NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 - Gravitation
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 102 |

|
| Page No. 104 |

|
| Page No. 106 |

|
| Page No. 109 |

|
| Page No. 110 |

|
| Page No. 111 |

|
| Page No. 112 |

|
Page No. 102
Q1. State the universal law of gravitation.Ans: Everybody in this universe attracts every other body with a force, which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres.
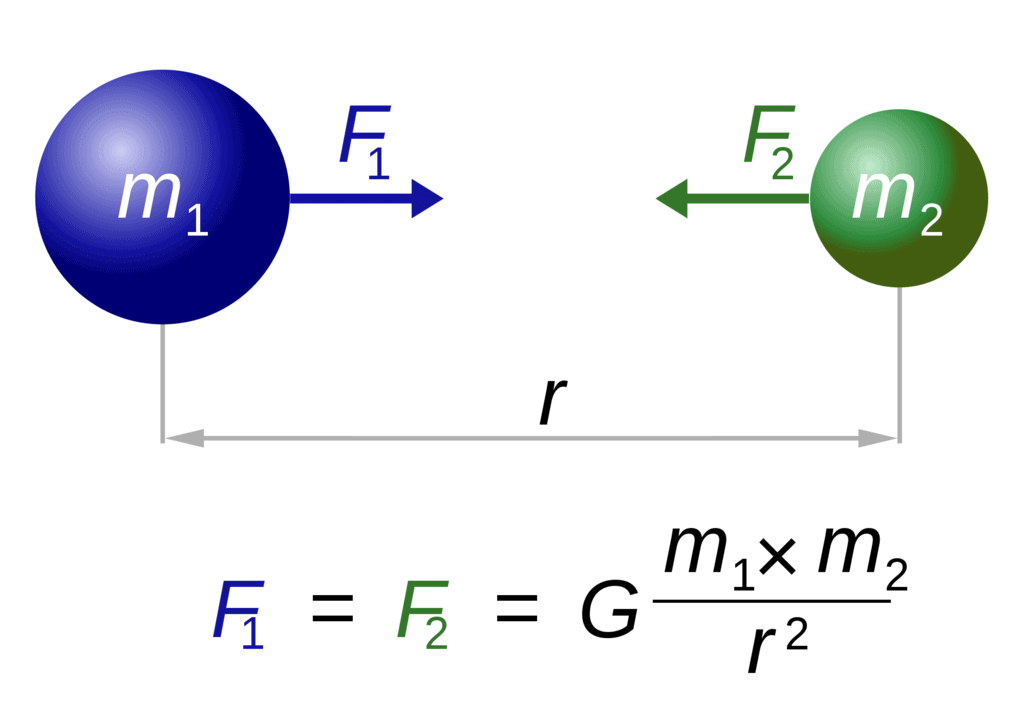 Universal Law of GravitationQ2. Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.
Universal Law of GravitationQ2. Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.Ans: Consider F as the force of attraction between an object on the surface of the earth and the earth.
Let the mass of earth = M
Mass of object = m.
If the radius of the object is comparatively negligible, r ≈ radius of earth = R
F = GMm/R2
Page No. 104
Q1. What do you mean by free fall?
Ans: When an object falls with a constant acceleration, under the influence of the force of gravitation of the Earth, the object is said to have a free fall.
Q2. What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity?
Ans: During the course of its free fall, a body accelerates due to the force of gravity acting on it. This acceleration is known as acceleration due to gravity.
Page No. 106
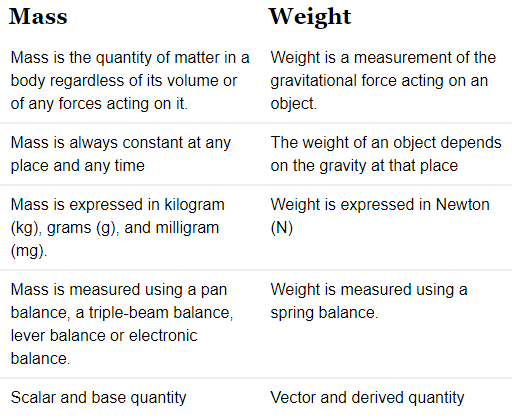
Q1. What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight?
Ans:
Q2. Why is the weight of an object on the moon 1/6th its weight on the Earth?
Ans:
Mass of the moon (M) = 7.4 × 1022 kg
The radius of the moon (R) = 1.74 × 106 m
Gravitational constant (G) = 6.7 × 1011 Nm2kg2
We know that acceleration due to gravity(g) = GM/R2
Also, weight, W = mg
W = GMm/R2
Let the mass of the object be m, let its weight of the moon be Mm and its radius be Rm
By applying the universal law of gravitation, the weight of the object on the moon will be:
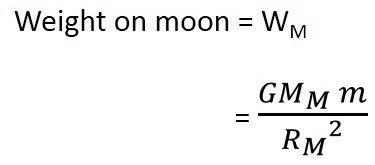 (1)
(1)
Let the weight of the same object on the earth be We. The mass of the earth is M and its radius is R.
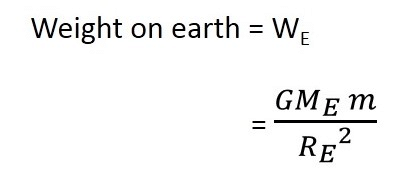 (2)
(2)
Substituting the values in equations (1) and (2) we get:
Wm= 2.431 x 1010G x m
and We = 1.474 x 1011 G x m
On dividing Wm and We we get:

∴ The weight of the object on the moon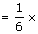 its weight on Earth
its weight on Earth
Page No. 109
Q1. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
Ans:
- It is difficult to hold a school bag having a thin strap because the pressure on the shoulders is quite large.
- This is because the pressure is inversely proportional to the surface area on which the force acts.
- The smaller is the surface area; the larger will be the pressure on the surface. In the case of a thin strap, the contact surface area is very small. Hence, the pressure exerted on the shoulder is very large.
Q2. What do you mean by buoyancy?
Ans:
- The upward force exerted by a liquid on an object immersed in it is known as buoyancy.
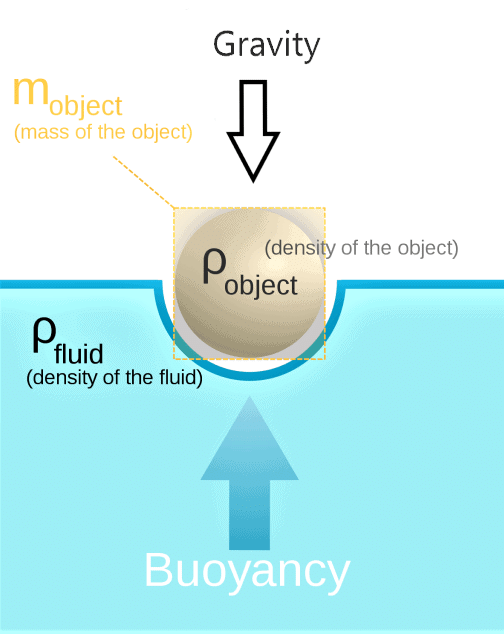
- When you try to immerse an object in water, then you can feel an upward force exerted on the object, which increases as you push the object deeper into water.
Q3. Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water?
Ans:
- If the density of an object is more than the density of the liquid, then it sinks in the liquid.
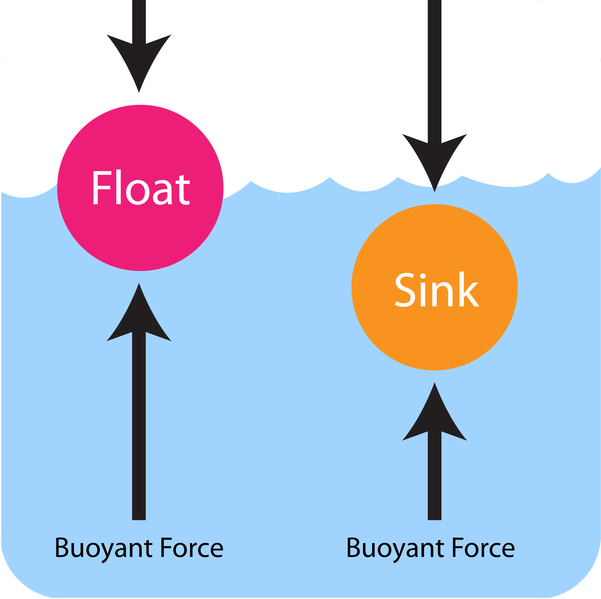
- This is because the buoyant force acting on the object is less than the force of gravity.
- On the other hand, if the density of the object is less than the density of the liquid, then it floats on the surface of the liquid.
- This is because the buoyant force acting on the object is greater than the force of gravity.
Page No. 110
Q1. You find your mass to be 42 kg on a weighing machine. Is your mass more or less than 42 kg?
Ans: Mass is always a constant quantity. Therefore, it cannot be more or less than 42 kg.
Q2. You have a bag of cotton and an iron bar, each indicating a mass of 100 kg when measured on a weighing machine. In reality, one is heavier than other. Can you say which one is heavier and why?
Ans: The correct answer is cotton bag is heavier than an iron bar.
The reason is:
True weight = (apparent weight + up thrust)
- The density of the cotton bag is less than that of the iron bar, so the volume of the cotton bag is greater than the iron bar. So the cotton bag experiences more upthrust due to the presence of air.
- Therefore in the presence of air, the true weight of a cotton bag is greater than the true weight of an iron bar.
Page No. 111
Q1. How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half?
Ans: The force of gravitation between two objects of masses m1 and m2 at separation r is given by:
F = (G m1m2)/r2
When the distance between them is reduced to half, the gravitational force.
F' = (G m1m2)/r2
= (G m1m2)/ (r/2)2
= (4 G m1m2)/(r2) = 4F
The gravitational force becomes four times.
Q2. Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object?
Ans: The acceleration due to gravity of a freely falling body is independent of the mass of the falling body. Thus, both heavy and light objects fall with the same acceleration.
Q3. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 106 m.)
Ans: Here, the mass of the earth, M = 6 x 1024 kg
Mass of the object, m = 1 kg, radius of the earth, R = 6.4 x 106 m, G = 6.7 x 10-11 Nm2kg-2
The magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and the object is given by:
The force of gravitation between them,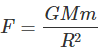
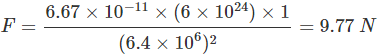
Q4. The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller force or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
Ans:
- Earth attracts the moon with an equal and opposite force as the moon attracts the Earth.
- This is in accordance with Newton’s law of gravitation according to which gravitational force is the mutual force of attraction which is also equal as per to the third law of motion.
Q5. If the moon attracts the Earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
Ans:
- The moon revolves around the earth because the gravitational force of the earth on the moon provides the necessary centripetal force for circular motion.
- The moon also attracts the earth, due to which the earth also revolves around the moon in a circular orbit, but due to the very large mass of the earth, the motion of the earth is not observed.
- It may be kept in mind that there is no linear motion of Earth towards the moon or the moon towards Earth. The gravitational force between them keeps on changing the direction of motion of the moon or earth in a circular orbit.
Q6. What happens to the force between two objects, if
(a) the mass of one object is doubled?
(b) the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
(c) the masses of both objects are doubled?
Ans: Let masses = m1 and m2, the distance between masses = r.
According to the universal law of gravitation F ∝ m1m2 and F ∝ 1/r2.
(a) If one mass, say m1 is doubled, and F ∝ m1, then F gets doubled.
(b) If distance is doubled and F ∝ 1/r2, force becomes one-fourth, i.e. 1/(2)2.
If the distance is tripled and F ∝ 1/r2, force becomes one-ninth, i.e. 1/(3)2.
(c) If both masses are doubled and F ∝ m1m2, force becomes 4 times, i.e. (2m1)(2m2) = 4m1m2
Q7. What is the importance of universal law of gravitation?
Ans: The universal law of gravitation has successfully explained the phenomena that were earlier considered to be separate:
(a) It explains the force which holds us on earth.
(b) It explains the motion of planets around the sun.
(c) It explains the motion of the moon around the Earth.
(d) It explains the occurrence of tides in the ocean.
Q8. What is the acceleration of free fall?
Ans: When a body falls freely and accelerates at every point of its motion due to gravitational force alone. This is called the acceleration of free fall. This acceleration is known as the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface. It’s denoted by ‘g’, and its value is 9.8m/s2, and it’s constant for all objects close to the earth’s surface (irrespective of their masses).
Q9. What do we call the gravitational force between the earth and an object?
Ans: Gravity is the name of the gravitational force between the earth and the object.
Q10. Amit buys few grams of gold at the poles as per the instruction of one of his friends. He hands over the same when he meets him at the equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why? [Hint: The value of g is greater at the poles than at the equator.]
Ans: Earth is not a perfect sphere. It is flattened at the poles. Thus, the value of ‘g’ is greater at the poles than at the equator (as g ∝ 1/r2). This means the weight of gold bought at the poles becomes lesser at the equator, and the friend does not agree with the weight.
Q:11. Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
Ans:
- A sheet crumpled into a ball has a small surface area as compared to that of an unfolded sheet. Therefore, the unfolded sheet will experience more friction due to air as compared to the crumpled ball in spite of the same force of gravity acting upon it.
- The larger friction of air slows down the unfolded sheet so it will fall slower than the sheet crumpled into a ball.
Q12. Gravitational force on the surface of the moon is only 1/6 as strong as gravitational force on the earth. What is the weight in newtons of a 10 kg object on the moon and on the earth?
Ans: Here, mass of object, m = 10 kg, g on the earth’s surface = 9.8 ms-2
Weight of the object on the earth’s surface = mg
= 10 kg x 9.8 ms-2
= 98.0 kg ms-2 = 98 N
The weight of an object on the moon is 1/6th that of the object on Earth, so the weight of the object on the moon:
= 1/6 x 98 N= 16.34 N.
Page No. 112
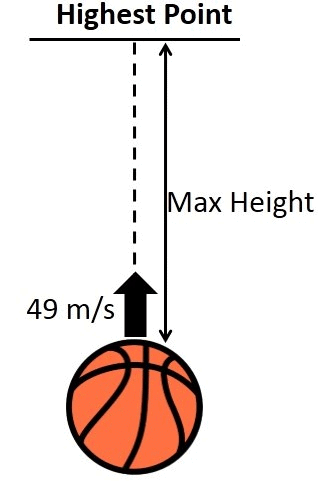
Q13. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 m/s. Calculate
(a) the maximum height to which it rises.
(b) the total time it takes to return to the surface of the earth.
Ans:
(a) Initial velocity, u = 49 ms-1, Final velocity, v = 0
Maximum height, H = ?
Acceleration due to gravity, g = + 9.8 ms-2 (downward)
 As object is moving upward, so a = -gFrom relation v2 = u2 + 2as , we have a = -g , s = H
As object is moving upward, so a = -gFrom relation v2 = u2 + 2as , we have a = -g , s = H
v2 = u2 - 2gH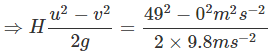
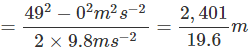
⇒ H = 122.5 m
(b) When the ball returns to the surface of the earth, displacement, s = 0
∴ Relation, s = ut + 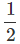 at2 gives s = ut -
at2 gives s = ut -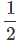 gt2
gt2
0 = (49 ms-1) t -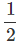 x 9.8 t2
x 9.8 t2
⇒ t (49 -4.9 t) = 0
t = 0 or 49 - 4.9 t = 0 ⇒ t =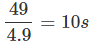
As t ≠ 0, so t = 10s
The maximum height is 122.5 m and the total time is 10 s.
Q14. A stone is released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 m. Calculate its final velocity just before touching the ground.
Ans: Initial velocity, u = 0, height, h = 19.6 m and g = 9.8 ms-2
Final velocity,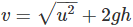
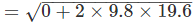
= 19.6 ms-1.
Q15. A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Taking g = 10 m/s2, find the maximum height reached by the stone. What are the net displacement and the total distance covered by the stone?
Ans: Initial velocity, u = 40 ms-1
g = -10 ms-2 (upward motion)
Final velocity, v = 0
During upward motion, g = -10 ms-2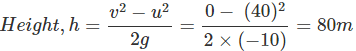
Net displacement on returning back = zero
Total distance = 80 m + 80 m = 160 m
Q16. Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 1011 m.
Ans: Mass of earth, Me = 6 x 1024 kg
Mass of sun Ms = 2 x 1030 kg and
Distance, r = 1.5 x 1011 m
Gravitational constant, G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2
Force, 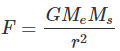
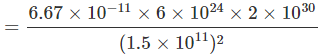
= 3.56 x 1022 N
Q17. A stone is allowed to fall from the top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time, another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Calculate when and where the two stones will meet.
Ans: u1 = 0
Let the stones meet at a height h above the ground. Stone 1 covers a distance (100 - h); g = 10 m/s2.
(100 - h) = 0 + 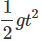
⇒ 100 - h = 5 t2 ...(i)
u2 = 25 m/s
Stone 2 covers a distance h
g = - 10m/s2
h = u2t - 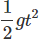
⇒ h = 25 t - 5 t2 ...(ii)
From (i) and (ii), we get
100 - 25 t + 5 t2 = 5 t2
100 - 25 t = 0
or t = 4 s (Stones meet 4 s after they are thrown)
h = 25(4) - 5(4)2 = 100 - 80 = 20 m above the ground.
Q18. A ball thrown up vertically returns to the thrower after 6s. Find
(a) the velocity with which it was thrown up.
(b) the maximum height it reaches.
(c) its position after 4s.
Ans:
Time of ascend = Time of descending
⇒ Time taken to reach the top, t = 3 s.
⇒ Final velocity, v = 0, g = -9.8 ms-2.
(a) Initial velocity, u = v - gt = 0 - (-9.8) (3)
= 29.4 ms-1
(b) Maximum height reached, h = (v2 - u2)/g = (29.4)2/(2 x 9.8)
= 44.1 m
(c) After 4s, the ball has started falling and has fallen by some distance h' for 1s.
Here, initial velocity u' = 0, t = 1s
g = + 9.8 ms-1
h' = u't + 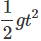 = 0 +
= 0 + 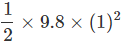
The ball is at a height, (44.1 - 4.9) = 39.2 m above the ground.
Q19. In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
Ans: An object immersed in a liquid experiences buoyant force in the upward direction.
Q20. Why does a block of plastic released under water come up to the surface of water?
Ans:
- Two forces act on an object immersed in water. One is the gravitational force, which pulls the object downwards, and the other is the buoyant force, which pushes the object upwards.
- If the upward buoyant force is greater than the downward gravitational force, then the object comes up to the surface of the water as soon as it is released within the water.
- Due to this reason, a block of plastic released under water comes up to the surface of the water.
Q21. The volume of 50g of a substance is 20 cm3. If the density of water is 1g cm-3, will the substance float or sink?
Ans:
- If the density of an object is more than the density of a liquid, then it sinks into the liquid. On the other hand, if the density of an object is less than the density of a liquid, then it floats on the surface of the liquid.
- Here, the density of the substance =
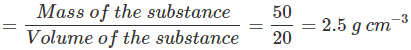
- The density of the substance is more than the density of water (1 g cm−3). Hence, the substance will sink in water.
Q22. The volume of a 500 g sealed packet is 350 cm3. Will the packet float or sink in water if the density of water is 1 g cm-3? What will be the mass of the water displaced by this packet?
Ans:
- Density of the 500 g sealed packet
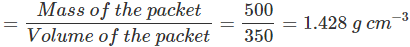
- The density of the substance is more than the density of water (
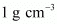 ). Hence, it will sink in water.
). Hence, it will sink in water. - The mass of water displaced by the packet is equal to the volume of the packet, i.e., 350 cm3 of water has a mass of 350 g.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 - Gravitation
| 1. What is the law of universal gravitation? |  |
| 2. How does gravitational force affect objects on Earth? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the strength of gravitational force between two objects? |  |
| 4. Why do planets orbit the Sun? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the gravitational constant (G)? |  |





















