Non-Integrated Accounting System - Cost Accounting Techniques, Cost Accounting | Cost Accounting - B Com PDF Download
Non-Integrated Accounting System
It is a system of accounting under which separate ledgers are maintained for cost and financial accounts by Accountants. Under such a system the cost accounts restricts itself to recording only those transactions which relate to the product or service being provided. Hence items of expenses which have a bearing with sales or, production or for that matter any other items which are under the factory management are the ones dealt with in such accounts.
A special feature of the non-integrated system of accounts is its ability to deal with notional expenses like rent or interest on capital tied up in the stock. The accounting of notional rent facilitates comparisons amongst factories (some owned and some rented). Similarly, recognition of interest on capital tied up in stock could help make the stores and works managers aware of the money being blocked because of holding stock.
Non Integrated Accounting Systems contain fewer accounts when compared with financial accounting because of the exclusion of purchases, expenses and also Balance Sheet items like fixed assets, debtors and creditors. Items of accounts which are excluded are represented by an account known as cost ledger control account.
Principal Ledgers
Subsidiary books maintained under non-integrated system of accounting
The following are some of the subsidiary books maintained under interlocking system of accounting
- Stores ledger: It is used to record both the quantity and amount of receipts, issues and balance of materials and supplies. It consists all store accounts.
- Payroll and wage analysis book: It is used to record the wages. The basis for recording the transactions are (a) clock cards,(b) time tickets, and (c)piece work tickets.
- Job ledger: It is used to record the material cost, wages, and overheads incurred in respect of a job.
- Finished goods stock ledger: It is used to record the receipt of finished goods from production department, the sale and stock of finished goods both in terms of quantity and value.
- Standing order ledger: It is used to record overheads incurred.
- Debtors’ Ledger: It contains personal accounts of all trade debtors.
- Creditors’ Ledger: It contains personal accounts of all trade creditors.
Control Accounts
The following important accounts are maintained under non-integrated accounting system:
(1) General ledger adjustment account: It is also known as cost ledger control account or nominal ledger control account. In this accounts transactions with only one entry is recorded and contra appears in financial book. All transactions of income and expenditure which originate in the financial Accounts must be entered in the ledger for eventual transfer to Cost Accounts and total of this account will be equal to total of all the balance of the impersonal accounts.
On the credit side of this account are recorded
(a) Opening Balance of materials, work in progress and finished stock,
(b) Expenses of material, wages and overheads on the credit side,
(c) On the debit side returns of materials to the supplier,
(d) Sales income and
(e) on the debit side balancing entries of P&L account and closing stock.
(2) Stores ledger control account: It is debited with purchase of materials for the stores and credited with issues of material.
(3) Wages control account: In this account the wages accrued and paid and allocation of wages in this account are recorded.
(4) Work in progress control account: It includes of all direct materials, direct wages, direct expenses, special purchases and expenses.
(5) Finished goods stock ledger control account: This account represents finished goods stock ledger transactions in total form.
(6) Selling, distribution, and administration overhead control account: This account represents selling, distribution and administration overheads.
Entries to Record Transactions under Non-Integrated System
(1) Materials purchased
Stores Ledger Control account Dr.
To General Ledger Adjustment a/c
(2) Material purchased for a special job
Work in Progress Control a/c Dr.
To General Ledger Adjustment a/c
(3) For issue of direct materials to production department
Work in Pprogress Control a/c Dr.
To Stores Ledger Control account
(4) For issue of indirect materials to production departments
Overhead Control a/c Dr.
To Stores Ledger Control a/c
(5) For returning materials to supplier
General Ledger Adjustment a/c Dr
To Stores Ledger Control a/c
(6) For materials returned from production department
Stores Ledger Control a/c Dr
To Work in Progress Control a/c
(7) For materials transferred from job to job
No entry is passed in control account
In work in progress ledger the following Entry is passed
Transferee Job a/c Dr.
To Transferor Job a/c
(8) For total salary and wages paid
Wages Control a/c Dr.
To General Ledger Adjustment a/c
(9) For allocation of direct and indirect labour
Work in Progress Control a/c Dr.
Overhead Control a/c Dr.
To Wages Control a/c
(10) For recording direct expenses
Work in Progress Control a/c Dr.
To General Ledger Adjustment a/c
(11) For recording overhead incurred and accrued
Overhead Control a/c Dr.
To General Ledger Adjustment a/c
(12) For adjusting under or over absorption overheads
The overhead control account is closed by transferring to overhead suspense account.
(13) For recording finished stock produced
Finished Goods Stock Ledger Control a/c Dr.
To Work in Progress Control a/c
(14) When finished goods are sold at cost
Cost of Sales a/c Dr.
To Finished Goods Stock Ledger Control a/c
(15) When finished goods are sold at total sales value
General Ledger Adjustment a/c Dr.
To Costing Profit and Loss a/c
(16) For recording sales returns
Costing Profit and Loss a/c Dr.
To General Ledger Adjustment a/c
(17) For recording total cost to make and sell
Cost of Sales a/c Dr.
To Costing Profit and Loss a/c
(18) For recording under absorption of overheads which is not yet adjusted
Costing Profit and Loss a/c Dr.
To Overhead Suspense a/c
(19) For recording over absorption of overheads which is not yet adjusted
Overhead Suspense a/c Dr.
To Costing Profit and Loss a/c
(20) For recording profit
Costing Profit and Loss a/c Dr.
To General Ledger Adjustment a/c
Advantages of Non-Integrated Accounting
The following are the main advantages of this accounting system:
- This system tends to coordinate the functions of different selections of the accounts department since all efforts are integrated and directed towards achievement of one aim that is providing a high level of efficiency.
- The accounting procedures can be simplified and the system can be centralised with the object of achieving a greater control over the organization.
- The system creates conditions which are eminently suitable for the introduction of mechanized accounting.
- There is no possibility of overlooking any expense under the system.
- As cost accounts are posted straight from the books of original entry, there is no delay in obtaining the data.
- There is automatic check on the correctness of the cost data. It ensures that all legitimate expenditure is included in Cost accounts and reliable and proved data is provided to the management for its decisions’.
- Integrated accounting widens the outlook of the accountant.
- It can be maintained according to convenience as it need not be statutorily maintained.
Limitations of Non-Integrated Accounting
The following are some of the limitations of this accounting system:
- The Financial transactions other than cost incurred are not recorded in the system.
- Transactions involving payment other than that of cost are not included in the system E.g: loss on fixed assets.
- There is always a diff between the profits reported as per the cost accounting system and the Financial Accounting System.
Non-integrated Accounting System
Q.1. What is the other name of cost control account system?
Answer: Other names of cost control accounts system with the Non-integrated system of accounting.
Q.2. What do you understand by the cost control system?
Answer: When separate books are maintained for cost and financial accounts, it is required to prepare cost control accounts for maintaining double entry system.
Therefore cost accounts are known as cost control accounts.
Q.3. What is non-integrated accounting system?
Answer: It is an accounting system where separate account books are maintained to record financial and cost transactions. Integrated and Non-Integrated Accounting System.
Q.4. How are many sets of account books kept in non-integral accounts?
Answer: Two sets of accounts books are kept in the system – one for recording financial transaction while another for recording cost transaction.
Q.5. What are the advantages of cost control accounts?
Answer:
- Control account presents detailed information recorded in memorandum account books in an abridged manner to help managers in Planning policy.
- Different employees can be interested in record transactions leading to saving in time.
- Control accounts serve the purpose of internal check too.
- It helps to prepare to costing profit and loss account.
Q. 6.What are the characteristics of the non-integrated accounting system?
Answer:
- Separate account books are maintained to record financial and cost transactions.
- Financial and cost accountant both are responsible to record transactions in the book separately.
- The double entry system is adapted for recording the transactions in both accounts books.
- Personal and real accounts are not opened in cost account books.
- General and cost ledger adjustment account is opened in cost books to complete the double entry system.
- Reconciliation statement is prepared to reconcile profits as revealed by cost account books and financial account books.
Q.7. Name the principal account to be opened in cost books under Non-integral Accounting system?
Answer: Principal Accounts
- Stores ledger control account.
- Work in progress control account.
- Finished good control account.
- General ledger control account.
- Wages ledger control account.
- Factory overhead control account.
- Administrative overhead control account.
- Selling and distribution overhead control account.
- Cost of self-control account.
- Cost and profit and loss account.
Integrated Accounting System Problem 1:
The following figures have been extracted from the costing records and financial books of a factory. You are required to pass the necessary entries in the cost journal:
Solution: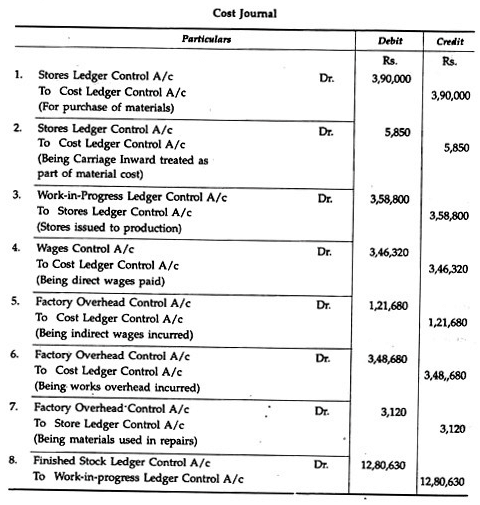
Integrated Accounting System Problem 2:
A manufacturing company has approximately 600 weekly paid direct and indirect production workers. It incurred the following costs and deductions relating to the payroll for the week ended May 2:
The employer’s national insurance contribution for the week was Rs.18,770.
From the wages analysis the following information was extracted:
Work done by building maintenance workers concerning floor area for a warehouse extension.
You are required to show journal entries to indicate clearly how each item should be posted into the accounts
(i) From the payroll, and
(ii) From the Wages Control Account to other accounts, based on the wages analysis.
Note:
Narrations for the journal entries are not required.
Solution: 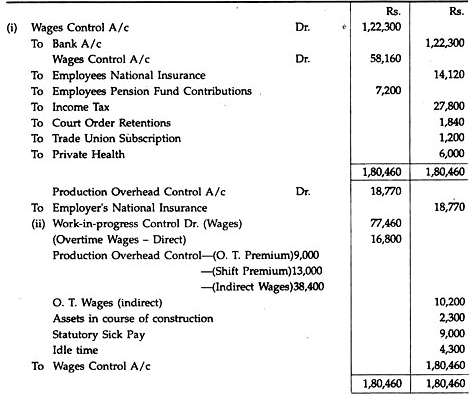
Integrated Accounting System Problem 3:
Dutta Enterprises operates an integral system of accounting. You are required to pass the Journal Entries for the following transactions that took place for the year ended 30. 6. 1990:
Solution: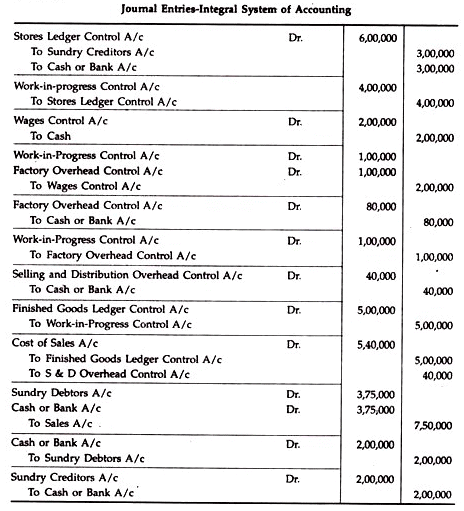
Integrated Accounting System Problem 4:
In the absence of the Chief Accountant, you have been asked to prepare a month’s cost accounts for a company which operates a batch costing system fully integrated with the financial accounts. The following relevant information is provided to you: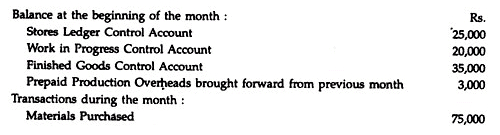
The production overhead absorption rate is 150% of direct wages charged to work-in- progress.
Required:
Prepare the following accounts for the month:
(a) Stores Ledger Control Account.
(b) Work in Progress Control Account.
(c) Finished Goods Control Account.
(d) Production Overhead Control Account.
(e) Profit and Loss Account.
Solution: 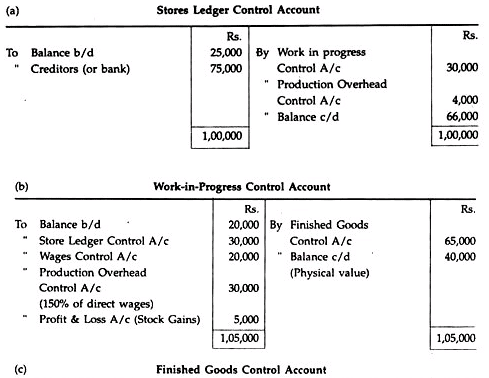
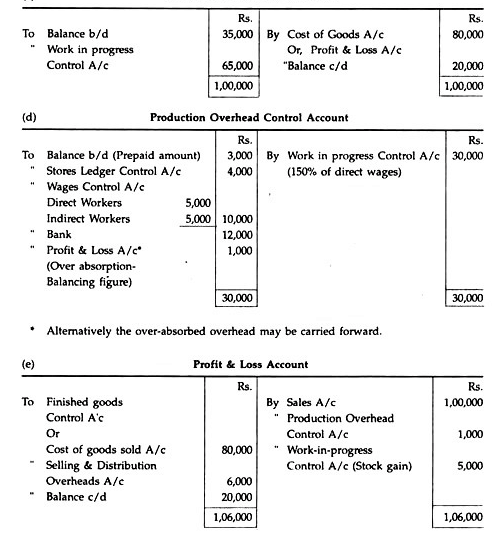
Notes:
1. Materials transferred between batches will not affect the Control Accounts.
2. Non-production time of direct workers is a production overhead and therefore will not be charged to work in progress control A/c
3. Production overheads absorbed in work in progress Control A/c will be equal to Rs.30,000 (150% of Rs.20,000)
4. In the work in progress control A/c the excess physical value of stock is taken resulting in stock gain. Stock gain is transferred to Profit & Loss A/c.
Integrated Accounting System Problem 5:
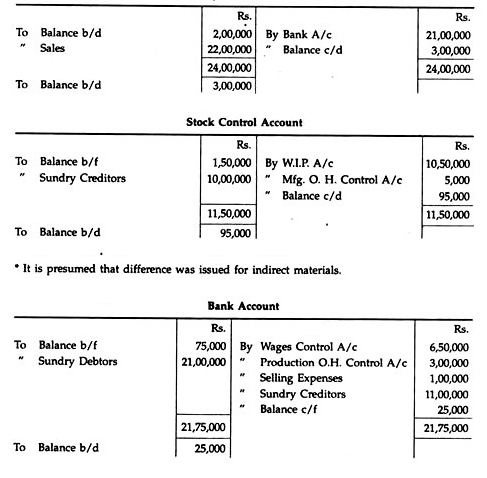
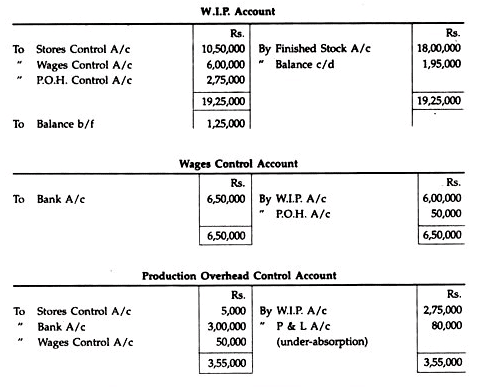
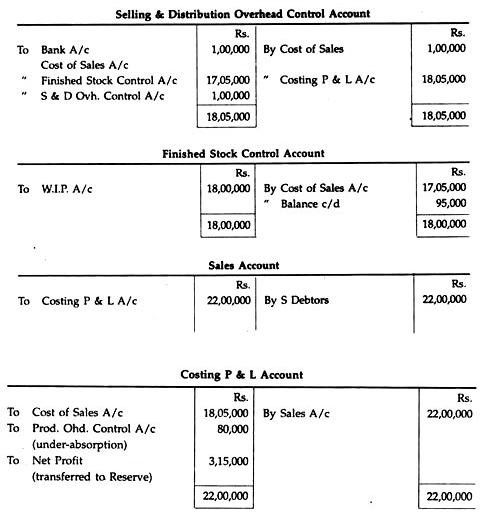
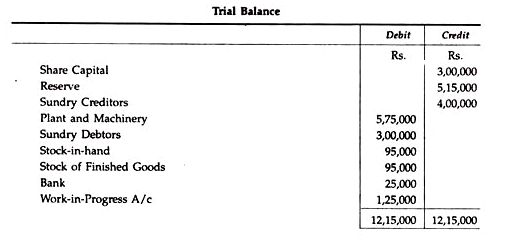
Messrs. Essbee Ltd. maintain Integrated Account of Cost and Financial Accounts. From the following details write control accounts in the general ledger of the factory and prepare a trial balance: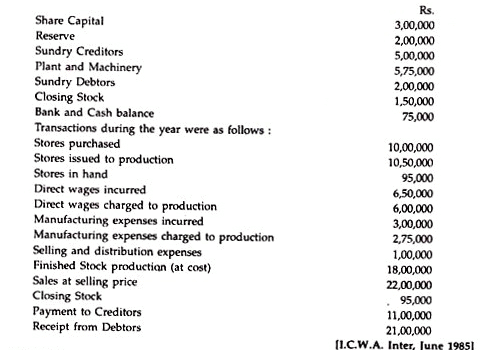
Solution: 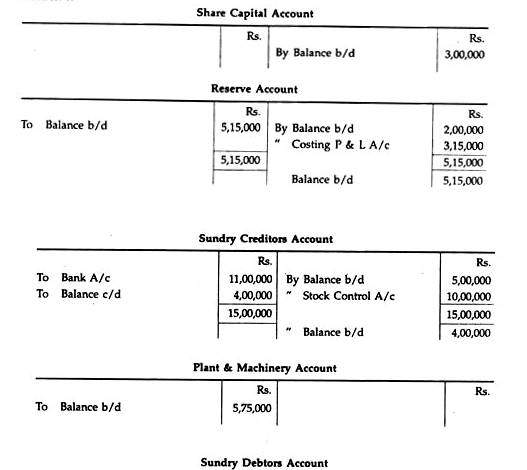
|
106 videos|173 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Non-Integrated Accounting System - Cost Accounting Techniques, Cost Accounting - Cost Accounting - B Com
| 1. What is a non-integrated accounting system? |  |
| 2. What are some cost accounting techniques used in non-integrated accounting systems? |  |
| 3. How can non-integrated accounting systems affect a business's financial performance? |  |
| 4. What are some advantages of integrating accounting systems? |  |
| 5. How can businesses transition from a non-integrated accounting system to an integrated accounting system? |  |























