Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > NCERT Solutions +extra questions of ch 1 science (nutrition in plants) class 7
NCERT Solutions +extra questions of ch 1 science (nutrition in plants) class 7 PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions +extra questions of ch 1 science (nutrition in plants) class 7
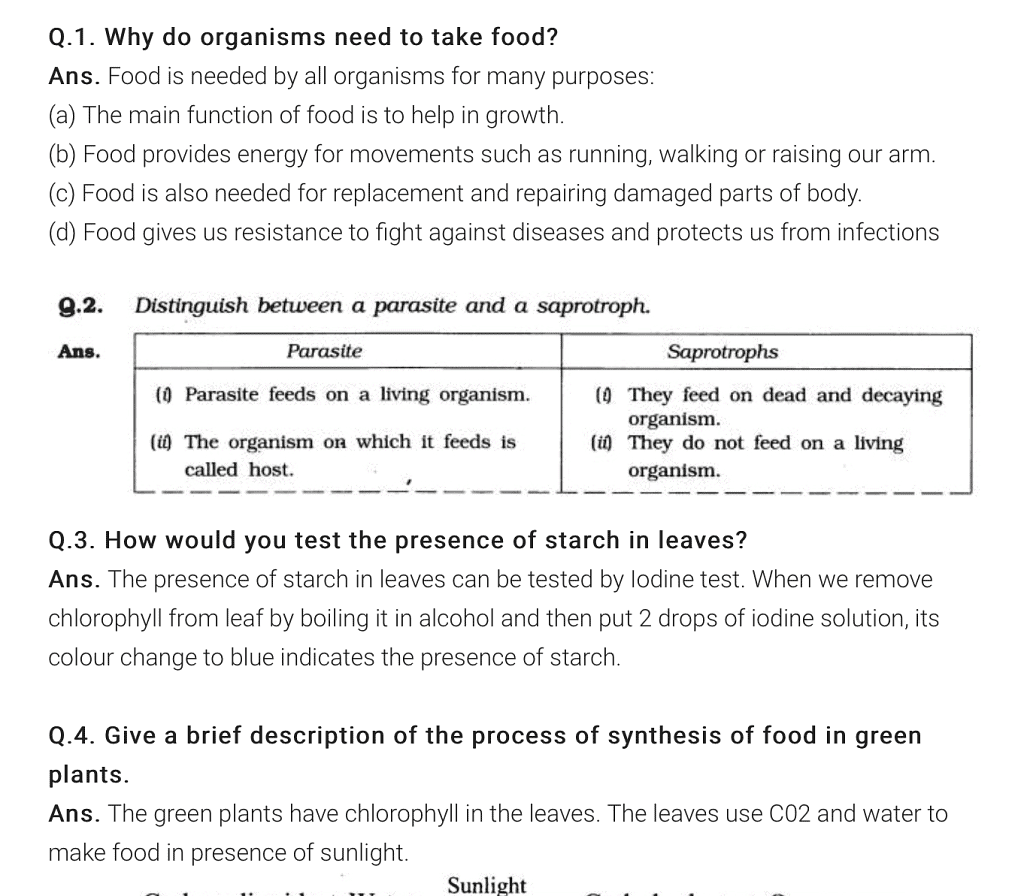
| 1. What is the process of nutrition in plants? |  |
Ans. Nutrition in plants is the process by which plants obtain and utilize essential nutrients for their growth and development. It involves the process of photosynthesis, where plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This glucose is further converted into various other organic compounds to fulfill the plant's nutritional needs.
| 2. Why is chlorophyll important for nutrition in plants? |  |
Ans. Chlorophyll is a pigment present in the chloroplasts of plant cells, responsible for capturing sunlight and initiating the process of photosynthesis. It plays a crucial role in nutrition in plants as it absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy, which is then used to produce glucose. Without chlorophyll, plants would not be able to synthesize their food and carry out essential metabolic processes.
| 3. How do plants obtain essential minerals for nutrition? |  |
Ans. Plants obtain essential minerals for nutrition from the soil. The roots of plants have root hairs that increase the surface area for absorption. When water is absorbed by the root hairs, it carries dissolved minerals with it. The minerals are then transported through the xylem vessels to different parts of the plant, where they are utilized for various metabolic processes.
| 4. What are the different modes of nutrition in plants? |  |
Ans. Plants exhibit various modes of nutrition. The primary mode is autotrophic nutrition, where plants synthesize their food through photosynthesis. However, some plants also exhibit heterotrophic nutrition, where they obtain their food from other organisms. This includes parasitic plants that obtain nutrients from host plants, saprophytic plants that obtain nutrients from dead organic matter, and insectivorous plants that capture and digest insects for nutrition.
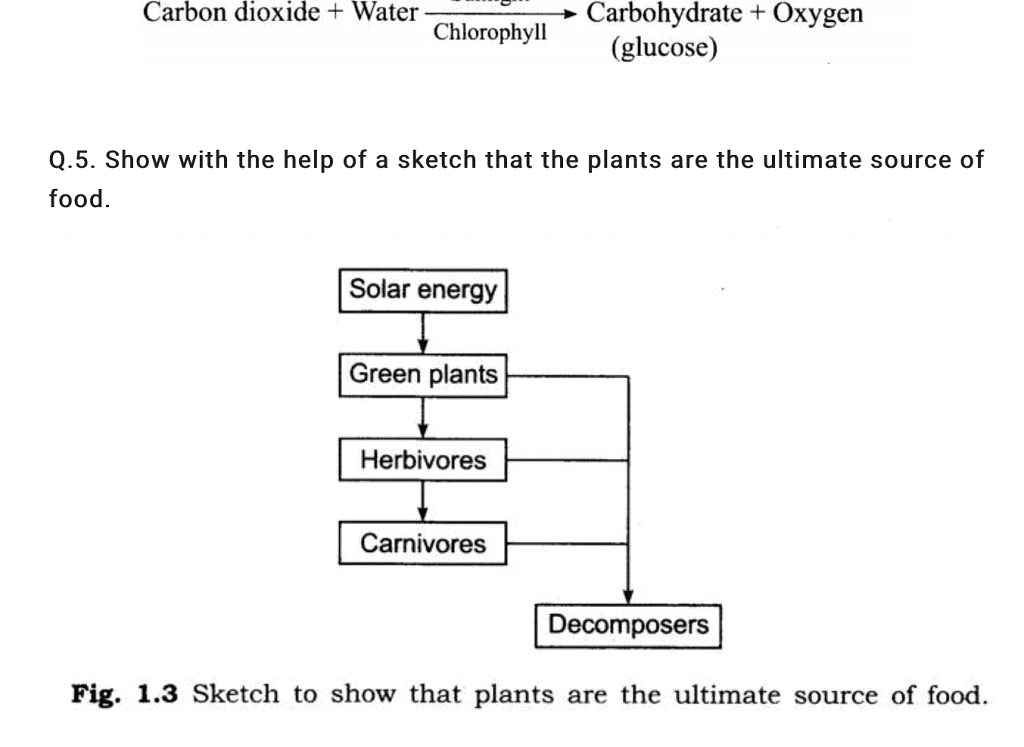
| 5. How does the process of nutrition in plants contribute to the overall ecosystem? |  |
Ans. The process of nutrition in plants is essential for the overall functioning of the ecosystem. Plants serve as primary producers, converting sunlight into chemical energy and producing oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen supports the respiration of other organisms. Additionally, plants provide food and shelter for various animals, contributing to the food chain and maintaining biodiversity in the ecosystem.
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches