NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Materials:Metals and Non-Metals
Exercises
Q1. Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets?
(a) Zinc
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Sulphur
(d) Oxygen
Ans: (a)
Solution: Zinc is a metal with malleability and ductility whereas Phosphorus, Sulphur, and Oxygen are non-metals that lack malleability and ductility.

Q2. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) All metals are ductile.
(b) All non-metals are ductile.
(c) Generally, metals are ductile.
(d) Some non-metals are ductile.
Ans: (c)
Solution: Ductility is a property where a substance can be drawn into thin wires, Generally, metals are ductile with mercury as the exception.
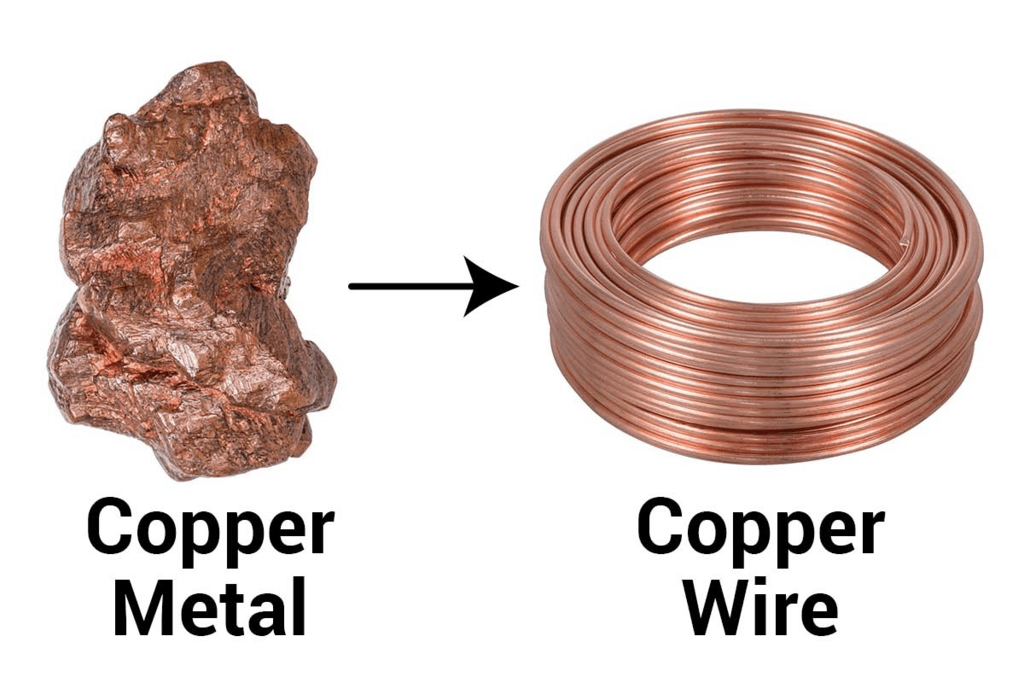 DuctilityQ3. Fill in the blanks :
DuctilityQ3. Fill in the blanks :
(a) Phosphorus is very ………….non-metal.
Ans: Reactive
(b) Metals are …………..conductors of heat and …………..
Ans: Good, Electricity
(c) Iron is …………..reactive than copper.
Ans: More
(d) Metals react with acids to produce …………..gas.
Ans: Hydrogen
Q4. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
(a) Generally, non-metals react with acids. (F)
(b) Sodium is a very reactive metal. (T)
(c) Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate solution. (F)
(d) Coal can be drawn into wires. (F)
Q5. Some properties are listed in the following Table. Distinguish between metals and nonmetals on the basis of these properties.
Ans:
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| Appearance | Lustrous | Dull |
| Hardness | Hard | Brittle |
| Malleability | Malleable | Non-malleable(Brittle) |
| Ductility | Ductile | Non-ductile(Brittle) |
| Heat Conduction | Conductor | Non-conductor |
| Conduction of Electricity | Conductor | Non-conductor |
Q6. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
Ans: Aluminium is one of the least reactive metals, so it does not react with food items and does not alter the taste. Moreover, being a metal aluminium is highly malleable and can be made into very thin foils which are perfect for wrapping food.
(b) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
Ans: Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances because metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. The immersion rod needs electric supply to get heated and in turn to heat liquids.
 Immersion Rod
Immersion Rod
(c) Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
Ans: Copper is less reactive than zinc. This is the reason, copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
(d) Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Ans: Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals. If kept in open, they readily react with oxygen in the atmosphere. The reaction is so quick and that sodium and potassium easily catch fire when exposed to air. To prevent accidental fire, they are stored in kerosene.
Q7. Can you store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Ans: Aluminium is a metal and most of the metals react with acid to produce hydrogen gas. Lemon pickle contains acid which would react with aluminium. Hence, lemon pickle should not be stored in an aluminium pickle.
Q8. In the following Table, some substances are given in Column I. In Column II some uses are given. Match the items in column I with those in Column II.
Column I | Column II |
Gold | Thermometers |
Iron | Electric wire |
Aluminium | Wrapping food |
Carbon | Jewellery |
copper | Machinery |
Mercury | Fuel |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
Gold | Jewellery |
Iron | Machinery |
Aluminium | Wrapping food |
Carbon | Fuel |
copper | Electric Wire |
Mercury | Thermometers |
Q9. What happens when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured onto a copper plate?
(b) Iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution?
Write word equations of the reactions involved.
Ans:
(a) Copper does not react with dilute sulphuric acid. So, no reaction takes place when dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate. But when concentrated sulphuric acid is poured over the copper plate, effervescence is observed. This happens because of the formation of hydrogen gas.
Cu + H2SO4 (conc.) → CuSO4 + H2
(b) When iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution, the blue colour of copper solution is replaced by a light green colour. This happens because iron; being more reactive than copper; displaces copper from copper sulphate and makes iron sulphate.
CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu
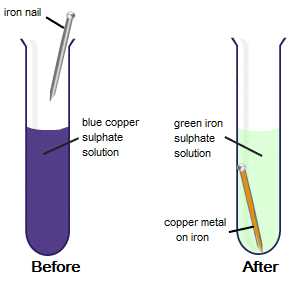 Iron Nails Dipped in Copper Sulphate Solution
Iron Nails Dipped in Copper Sulphate Solution
Q10. Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube.
(a) How will she find the nature of the gas?
Ans: For this, the evolved gas should be passed into a test tube which is filled with lime water. If the lime water turns milky, it shows that the evolved gas is carbon dioxide.
(b) Write down word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Ans: Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide↑ + Heat.
Q11. One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. Next day when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight?
Ans: The goldsmith uses a mixture of acids to clean jewellery.
 Gold Jewellery
Gold Jewellery
Gold usually doesn’t react with acids. But the mixture which is used by goldsmith is Aqua regia which can even dissolve gold. Due to this, some gold is lost during the polishing process. This explains the loss in weight.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Materials:Metals and Non-Metals
| 1. What are metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. What are the physical properties of metals? |  |
| 4. What are the physical properties of non-metals? |  |
| 5. How are metals and non-metals used in everyday life? |  |























