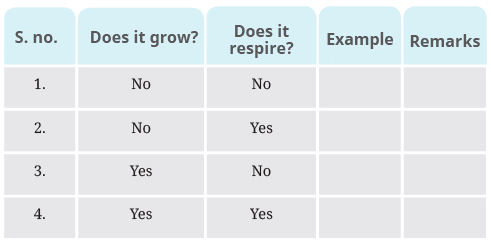
Ans:
Q3. You have learnt that different conditions are required for seed germination. How can we use this knowledge for proper storage of grains and pulses?
Ans: To ensure proper storage of grains and pulses and prevent germination:
- Keep Dry: Store in a dry environment to avoid moisture that can trigger germination.
- Cool Storage: Keep in a cool place to slow down biological processes.
- Airtight Containers: Use airtight containers to reduce exposure to air, which is essential for germination.
Q4. You have learnt that a tail is present in a tadpole but it disappears as it grows into a frog. What is the advantage of having a tail in the tadpole stage?
Ans: The tail in the tadpole stage of a frog offers several advantages:
- Swimming Ability: It enables the tadpole to swim effectively in water, helping it find food and evade predators.
- Balance and Stability: The tail aids in maintaining balance while moving through the water.
Q5. Charan says that a wooden log is non-living as it cannot move. Charu counters it by saying that it is living because it is made of wood obtained from trees. Give your arguments in favour or against the two statements given by Charan and Charu.
Ans:

Q6. What are the similarities and distinguishing features in the life cycles of a mosquito and a frog?
Ans:
Similarities:
- Both undergo metamorphosis with distinct life stages.
- Both start life as eggs.
Differences:
- Mosquitoes have four stages: egg, larva, pupa, adult.
- Frogs have four stages: egg, tadpole, froglet, adult.
- Mosquitoes are entirely terrestrial in their adult stages, while frogs can live both on land and in water.
Q7. A plant is provided with all the conditions suitable for its growth (Fig. 10.9). Draw what you expect to see in the shoot and the root of the plant after one week. Write down the reasons.
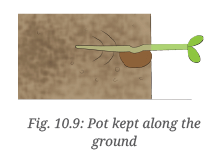
Ans: Expected Plant Growth After One Week:
- Shoot Growth: The shoot will grow upwards towards the light. Leaves will spread, and new ones may emerge to help the plant make food using sunlight.
- Root Growth: The roots will grow downwards into the soil, anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients. New small roots, known as root hairs, will develop to enhance absorption.
Reasons:
- Light Attraction: The shoot grows towards the light to capture more sunlight, which is vital for food production.
- Gravity: Roots grow downwards due to gravity, ensuring stability and aiding in water and nutrient acquisition.
- Water and Nutrients: Roots absorb water and essential nutrients from the soil, supporting the plant's growth.
Q8. Tara and Vijay set up the experiment shown in the picture (Fig. 10.10). What do you think they want to find out? How will they know if they are correct?
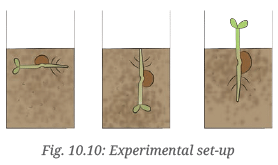
Ans: Objective: To determine the effect of light direction on plant growth.
Confirmation: If the plant in the experiment grows towards the light source (hole in the box), they can conclude that light direction influences plant growth.
Q9. Design an experiment to check if temperature has an effect on seed germination.
Ans: Experiment:
- Take three identical pots filled with garden soil and sow bean seeds in each.
- Place one pot in a warm environment, one in a cool environment, and one at room temperature.
- Ensure all other conditions (light, water, soil) are identical.
- Observe and record the germination rate and seedling growth over 10 days.
Expected Observation: Seeds in the warm environment may germinate faster than those in cooler temperatures, demonstrating the effect of temperature on germination.
Intext Questions
Q1. How would you now categorise a seed, as living or non¬living? (Page 191)
Ans: A Seed is a living thing. Seed can grow into a plant under the right conditions.
Q2. How can the life cycle of a mosquito be disrupted? (Page 197)
Ans: Larvicides (a substance used to kill larvae) target larvae in the breeding habitat before they can mature into adult mosquitoes and disperse. Larvicide treatment of breeding habitats helps reduce the adult mosquito population in nearby areas.
Liquid larvicide products are applied directly to water using backpack sprayers and truck or aircraft-mounted sprayers. Tablet, pellet, granular, and briquet formulations of larvicides are also applied by mosquito controllers to breeding areas.
|
69 videos|288 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics NCERT Solutions - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the main characteristics that define living creatures? |  |
| 2. How do living creatures reproduce, and what are the different types of reproduction? |  |
| 3. What role do adaptations play in the survival of living creatures? |  |
| 4. How do living creatures interact with their environment? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to study the characteristics of living creatures? |  |






















