Natural Resources | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Natural Resources? |

|
| The Breath of Life: Air |

|
| Water: A Wonder Liquid |

|
| Soil |

|
What are Natural Resources?
The materials present in natural environment and useful to living organisms are called natural resources.
A resource satisfies human wants. Water, air, sunshine, land, soil, forests, wildlife, fishes, minerals and power resources all are useful to man. All basic needs of food, shelter and clothing are supplied by natural resources on earth. 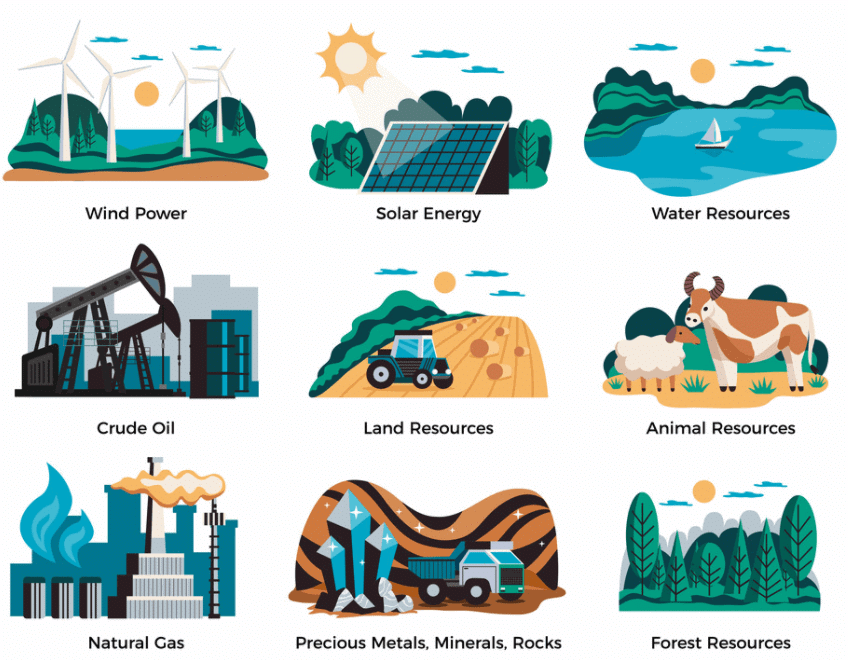 Natural Resources
Natural Resources
- Natural resource includes the total natural environment, that is the entire surface layer of the earth because all parts of earth's surface are of some use to man in they contribute to the production of necessities and comforts of mankind.
- The word resource is used for "means of supplying a material generally held in reserve".
- The resources available on earth include land (Lithosphere), water (Hydrosphere) and Air (Atmosphere).
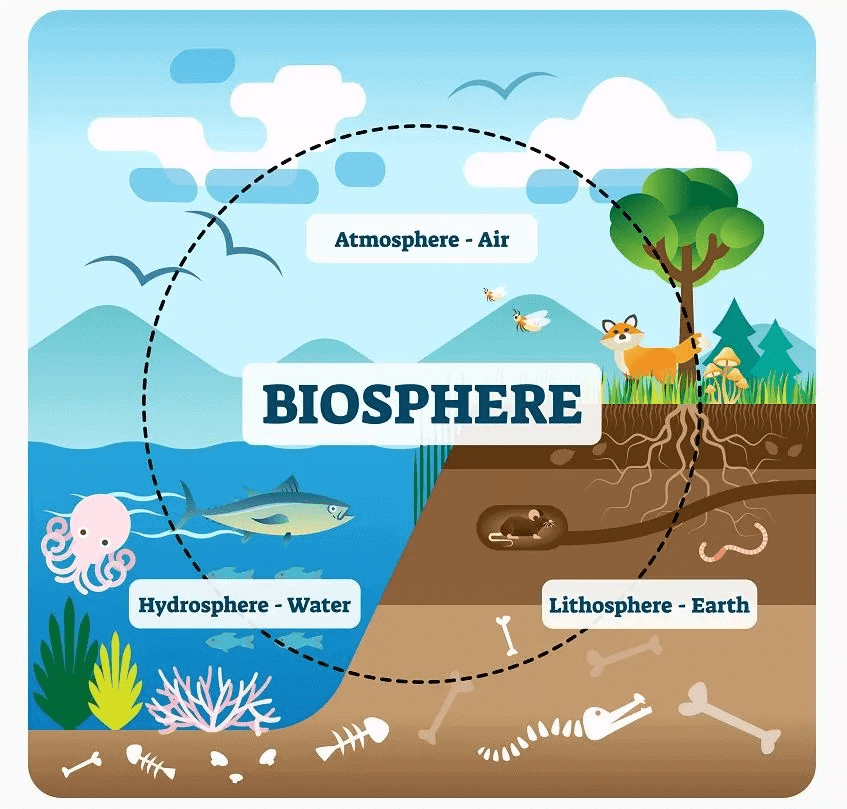
- Probably, the earth is the only planet on which life exists.
- Life exists on earth because it has all the physical conditions necessary for sustaining it. An ambient temperature, water and food are the basic need of all life forms. These basic needs of the life forms are to be met by the resources available on the earth and the energy from the sun.
- The outer crust of the earth is called lithosphere.
- The water present on the earth's surface and underground constitute hydrosphere.
- The air that covers the whole of the earth like a blanket is called atmosphere.
- About 75% of the earth's surface is covered with water.
- The life-sustaining zone of the earth where the lithosphere, the hydrosphere and the atmosphere interact and make life possible is called the biosphere.
Differences between Renewable and Non-renewable Resources
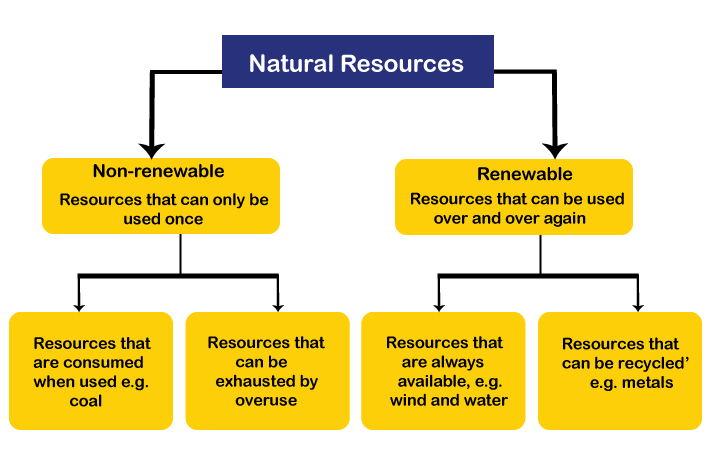
Renewable Resources
- Exhaustible resources which can be regenerated or recycled within reasonable time.
- Can be made to last indefinitely if used judiciously.
- Availability can be enhanced by increasing their capability of regeneration extraction.
Examples: Ground water, Wildlife, Grasslands, Forests.
Non-renewable Resources
- Exhaustible resources which cannot be regenerated or recycled in reasonable time.
- Will get exhausted whether or not used judiciously.
- Availability can be enhanced by increased but it will cause early depletion
Examples: Minerals, Fossil fuels like coal & Soil fertility and petroleum.
Differences between Inexhaustible and Exhaustible Resources
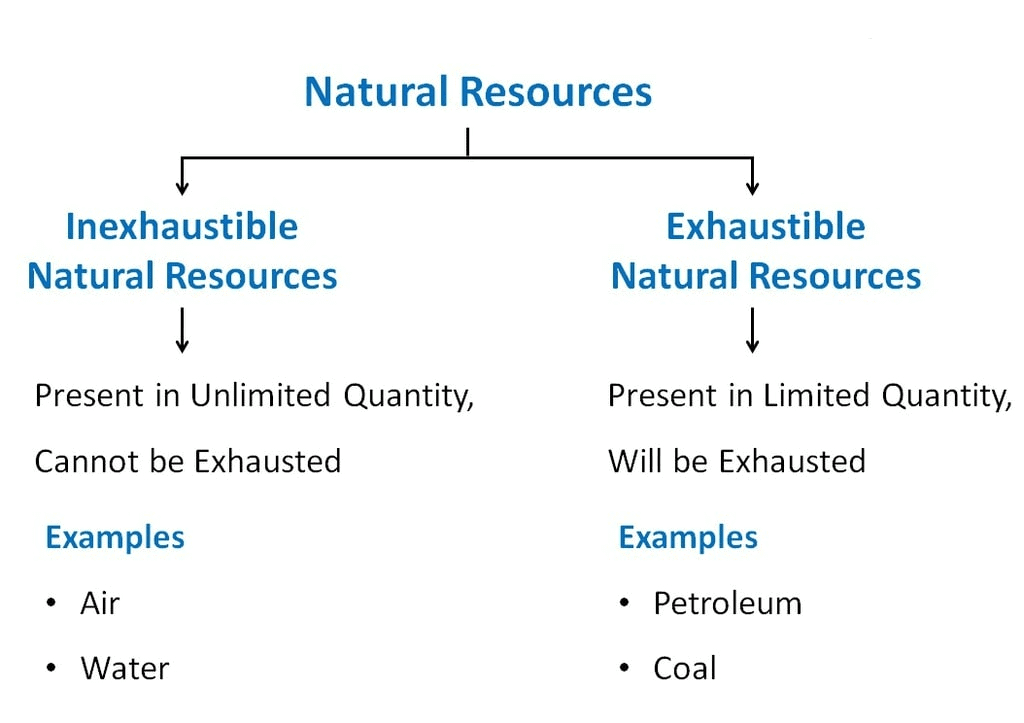
Inexhaustible
- These resources have no chance of getting exhausted.
- These resources are unlimited e.g. wind energy, solar energy, hydropower, tidal energy etc.
Exhaustible
- These resources have every chance of getting exhausted.
- These resources are limited, e.g. coal, petroleum, forests etc.
The Breath of Life: Air
- Air is a mixture of many gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and some others present in the atmosphere.
- Air is an important inexhaustible natural resource.
- Nitrogen and oxygen are the major components of the air.
N2 - 78%
O2 - 20.9%
Other gases - 1%
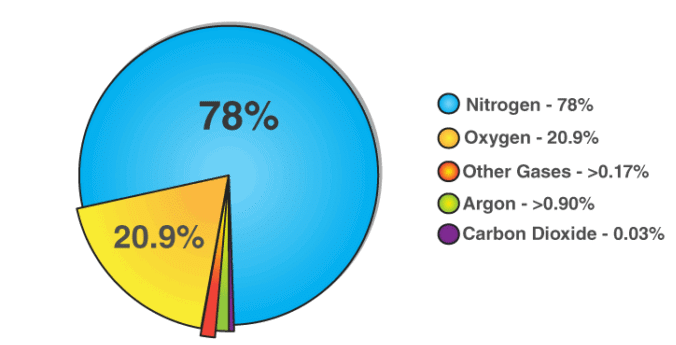 Composition of Air
Composition of Air
- Venus and Mars
CO2 → 95 -97% of the atmosphere. That's why no life on these planets
CO2 in Earth atmosphere - 0.03%
Small amount of water vapours, dust, salts, smoke is also found.
Importance of Air/Atmosphere
- It is essential for the survival of life. It supplies oxygen for respiration of all living organisms and carbon dioxide for the photosynthesis in green plants.
- Air (oxygen) is essential for burning and making fire.
- Air acts as a medium for locomotion of flying animals : insects, birds, bats etc.
- Air maintains the temperature of the earth.
- Air helps in the dispersal of spores, pollen grains, seeds and fruits.
The Role of the Atmosphere in the Climate Control
- The atmosphere covers the earth like blanket.
- Since, the air is a bad-conductor of heat, the atmosphere keeps the average temperature of the earth fairly constant during the day and also during the course of the whole year.
- The atmosphere acts as a buffer.
- The day and night temperatures show a great difference where atmosphere is absent.
- Moon → temperature range → -190° C to 110°C.
Activity
- Aim
To show the possible directions in which hot and cold air move. - Procedure
Take a candle. Fix it in a beer and light it as in figure.
Take one incense stick. Light it and bring it to the mouth of beaker. - Result
Note the result with following actions:
(i) Which way smoke flows, when incense stick is brought near the margin of
beaker's mouth ?
(ii) Tell the direction of smoke when incense stick is brought little above the burning candle.
(iii) Which way smoke flows when incense stick is taken to other areas
Give the possible reasons.
Movement of Air in Coastal Regions
- In coastal regions, the air above the land gets heated faster than the air over the sea.
- The heated air over the land rises up and creates a region of low pressure.
- The movement of air from one region to the other creates winds. Thus, the direction of the wind would be from the sea to the land during the day time.
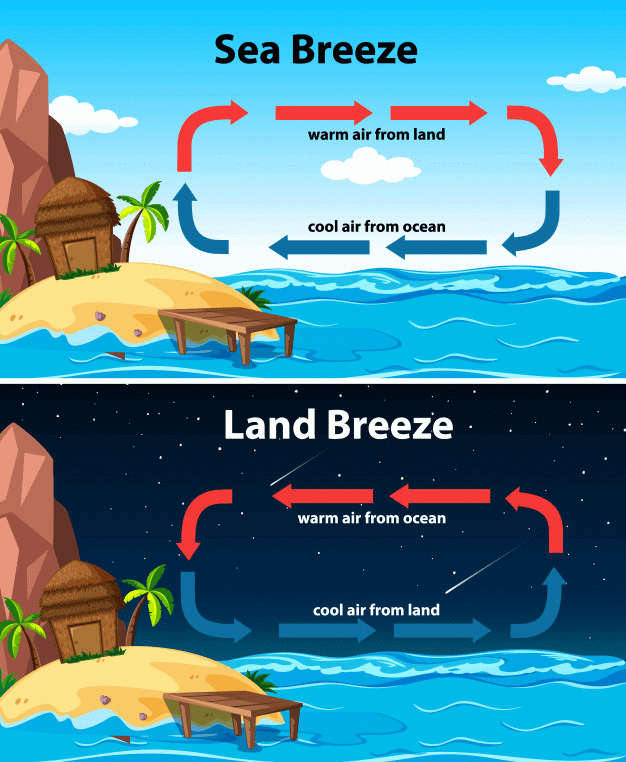 Movement of Air during Day and Night
Movement of Air during Day and Night
- After the sunset, both land and sea start to cool. The water cools slower than the land. Consequently, the air above water would be warmer than the air above the land. This, would cause blowing of winds from land to the sea.
Water: A Wonder Liquid
- Water is a basic human need.
- About 3/4 of the earth surface is occupied by water.
- Most of the water on earth's surface (about 97.5%) is found in seas and oceans. It is strongly alkaline.
- The rest (2.5%) is fresh water
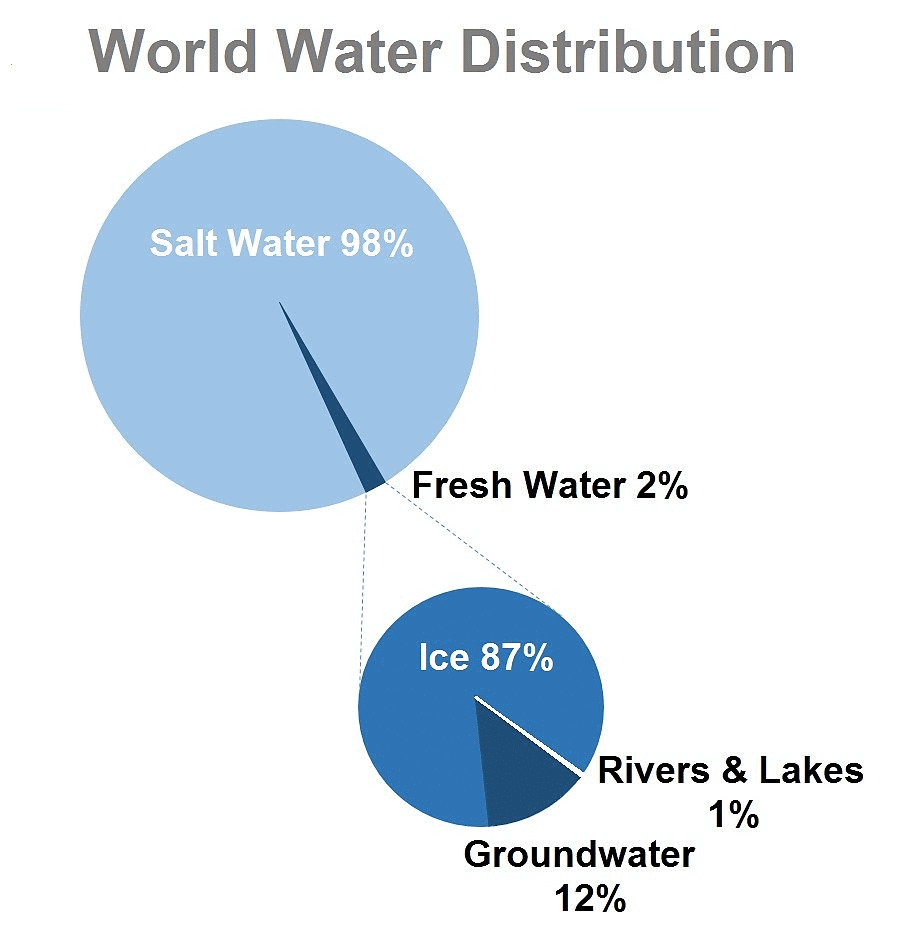
Importance of water to the living organisms
No life can exist without water because of:
- All cellular processes take place in a water medium.
- Water is essential for the process of digestion.
- Water helps in maintaining body temperature.
- All the biochemical reactions that take place within our body and within the cells occur between the substances that are dissolved in water.
- Substances are also transported from one part of the body to the other in dissolved form. Hence, organisms need to maintain the level of water within their bodies in order to stay alive.
- Water is also required for cooking, cleaning, irrigation, in industries and generating electricity.
- Terrestrial life-forms require fresh water because their bodies cannot tolerate or get rid of the high amounts of dissolved salts in saline water.
Therefore, water sources must be easily accessible for animals and plants to survive on land.
Soil
Definition
- Soil is a portion of earth's a surface consisting of disintegrated rock and decaying organic material.
- It provides support for many plants and animals. Thickness of soil on the earth's surface ranges from a few millimeters to 34 meters.
- Terrestrial plants depends for their nutrients, water supply and anchorage upon the soil. Even for the aquatic plants, the solid is important as chief storage of all the nutrients which are made available to the water medium.
Mineral Riches in the Soil
- Our planet earth has three distinct regions innermost core region (about 2200 miles in thickness), middle mantle region (about 1800 miles in thickness) and the outermost crust region (about 2025 miles in thickness). The outermost crust region has huge rocks containing variety of bound minerals, some of which become available to us.
- About one-fifth of the surface of the earth is exposed solid and distinct from oceans, lakes etc. It is called the land. The top surface layer of this exposed, solid part of crust capable of supporting plant growth is called soil. Over millions of years of long periods of time, the rocks at or near the surface of the earth are broken down by various physical, chemical and some biological processes to form fine soil particles.
- Soil is a dynamic layer in which many complex physical, chemical and biological activities are going on constantly. It is and important resource that decides the diversity of life in an area.
- The soil is a complex mixture. It consists of five components:
(i) Mineral matter = 45%
(ii) Organic matter = 5%
(iii) Water = 25%
(iv) Air = 25%
(v) Living organisms.
All these components are essential for proper plant growth.
Soil Profile
- Soil profile shows four distinct layers, called Horizons.
- Horizon A is the topsoil. It is darker and of a looser texture than the underlying horizon B. Plant and animal matter collects at the surface of this horizon, forming the litter. Below the litter is the humus, i.e., organic matter undergoing decay by microbial action. The rest of the horizon is rich in organic and mineral contents.
- The Horizon B has soil particles smaller and usually more compacted than in the horizon C. Minerals brought by rain water from the upper horizon accumulate in this horizon.
- Horizon C consists of the weathered material derived from the intact parent rock.
- The parent rock forms the Horizon R.
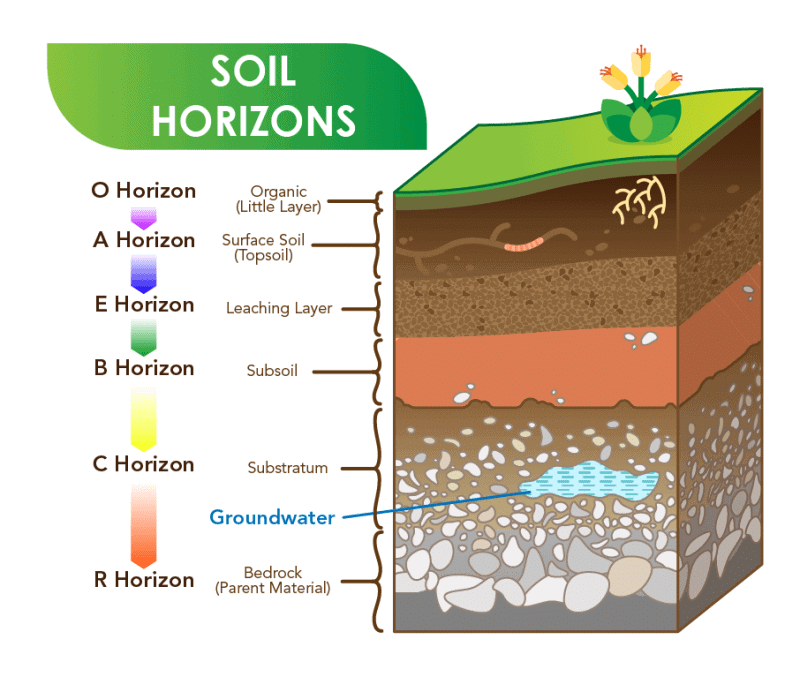
- Humus is partially decayed organic matter. It makes the soil porous, there by increasing its air and water holding capacity. Humus is rich in nutrients that promote plant growth. Being black, it absorbs heat to warm up the soil.
Composition of Top Soil
Soil particles differ in their size, look and texture.
Mainly four types of soil particles are commonly found in top soil. These are:
- Gravels: These are large particles having size of greater than 2 mm in diameter. These can be easily picked up by hands.
- Sand particles: These are still smaller in size ranging between 0.005 mm to 2 mm. These are rough to touch and can be seen with naked eye.
- Silt particles: These are still smaller in size ranging between 0.005 mm to 0.05 mm in diameter.
- Clay particles: These are the smallest soil particles having size less than 0.005 mm.
Types of Soils
Depending upon the presence of relative amounts of soil particles, soils are classified into the following three types:
- Sandy soil: It contains very large proportion of sand particles and very small quantity of silt and clay. Since sand particles are relatively larger in size, this soil can not hold much water. It is found in deserts and is unfit for plant growth.
- Clayey soil: It contains large proportion of clay particles (40% or more) and small amounts of humus and silt. Clayey soil, being compact, can hold water. However, it is poorly aerated as it can not trap air. It is also not suitable for plant growth.
- Loamy soil: Loamy soil contains relatively larger quantities of clay, silt, sand particles and humus. In fact, it contains about one part clay, two parts silt and two parts sand.
Therefore, it is porous has very good water holding capacity and also allows aeration of roots.
Major types of Soils in India
The soil is classified on the basis of its composition and nature. The major types of soils found in our country and their composition are presented in table.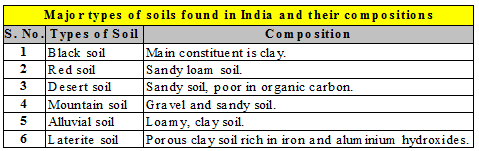
|
75 videos|131 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on Natural Resources - Chemistry for Grade 10
| 1. What are natural resources? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of air as a natural resource? |  |
| 3. How is water considered a wonder liquid? |  |
| 4. Why is soil considered a natural resource? |  |
| 5. What are fossil fuels? |  |
















