Year 6 Exam > Year 6 Notes > Year 6 Computing > Networks
Networks | Year 6 Computing PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding the Use of Networks |

|
| Accessing networks |

|
| How is information delivered? |

|
| Different types of networks |

|
Understanding the Use of Networks
- Networks play a crucial role in connecting various computing devices, such as computers or laptops, together. When multiple computers are linked, they form a network.
- Through this connectivity, information can be easily exchanged between these devices, offering several advantages.

Benefits of Network Connectivity
- Hardware Accessibility: Printers and photocopiers connected to the network can be accessed by all devices within the network.
- Centralized File Storage: Servers, acting as networked computers, manage and store data files that can be accessed, modified, and saved by any connected user. Compared to personal computers, servers can store significantly more data.
- User Profiles and Access Control: Different user profiles can be set up within the network, granting access to specific resources while restricting others. For instance, in a school network, adults may have access to certain resources that are off-limits to students.
Accessing networks
- If we wish to utilize the services offered by a network, we must be registered as users of that network.
- Details about each user, such as usernames and passwords, are stored on the server.
- The server also maintains information about which files each user is permitted to access. This system helps safeguard both the files stored on the network and the users' personal information.
Question for NetworksTry yourself: Which of the following is a benefit of network connectivity mentioned in the passage?View Solution
How is information delivered?
- Switches play a crucial role in ensuring that data packets are routed to the correct destinations within a network.
- Every device connected to a network possesses a unique MAC address. Switches utilize these addresses to accurately direct data packets to their intended devices.
- At times, network congestion may occur, preventing the timely transmission of information. This congestion is typically due to the network reaching its bandwidth limit.
- Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over a network simultaneously. Before transmitting any data, a device checks if sufficient bandwidth is available. If not, it waits and retries until space becomes available for transmission.
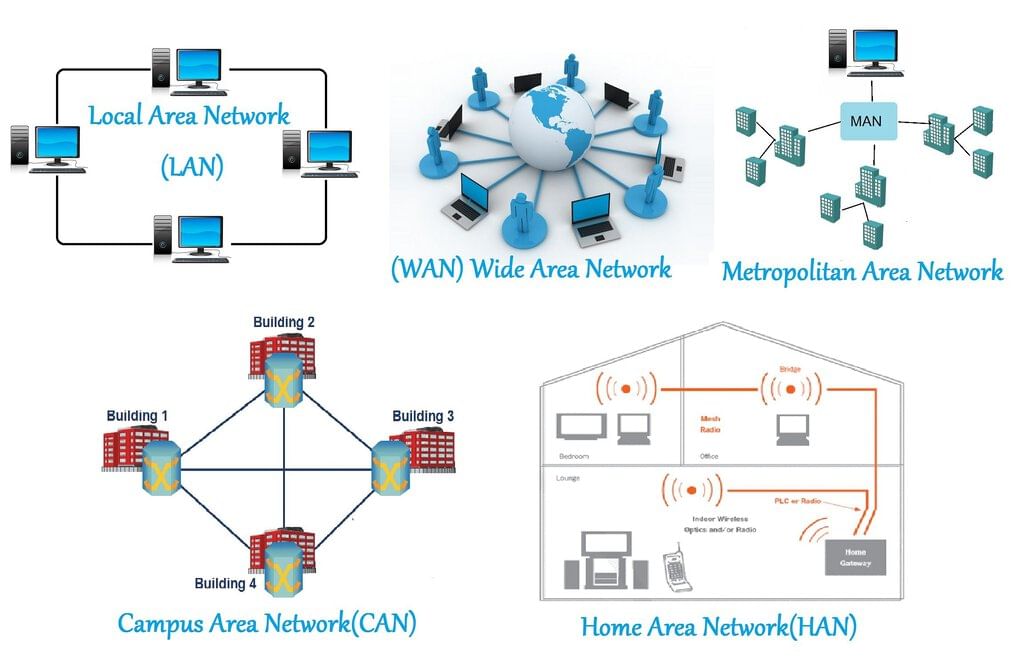
Different types of networks
- A network where all devices are located within the same geographical area is termed a local area network (LAN).
- Examples of LANs include school networks and home networks.
- LANs can be interconnected to form larger networks known as wide area networks (WANs).
- In banking, computers within a single bank are connected in a LAN to facilitate information sharing.
- When banks need to exchange information with each other, they connect their LANs together, creating a Wide Area Network (WAN).
- The internet itself is the largest example of a Wide Area Network, spanning globally to connect millions of devices and networks worldwide.
Question for NetworksTry yourself: What is the purpose of switches in a network?View Solution
The document Networks | Year 6 Computing is a part of the Year 6 Course Year 6 Computing.
All you need of Year 6 at this link: Year 6
|
19 videos|26 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on Networks - Year 6 Computing
| 1. What are some common types of networks used in UK schools? |  |
Ans. UK schools commonly use Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for their networking needs.
| 2. How do networks benefit UK schools? |  |
Ans. Networks in UK schools help facilitate communication, collaboration, and resource sharing among students, teachers, and staff. They also provide access to online resources and educational tools.
| 3. What security measures are in place to protect networks in UK schools? |  |
Ans. UK schools implement firewalls, antivirus software, encryption protocols, and access controls to secure their networks and protect sensitive data from cyber threats.
| 4. How do UK schools manage their networks effectively? |  |
Ans. UK schools employ network administrators who oversee network operations, troubleshoot issues, and ensure smooth functioning of the network infrastructure.
| 5. How are network outages handled in UK schools? |  |
Ans. In the event of a network outage, UK schools have backup plans in place to minimize disruption, such as using alternative communication methods or temporary solutions until the network is restored.
Related Searches



















