Natural Resources of the Earth | Science Olympiad Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Environment? |

|
| Resources on the Earth |

|
| Breath of Life : Air |

|
| Water: A Wonder Liquid |

|
| Mineral Riches in the Soil |

|
What is Environment?
Everything that surrounds us is collectively termed as the environment.
Environment acts as a life support system for us, since it is from the environment that we get food to eat, water to drink, air to breath and all other requirements of our day–to–day life.
Resources on the Earth
The resources which are provided to us by the nature are called natural resources.
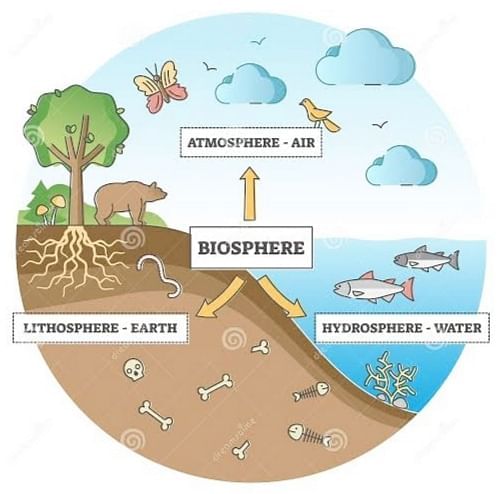
Earth is the only planet where life exists. The natural resources of the earth are land, water and air. The outer crust of the earth is called the lithosphere. Water covers 75% of the earth surface and these comprise the hydrosphere. Air form the blanket over the surface of earth called atmosphere. All the components atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere together constitute biosphere. There are two components of ecosystem biotic and abiotic components. The biotic components include living organisms like plants and animals, whereas abiotic components include air, water and land.
Breath of Life : Air
On earth, we human beings along with all other biota are surrounded with air.
Air is a mixture of gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour.
On the planets venus and Mars carbondioxide forms the major component constituting up to 95–97% of the atmosphere no life is known to exist there. On the contrary, on the earth, air forms the blanket around the earth having mixture of many gases. It has life on it. Oxygen is required by all living beings (eukaryotic cell and many prokaryotic cells) for respiration and for burning (combustion) of materials. Air contains about 20% oxygen and its percentage in air is balanced by the process of photosynthesis. Despite this, the percentage of carbondioxide in our atmosphere is a mere fraction of a percent because carbondioxide in two ways : (i) Green plants convert carbon-dioxide into glucose in the presence of sunlight and (ii) many marine animals use carbonates dissolved in sea–water to make their shells.
Role of Atmosphere in Climate Control
Air is an inexhaustible natural resources. In a world without air, there would be no plant or animal life no winds, no fires and no protection against harmful solar radiations. This is because the atmosphere covers the earth like a blanket. Atmosphere also maintain the variation of temperature and pressure. It do not allow the drastic variation of temperature during day and nights. For instance moon, which is about the same distance from the sun that the Earth is, but it lacks atmosphere. As a consequence, on the surface of the moon, the temperature ranges from –190°C to 110°C. Thus moon’s temperature rises during the sunlight period (day) to about 110°C, and cools to –190°C during dark period (night).
The movement of Air: Winds
A cool evening breeze after a hot day or rain after a few days of hot weather bring us considerable relief. Some questions may strike our mind: What the movement of air? What decides whether this movement of air will be in the form of a gentle breeze, a strong wind or a terrible storm? What brings the rain?
All the above phenomena are the result of changes that take place in our atmosphere due to the heating of air and the formation of water vapours.
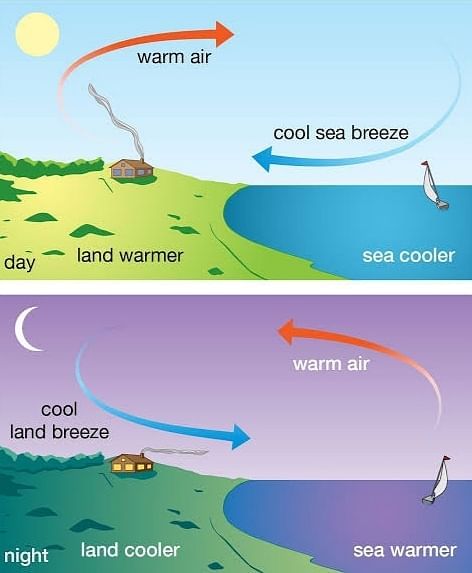
The movement of wind is due to the difference of pressure in the lower layer and upper layer of the atmosphere, on land and water bodies, when solar radiation falls on the earth, some are absorbed. But most of them are reflected back into the atmosphere by the land and water bodies. These reflected radiation heat up the lower layer of the atmosphere, as a result convection current sets up in the air. But since the land get heated faster than the water bodies, the air over the land also gets heated and create a region of low pressure on land. Thus, wind moves to the region of lower pressure over land from the region of high pressure on the water bodies and create winds. During day time the wind blow from sea to land and during night the process is reversed, as the wind blow from land to sea.
This temperature difference across the earth generates the development of major wind belt over the
earth surface, which forms the climatic zone of the world.
Factors Influencing Movements of Air
(i) Uneven heating of land at different parts of Earth.
(ii) Vaporisation and condensation of water vapours.
(iii) Rotation of earth.
(iv) Differences in heating and cooling of land and water bodies.
(v) Presence of high mountain ranges in the path of winds.
(vi) Difference in topography over which the wind passes.
Rain
When the water bodies heats up during the days, the upper layer of the water bodies change into the vapour and goes up in the atmosphere with the air. As these air reaches the upper layer of the atmosphere it expands and cools. On cooling, there watervapours get condensed in the form of tiny droplets of water.An enormous collection of tiny droplets of water appear in the form of clouds. When there collection of water vapour become heavier and bigger, it falls down in the form of rain.
When the temperature of air is very low, precipitation then may occur in the form of snow, sheet or hail.
The rain fall pattern is decided by the prevailing wind pattern. In the country like India, the rain is mostly brought by the south-west or north east monsoons. The south west monsoons blows from sea to land during the month of April and May. Local rain in coastal regions are caused due to sea breezes and rains in the great topographic relief are caused by mountains and valley breezes.
Air Pollution
Contamination of air of poisonous gases released by various means and many other chemicals is called air pollution.
The main reason for air pollution is the rapid industrialization and urbanization. Air pollution is the addition of air pollutants such as particulate matter, gases and vapours into the atmosphere has an adverse effect on humans, animals, vegetation and human assets. Particular air pollutants are also called suspended particulate matter or SPM because they remain suspended in air for a good period of time.
The combustion of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum increases the amount of suspended particle in air. These suspended particles could be unburnt carbon particles or substances called hydrocarbons. Presence of high level of all these pollutants cause visibility to be lowered, especially in cold weather when water also condenses out of air. This is known as smog and is a visible indication of air pollution.
Water: A Wonder Liquid
Oceans rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, pools, polar ice caps, water vapour etc. collectively form the hydrosphere. Hydrosphere comprises of water which is an inexhaustible natural resource. About 75% of the earth surface is covered with water, but the concentration of fresh water i.e., potable water is very less and is nearly 2.5%. the fresh water are found in river, ponds, lakes, glacier of mountains, and underground water is considered to be essential because all the reaction takes place within our body and within the cells occur in the liquid medium only. The movement of substance from one part of the body to the another part cannot take place in the form of solid molecule, it flows in the form of liquid, dissolved in water.
Terristrial life-forms require fresh water for this because their bodies cannot tolerate or get rid of the high amounts of dissolved salts in saline water. Thus, water sources need to be easily accessible for animals and plants to survive on land.
The availability of water decides not only the number of individuals, of each species that are able to survive of life there and many other factors like temperature and nature of soil also matter.
Water Pollution
An undesirable change in the physical, biological or chemical qualities of water (due to addition of foreign organic, inorganic, biological or radioactive substances) that adversely affects the aquatic life and makes the water unfit for use, is called water pollution.
The water pollution is of three types; inland water pollution, underground water pollution, and marine water pollution.
Mineral Riches in the Soil
Soil is an important resource that decides the diversity of life in an area. The outermost layer of our earth is called the crust. Over long periods of time, thousands and millions of years, the rocks at or near the surface of the earth are broken down by various physical, chemical and some biological processes. The end product of this breaking down is the fine particles of soil. Soil is a mixture of small particles of rocks and humus (i.e., organic matter obtained from decaying of living organisms or their wastes). Temperature variations due to radiations of the sun, rain water, winds and living organisms influence the formation of soil from the rocks involving two processes: weathering and paedogenesis.
Breaking down of bigger rocks into small, fine soil particles is called weathering.
Under the influence of solar radiations, rocks heat up and expand. At night these rocks cool down and contract. Since all the parts of rocks do not expand and contract at the same rate, cracks appear in the rocks and ultimately the large rocks breakdown into smaller pieces. Flow of water through or over the rocks make the cracks bigger. On freezing the water expands in rocks crevices and break the rocks. Similarly strong winds continue to rub against hard rocks and erode them. Growth of lichens, mosses and other plants also influence the formation of soil by eroding the rocks over which they are growing.
Paedogenesis involves the decomposition of organic materials by bacteria and fungi and humification and mineralization of decomposed organic matter. Earthworms also play an important role in soil formation.
|
28 videos|115 docs|52 tests
|















