NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths - Comparing Quantities - 1 (Exercise 7.1)
Try These Questions (Page No. 81)
Q1:In a primary school, the parents were asked about the number of hours they spend per day in helping their children to do homework. There were 90 parents who helped for 1/2 hour to hours. The distribution of parents according to the time for which, they said they helped is given in the adjoining figure; 20% helped for more than
hours per day; 30% helped for 1/2 hour to
hours; 50% did not help at all.
Using this, answer the following:
(i) How many parents were surveyed?
(ii) How many said that they did not help?
(iii) How many said that they helped for more than hours?
Ans:
(i) Since, 30% of total surveyed parents helped their children for "1/2 hours to hours”. And 90
parents helped their children for “ 1/2 hours to hours”.
∴ 30% [surveyed parents] = 90
or 30/100 * [surveyed parents] = 90
or surveyed parents = 90 *100/30
= 3 * 100
= 300
(ii)Since 50% of surveyed parents did not help their children.
∴ Number of parents who did not help = 50% of surveyed parents
= 50% of 300
= 50/100 * 300 = 150
(iii) Since, 20% of the surveyed parents help their children for more than hours.
i.e. 20% of surveyed parents help for more than hours.
∴ Number of parents who helped for more than hours = 20% of 300
= 20/100 * 300
= 20 * 3 = 60
Note: ‘of’ means multiplication.
Exercise 7.1
Q1: Find the ratio of the following.(a) Speed of a cycle 15 km per hour to the speed of scooter 30 km per hour.
(b) 5 m to 10 km
(c) 50 paise to ₹ 5
Sol:(a)Ratio of the speed of the cycle to the speed of the scooter = 15/30 = 1/2 = 1 : 2
(b) Since 1 km = 1000 m
5m/10 km = 5 m/(10 × 1000)m = 5/10000 = 1/2000 = 1 : 2000
The required ratio is 1 : 2000
(c) Since, ₹1 = 100 paise
50 paise/₹5 = 50/(5 × 100) = 50/500 = 1/10 = 1 : 10
The required ratio is 1 : 10
Q2: Convert the following ratios to percentages.
(a) 3 : 4
(b) 2 : 3
Sol:
(a)3 : 4 = 3/4 = 3/4 × 100% = 0.75 × 100% =75%
(b) 2 : 3 = 2/3 = 2/3 × 100% = 0.666 × 100% = 66.66% =66⅔%
Q3: 72% of 25 students are interested in mathematics. How many are not interested in mathematics?
Sol: It’s given that 72% of 25 students are good in mathematics
So, the percentage of students who are not good in mathematics = (100 – 72)% = 28%
Here, the number of students who are good in mathematics = 72/100 × 25 = 18
Thus, the number of students who are not good in mathematics = 25 – 18 = 7
[Also, 28% of 25 = 28/100 × 25 = 7]
Therefore, 7 students are not good in mathematics.
Q4:A football team won 10 matches out of the total number of matches they played. If their win percentage was 40, then how many matches did they play in all?
Sol: Number of matches won by the team = 10
∵ The team won 40% of total number of match.
∴ 40% of [Total number of match] = 10
or 40/100 * [Total number of match] = 10
Total number of matches = = 25
Thus, the total number of match played = 25
Q5:If Chameli had ₹ 600 left after spending 75% of her money, how much did she have in the beginning?
Sol: ∵ Chameli made spending of Rs 75%.
∴ She is left with Rs (100 – 75)% or Rs 25%.
But she is having Rs 600 now.
∴ 25% of total money = Rs 600
or 25/100 of total money = Rs 600
or Total money = = Rs 600 × 4
= Rs 2400
Thus, she had Rs 2400 in the beginning.
Q6: If 60% people in a city like cricket, 30% like football and the remaining like other games, then what per cent of the people like other games? If the total number of people is 50 lakh, find the exact number who like each type of game.
Sol:∵ People who like cricket = 60%
People who like football = 30%
∴ People who like other games = [100 – (60 + 30)]%
= [100 – 90]%
= 10%
Now, Total number of people = 50,00,000
∴ No. of people who like Cricket = 60% of 50,00,000 = 60/100 * 5000000
= 6 × 500000
= 30,00,000
No. of people who like Football = 30% of 5000000 = 30/100 * 5000000
= 3 × 500000
= 15,00,000
No. of people who like Other games = 10% of 5000000 = 10/100 * 5000000
= 1 × 500000
= 5,00,000
Thus, number of people who like
Cricket = 30,00,000
Football = 15,00,000
Other games = 5,00,000
Try These Questions (Page No. 83)
Q1: A shop gives 20% discount. What would the sale price of each of these be?
(a) A dress marked at ₹ 120
(b) A pair of shoes marked at ₹ 750
(c) A bag marked at ₹ 250
Ans:(a)Marked price of the dress = Rs 120
Discount rate = 20%
∴ Discount = 20% of Rs 120
= Rs 20/100 × 120
= Rs 2 × 12 = Rs 24
∴ Sale price of the dress = [Marked price] – [Discount]
= Rs 120 – Rs 24
= Rs 96
(b) Marked price of the pair of shoes = Rs 750
Discount rate = 20%
∴ Discount = 20% of Rs 750
= Rs 20/100 × 750
= Rs 2 × 75 = Rs 150
Now,
Sale price of the pair of shoes = [Marked price] – [Discount]
= Rs 750 – Rs 150 = Rs 600
(c)Marked price of the bag = Rs 250
Discount rate = 20%
∴ Discount = 20% of Rs 250
= Rs 20/100 × 250
= Rs 2 × 25 = Rs 50
∴ Sale price of the bag = [Marked price] – [Discount]
= Rs 250 – Rs 50 = Rs 200
Q2:A table marked at ₹ 15,000 is available for ₹ 14,400. Find the discount given and the discount per cent.
Ans:Marked price of the table = ₹ 15000
Sale price of the table = ₹ 14400
∴ Discount = [Marked price] – [Sale price]
= [₹ 15000] – [₹ 14400]
= ₹ 600
Discount per cent = Discount/Marked price × 100
= 600/15000 × 100%
= (2 × 2)%
= 4%
Q3:An almirah is sold at ₹ 5,225 after allowing a discount of 5%. Find its marked price.
Ans:Sale price of the almirah = ₹ 5225
Discount rate = 5%
Since, Discount = 5% of marked price
∴ [Marked price] – Discount = Sale price
or [Marked price] – 5/100 × [Marked price] = Sale price
or Marked price [1 - 5/100] = Sale price
or Marked price 95/100 = Sale price (= ₹ 5225)
or Marked price = ₹ 5225 × 100/95
= ₹ 5500
Think, Discuss, and Write Questions (Page No.84)
Q1: Two times a number is a 100% increase in the number. If we take half the number, what would be the decrease in per cent?
Sol:Let the number be x.
∴ Decrease in the number = 1/2 of x
= 1/2 of x = x/2
= 1/2 *100 % = 50%
Q2: By what per cent is ₹ 2,000 less than ₹ 2,400? Is it the same as the per cent by which ₹ 2,400 is more than ₹ 2,000?
Sol:Case I
Here 2000 < 2400.
i.e. 2400 is reduced to 2000.
∴ Decrease = 2400 – 2000 = 400
Thus Decrease % =
Thus, Decrease % =
Case II
2000 is increased to 2400.
∴ Increase = 2400 – 2000 = 400
∴ Decrease % = 400/2000 x 100% = 20%
Thus, Decrease % = 20%
Obviously, they are not the same.
Exercise 7.2
Q1: During a sale, a shop offered a discount of 10% on the marked prices of all the items. What would a customer have to pay for a pair of jeans marked at ₹ 1450 and two shirts marked at ₹ 850 each?
Sol:Total marked price = ₹ (1,450 + 2 × 850)
= ₹ (1,450 +1,700)
= ₹ 3,150
Given that, the discount percentage = 10%
Discount = ₹ (10/100 x 3150) = ₹ 315
Also, Discount = Marked price − Sale price
₹ 315 = ₹ 3150 − Sale price
∴ Sale price = ₹ (3150 − 315)
= ₹ 2835
Therefore, the customer will have to pay ₹ 2,835.
Q2: The price of a TV is ₹ 13,000. The sales tax charged on it is at the rate of 12%. Find the amount that Vinod will have to pay if he buys it.
Sol:On ₹ 100, the tax to be paid = ₹ 12
Here, on ₹ 13000, the tax to be paid will be = 12/100 × 13000
= ₹ 1560
Required amount = Cost + Sales Tax
= ₹ 13000 + ₹ 1560
= ₹ 14560
Therefore, Vinod will have to pay ₹ 14,560 for the TV.
Q3: Arun bought a pair of skates at a sale where the discount given was 20%. If the amount he pays is ₹ 1,600, find the marked price.
Sol:Let the marked price be x
Discount percent = Discount/Marked Price x 100
20 = Discount/x × 100
Discount = 20/100 × x
= x/5
Also,
Discount = Marked price – Sale price
x/5 = x – ₹ 1600
x – x/5 = 1600
4x/5 = 1600
x = 1600 x 5/4
= 2000
Therefore, the marked price was₹ 2000.
Q4: I purchased a hair-dryer for ₹ 5,400 including 8% VAT. Find the price before VAT was added.
Sol:The price includes VAT
So, 8% VAT means that if the price without VAT is ₹ 100,
Then, the price including VAT will be ₹ 108
When price including VAT is ₹ 108, original price = ₹ 100
When price including VAT is ₹ 5400, original price = ₹ (100/108 × 5400)
= ₹ 5000
Therefore, the price of the hair dryer before the addition of VAT was ₹ 5,000.
Q5: An article was purchased for ₹ 1239 including GST of 18%. Find the price of the article before GST was added?
Sol:Let the Price of the article before including GST be x
Price of article including GST = ₹ 1239
GST(Goods and Service Tax) = 18 % of x = (18 × x) = 0.18 × x
∴ Price of article including GST = Price before GST + GST
⇒ x + (0.18x) = 1239
⇒ 1.18x = 1239
∴ x = 1239/1.18 = ₹ 1050
So, the price of article before GST was added= ₹ 1050.
Try These Questions (Page No. 85)
Q1: Find interest and amount to be paid on rupees 15000 at 5% per annum after 2 years
Sol:Formula for Simple Interest: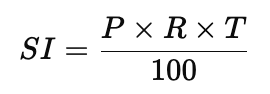
Substituting all the given values in formula, we get : 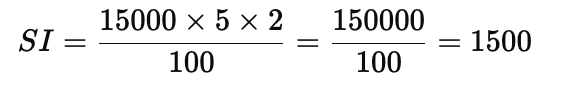
Total Amount to be Paid: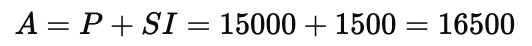
Therefore , 
Try These Questions (Page No. 85)
Q1: Find CI on a sum of rupees 8000 for 2 years at 5% per annum compounded annually.
Sol: Formula for Total Amount: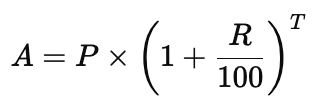
Where:
- 8000 (Principal)
- (Rate of Interest per annum)
- 2 years (Time)
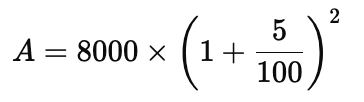
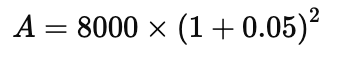
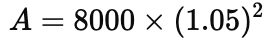
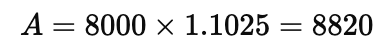
Calculate Compound Interest (CI)
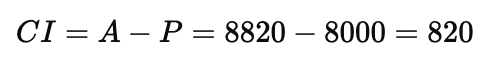
therefore, 
Exercise: 7.3
Q1: The population of a place increased to 54,000 in 2003 at a rate of 5% per annum.
(i) Find the population in 2001.
(ii) What would be its population is 2005?
Sol:Population in 2003 is P = 54000
(i) Let the population in 2001 (i.e. 2 years ago) = P
Since rate of increment in population = 5% p.a.
∴ Present population 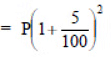
or 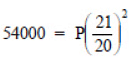
or 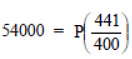
or 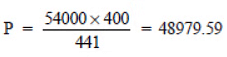
= 48980 (approx.)
Thus, the population in 2001 was about 48980.
(ii) Initial population (in 2003), i.e. P = 54000
Rate of increment in population = 5% p.a.
Time = 2 years ⇒n = 2
∴ 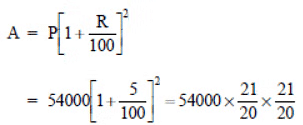
= 135 * 21 * 21 = 59535.
Thus, the population in 2005 = 59535.
Q2:In a laboratory, the count of bacteria in a certain experiment was increasing at the rate of 2.5% per hour. Find the bacteria at the end of 2 hours if the count was initially 5,06,000.
Sol:Initial count of bacteria (P) = 5,06,000
Increasing rate (R) = 2.5% per hour
Time (T) = 2 hour. ⇒ n = 2
∵ 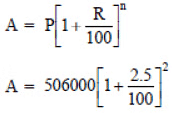
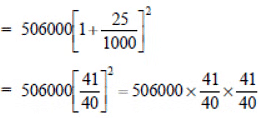
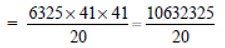
= 531616.25 or 531616 (approx.)
Thus, the count of bacteria after 2 hours will be 531616 (approx.).
Q3:A scooter was bought at ₹ 42,000. Its value depreciated at the rate of 8% per annum. Find its value after one year.
Sol: Initial cost (value) of the scooter (P) = Rs 42000
Depreciation rate = 8% p.a.
Time = 1 year ⇒ n = 1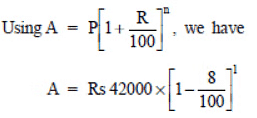
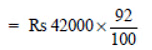
= ₹ 420 × 92 = ₹ 38640
Thus, the value of the scooter after 1 year will be ₹ 38640.
Try These Questions (Page No. 90)
Q1: Machinery worth Rs 10,500 depreciated by 5%. Find its value after one year.
Sol:Here, P = Rs 10,500, R = –5% p.a., T = 1 year, n = 1
∵ 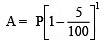 [∵ Depreciation is there, ∴ r = –5%]
[∵ Depreciation is there, ∴ r = –5%]
∴ 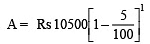
= Rs10500 * 19/20
= Rs 525 * 19 = Rs 9975.
Thus, machinery value after 1 year = Rs 9975
Q2: Find the population of a city after 2 years, which is at present 12 lakh, if the rate of increase is 4%
Sol:Present population, P = 12 lakh
Rate of increase, R = 4% p.a.
Time, T = 2 years
∴ Population after 2 years = 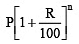
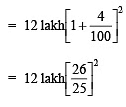
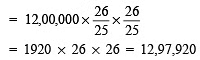
Thus, the population of the town will be 12,97,920 after 2 years.
Note: For depreciation, we use the formula as
|
81 videos|423 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths - Comparing Quantities - 1 (Exercise 7.1)
| 1. What are the main concepts covered in Exercise 7.1 of Comparing Quantities? |  |
| 2. How can I calculate the percentage increase or decrease based on the questions in Exercise 7.1? |  |
| 3. What strategies can I use to solve the profit and loss problems in Exercise 7.1? |  |
| 4. How is simple interest calculated in the context of Exercise 7.1? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand comparing quantities in daily life? |  |