Grade 9 Exam > Grade 9 Notes > AP World History > Networks Of Exchange
Networks Of Exchange | AP World History - Grade 9 PDF Download
Height of the Middle Ages: Trading and Crusading
- Merchants in Towns (Burghers)
- Merchants emerged in towns and were known as Burghers, gaining significant political influence.
- Town Alliances
- Towns frequently established alliances with one another for various purposes.
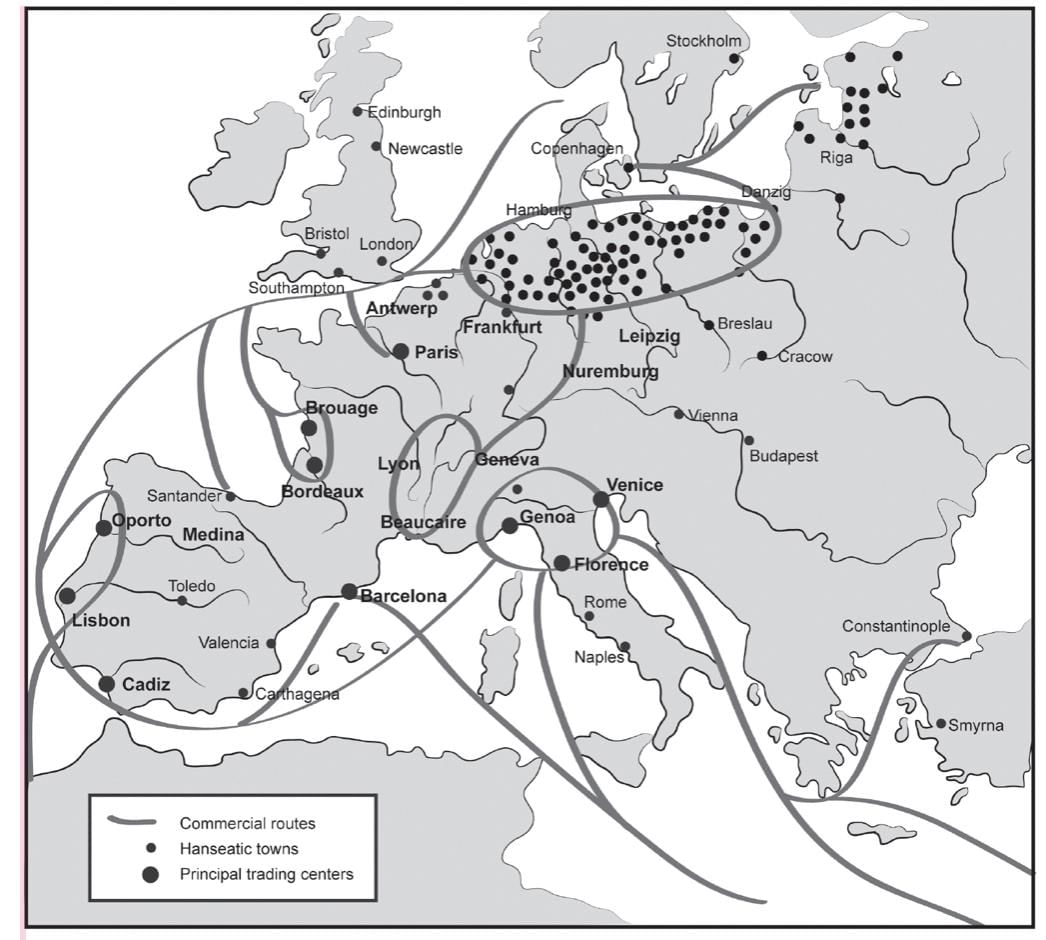
- Hanseatic League
- The Hanseatic League, established in 1358, was a trade alliance across northern Europe aimed at fostering nationhood and enhancing social mobility.
Medieval European Architecture
- Romanesque to Gothic Architecture
- Flying Buttresses
- Art and Sculpture in Cathedrals
Romanesque to Gothic Architecture
- Transition from Romanesque to Gothic styles, prominently seen in cathedrals
Flying Buttresses
- Tall windows and vaulted ceilings supported by flying buttresses
Art and Sculpture in Cathedrals
- Cathedrals often adorned with intricate art, sculptures, and musical elements
Medieval Intellectual and Religious Developments
- Scholasticism
- Crusades
- Papal Influence
- Thomas Aquinas
Scholasticism
- Era marked by the growth of education and knowledge
- Universities founded for men; studies in philosophy, law, and medicine
- Clash between traditional religious beliefs and ideas from Muslim and Greek scholars
Crusades
- Series of military campaigns by European Christians in the 11th-14th centuries
- Objective to convert non-Christians, particularly Muslims, and combat religious deviations
Papal Influence
- Pope Innocent III issued stringent decrees on church doctrine, leading to persecution of heretics and Jews
- Pope Gregory IX established the Inquisition for prosecuting heretics, employing severe punishments like excommunication, torture, and execution
- Church referred to as the Universal Church or Church Militant during this period
Thomas Aquinas
- Christian theologian known for reconciling faith with reason
- Made significant advancements in Christian thought during his lifetime
Impact of Urbanization and Trade
- Urban Culture Growth
- Key Urban Centers
Urban Culture Growth
- Urbanization and trade fostered the development of urban culture
Key Urban Centers
- Cities like Constantinople, Paris, and Italian city-states emerged as major urban hubs
- Silk Route cities such as Baghdad, Merv, and Chang'an thrived due to trade routes
Crusades
- Combatting Heresies: These are religious practices or beliefs that do not align with traditional church doctrine.
- Pope Innocent III: He issued strict decrees on church doctrine and often persecuted heretics and Jews. Notably, the 4th crusade was unsuccessful.
- Pope Gregory IX: He initiated the Inquisition, a formal process of interrogating and prosecuting perceived heretics. Punishments included excommunication, torture, and execution. The church was frequently referred to as the Universal Church or Church Militant.
Heresies
- Pope Innocent III: He enforced strict decrees on church doctrine, leading to frequent persecutions of heretics and Jews. The 4th crusade under his rule was also unsuccessful.
Pope Gregory IX
- Inquisition: Under Pope Gregory IX's leadership, the Inquisition was established as a formal process to deal with perceived heretics. Punishments included severe measures like excommunication, torture, and execution. The church was commonly known as the Universal Church or Church Militant during this period.
Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX: Leader of the Universal Church and advocate of the Church Militant.
Thomas Aquinas
- Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274): Notable Christian theologian who significantly contributed to Christian thought by emphasizing that faith and reason are not contradictory.
Urbanization
Urbanization: The process where trade activities fostered the development of urban culture.
Impact of Trade on Urbanization
- Trade spurred the growth of urban culture, with cities often emerging near trade routes.
- Silk Route cities such as Baghdad, Merv, and Chang'an stood out as highly populated urban centers.
- Key European cities like Constantinople, Paris, and Italian city-states flourished due to trade, with Constantinople thriving before 1400 and Paris and Italian cities prospering after 1400.
The Rise and Fall of the Mongols
The Mongols were a set of tribes and clans known for their exceptional skills in horseback riding and archery.
Key Figures and Events
- Genghis Khan: He successfully unified the Mongolian tribes during the early 1200s, leading them to expand their dominance by invading China in 1234.
- Kublai Khan: Following Genghis Khan, Kublai Khan rose to power and ruled over China.
- Timur Lang: A Mongol leader who conquered parts of India, spreading Islam in the region.
Mongol Empire and its Impact
- The Mongol Empire stretched from the Pacific Ocean to Eastern Europe, demonstrating their vast territorial reach.
- Despite their initial reputation as ruthless warriors who destroyed cities, the Mongols transitioned to a more peaceful existence after settling in urban areas.
- They did not impose a specific culture, religion, or way of life on the regions they conquered, but they did not actively promote cultural advancements either.
Consequences and Legacy
- The Mongols were significant diffusers of culture, facilitating the exchange of ideas and practices across their vast empire.
- Their military actions prevented Russia from evolving culturally in isolation.
- As they traversed through Europe, the Middle East, and Asia, the Mongols played a crucial role in enhancing world trade and promoting cultural diffusion and global awareness.
Genghis Khan
- Mongol Empire: The vast empire extended from the Pacific Ocean to Eastern Europe. It fragmented into hordes following Genghis Khan's demise. Initially known for their fierce conquests and city destructions, the Mongols transitioned to a more peaceful phase after settling in cities.
- Golden Horde: This faction conquered what is now modern-day Russia.
- Kublai Khan: Successor to Genghis Khan, he ascended to power and ruled over China.
Golden Horde
- The Golden Horde, under Mongol rule, successfully conquered territories in modern-day Russia.
Kublai Khan
- Kublai Khan, the heir of Genghis Khan, notably governed China.
Cultural Impact
- The Mongols did not impose a specific culture on the regions they conquered. They refrained from enforcing a particular religion or way of life on subjugated nations. However, they did facilitate certain cultural advancements.
Timur Lang
- Timur Lang, a Mongol leader, seized control of India and undertook widespread destruction. He notably influenced the spread of Islam in the region.
Additional Insight on Timur Lang
- In situations where the Mongols faced resistance from the inhabitants of conquered territories, they resorted to immediate and severe measures, often resulting in capitulation. Renowned for their merciless fighting tactics, the Mongols were highly organized and possessed exceptional mobility.
Impact of Diffusers of Culture
- Diffusers of culture played a significant role in spreading cultural influences.
- They hindered Russia's cultural development.
- World trade expanded, leading to cultural diffusion and increased global awareness across Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
Mali and Songhai Overview
- Mali possessed abundant gold reserves that attracted Islamic traders.
- Mansa Musa, a Malian ruler, established the city of Timbuktu and extended Mali's territory past Ghana.
Sonni Ali and Songhai Empire
- Sonni Ali, a ruler of Songhai, conquered regions in West Africa during the 15th century.
- Under his reign, Songhai evolved into a prominent cultural hub until around 1600.
Mansa Musa
- Sonni Ali: Songhai ruler who conquered the region of West Africa in the 15th century, establishing it as a significant cultural center until 1600.
Sonni Ali
Chinese Technology
- Song Dynasty: Implemented a bureaucratic system based on merit and civil service examinations, fostering a loyal workforce and enhancing transportation, communication, and business practices.
- Emphasized the development of an industrial society, promoting literacy through the use of printed books to boost productivity and economic growth.
Review of Interactions Among Cultures
- Interactions Among Cultures: This section delves into the examination of cultural exchanges and encounters between different societies throughout history.
- Increased Cultural Exchange: Instances of cultural diffusion and trade interactions led to the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and technologies among diverse civilizations.
- Artistic Influences: Cultural interactions often resulted in the amalgamation of artistic styles, leading to the creation of unique and diverse art forms.
- Technological Innovations: Cross-cultural exchanges facilitated the spread of technological advancements, such as agricultural techniques, architecture, and navigation methods.
Trade Networks and Cultural Diffusion
Trade networks and the exchange of culture
- Trade flourished between 1200-1450
- Enhanced by advancements in transportation and monetary systems
- Main Global Trade Routes:
- The Hanseatic League
- The Silk Road
- The land routes used by the Mongols
- Trade paths connecting China and Japan
- Trade routes linking India and Persia
- The Trans-Saharan trade routes between West Africa and the Islamic Empire
Cultural Diffusion
Spread of customs and ideas
- Facilitated the dissemination of religions, languages, literature, art, and diseases
- Bubonic Plague:
- Originated in Asia during the 14th century and was transmitted by merchants
- Resulted in the loss of approximately one-third of the population
Cultural Diffusion
- Cultural diffusion refers to the spread of religions, languages, literature, art, ideas, and diseases across different regions.
Bubonic Plague
- The Bubonic Plague originated in Asia during the 14th century and was transmitted by merchants. It resulted in the death of approximately one-third of the population it affected.
Indian Ocean Trade
- The Indian Ocean Trade was dominated by Persians and Arabs, extending from western India to the Persian Gulf and eastern Africa.
- Great Zimbabwe was a prominent trading empire in Africa that flourished from the 11th to the 15th centuries.
Vibrant Indian Ocean Communities
- Sailors who married local women facilitated a rich blend of cultures.
Silk Road
- The ancient Silk Road linked China with Mediterranean societies, fostering cultural exchanges.
- Travellers journeying through trade hubs like Kashgar and Samarkand shared silk, porcelain, paper, religious beliefs, cuisine, and military technologies.
Hanseatic League
- A group comprising more than 100 cities
- Fostered the growth of a significant middle class in northern Europe
- Established a model for extensive trading activities in Europe
Expansion of Religion and Empire: Cultural Clash
- The expansion of religion and empires led to cultural clashes
- Religion spread naturally through trade connections, missionary endeavors, and religious conflicts
Other Reasons People Were on the Move
- Rapid urban growth led to limited space in some areas while cities expanded due to increasing opportunities.
- The emergence of new cities and empires attracted individuals seeking better prospects.
- Individuals embarked on Muslim pilgrimages for religious reasons and spiritual fulfillment.
Notable Global Travellers
- Xuanzang: A Chinese Buddhist monk who journeyed during the T'ang Dynasty to India in pursuit of exploring Buddhism.
- Marco Polo: A merchant hailing from Venice who traveled to China and various parts of Europe for trade and exploration.
- Ibn Battuta: An Islamic traveler whose voyages took him across the Islamic world, India, and China for cultural exchange and exploration.
- Margery Kempe: An English Christian who undertook pilgrimages through Europe and the Holy Land for religious devotion and personal growth.
Technology and Innovations
- Islamic World
- Developments in the Islamic World included advancements such as paper mills and gunpowder cannons. Paper mills revolutionized the production of paper, making written communication more accessible and widespread. Gunpowder cannons transformed warfare, leading to significant changes in military strategies and tactics.
- China
- China saw remarkable progress with innovations like universities and movable type. Universities became centers of learning and intellectual exchange, fostering the development of knowledge and skills. The invention of movable type revolutionized printing, enabling the mass production of books and spreading information more efficiently.
- Notable Inventions:
- The astrolabe and sextant were crucial tools for navigation and astronomy, aiding explorers and scientists in understanding the celestial bodies and mapping the world. Paper currency revolutionized trade and commerce, simplifying transactions and promoting economic growth.
- Algebra and porcelain were significant contributions to mathematics and art, respectively, enriching these fields and influencing future developments.
- Chess, a strategic board game, and terrace farming techniques improved agricultural practices, enhancing food production and sustainability.
- The introduction of modern soap formulas and water-powered mills revolutionized hygiene practices and industrial production processes.
- Advancements such as guns and cannons, cotton sails, mechanical pendulum clocks, and water clocks transformed warfare, navigation, timekeeping, and trade, respectively.
- Furthermore, innovations like distilled alcohol, the magnetic compass, surgical instruments, and state-run factories played crucial roles in medicine, navigation, healthcare, and governance, contributing to societal progress and development.
The document Networks Of Exchange | AP World History - Grade 9 is a part of the Grade 9 Course AP World History.
All you need of Grade 9 at this link: Grade 9
FAQs on Networks Of Exchange - AP World History - Grade 9
| 1. What were some key trading routes during the height of the Middle Ages? |  |
Ans. During the height of the Middle Ages, key trading routes included the Silk Road, connecting Europe to Asia; the Mediterranean Sea, which facilitated trade between Europe, Africa, and Asia; and the Trans-Saharan trade route, linking North Africa to West Africa.
| 2. How did the Crusades impact trade and exchange networks in the medieval period? |  |
Ans. The Crusades had a significant impact on trade and exchange networks in the medieval period by increasing cultural exchange between Europe and the Middle East, introducing new goods and technologies to Europe, and stimulating economic growth in urban centers along the Mediterranean.
| 3. How did urbanization contribute to the growth of networks of exchange during the Middle Ages? |  |
Ans. Urbanization during the Middle Ages led to the development of market towns and cities, which served as hubs for trade and exchange. The concentration of people and resources in urban centers facilitated the flow of goods, ideas, and technologies between different regions.
| 4. What role did Pope Gregory IX play in promoting networks of exchange during the medieval period? |  |
Ans. Pope Gregory IX played a key role in promoting networks of exchange during the medieval period by supporting the establishment of market fairs and trade routes, encouraging merchants to engage in international trade, and fostering cultural exchange between different regions.
| 5. How did the rise and fall of the Mongols impact networks of exchange in the medieval world? |  |
Ans. The rise and fall of the Mongols had a significant impact on networks of exchange in the medieval world by facilitating trade along the Silk Road, connecting Europe to Asia, and promoting cultural exchange between different civilizations. However, the collapse of the Mongol Empire led to the disruption of trade routes and the decline of long-distance trade in the region.
Related Searches















