Notes: Noun Clause | Writing for Academic IELTS PDF Download
A Noun clause is another type of complex sentence that you are likely to use when you do any form of writing or speaking, so you need to be aware of them for IELTS.
And remember that to score at a band 6 or above for the grammatical range and accuracy criteria in the IELTS writing marking, you must show that you are able to use complex sentences with at least some accuracy.
For a band 6 you may still make some errors with them, but errors are a lot less likely for someone scoring a band 7 or higher.
This of course does not mean you have to them in your writing! There are lots of other types of complex sentence, but it is likely you will use some.
For your speaking too, you need to be able to use a mix of complex structures with some flexibility.
What is a Noun Clause?
Noun clause definition:
- A group of words (which do what a noun does) with a subject and a verb that can be a subject, an object, or an object of a preposition.
Here are 4 common types of noun clauses (NC):
- Subject NC
- Direct Object NC
- Object of Preposition NC
- Subject as Complement NC
It is a dependent clause which means it must also have an independent clause, but we will look at this further when we analyse each type.
Before we look at these in turn, let's look at how this type of clause begins.
Starting the Clause
They start with a relative or adverb pronoun. These are the words that commonly commence such a clause:
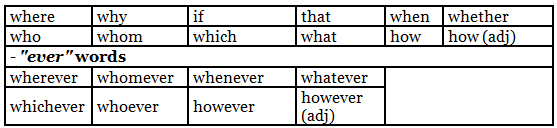
Types of Clauses
Now we'll look at the different types. Before we do this, take a look at these noun clause examples (the whole clause is in bold and the relative or adverb pronoun is in underline). Each different type is shown:
- Subject NC
- How governments are fighting global warming is being scrutinised by the media.
- Direct Object NC
- Most people believe that obesity cannot be reduced just by reducing calorie intake.
- Object of Preposition NC
- He talked with whichever person arrived first.
- Subject as complement NC
- It is important that the individuals do everything they can to help educate their children.
1. Subject Noun Clauses
For these explanations, the subjects will be in bold, the verbs in 'single quote', and the objects in Italic.
In this type of sentence the NC (underlined) is the subject of the sentence:
What causes so many difficulties in the IELTS test 'is' the writing section.
So looking at the whole sentence above, we have a subject, a verb and an object.
But remember that a NC is a 'clause', so it too must have a subject and a verb (and possibly an object):
What 'causes' so many difficulties in the IELTS test is the writing section.
In the above example, the adverb pronoun ("what") is the subject. It does not have to be as in this example, where "I" is the subject:
Whether I 'go' or not is up to me.
Important: Note that the verb "is" is singular. A NC is counted as a singular subject, so it takes a singular verb.
2. Direct Object Noun Clauses
When the clause is the direct object, then it comes after the verb in the independent clause:
This history book 'describes' how England became the first industrialised nation.
Again, remember that the NC has a subject and a verb (and possibly an object):
This history book describes how England 'became' the first industrialised nation.
A common NC you will know from IELTS is the "that" clause, following verbs such as "think", "believe" and "feel", for example as in this Task 2 essay question:
A growing number of people feel that animals should not be exploited by people and that they should have the same rights as humans, while others argue that humans must employ animals to satisfy their various needs, including uses for food and research.
Discuss both views and give your opinion.
And you may then give your opinion:
Personally, I do not believe that it is necessary to exploit animals for our own satisfaction.
Note that if you are speaking it is fine to leave "that" out of the sentence (this is then a reduced noun clause).
I believe students should not have to wear a uniform.
But for formal writing such as you do in IELTS you should keep the "that" in the sentence.
I believe that students should not have to wear a uniform.
3. Object of the Preposition Noun Clauses
In this case, the NC comes after a preposition:
My Aunt is very chatty. She speaks to whoever will listen!
And here it is with the subject and verb of the NC highlighted:
My Aunt is very chatty. She speaks to whoever 'will listen'!
4. Subject as Complement Noun Clauses
These type of sentences have the following structure:
It + be + adjective + (NOUN CLAUSE: that + S + V)
It is important that the government tackles obesity.
It is essential that children have enough leisure time.
|
30 videos|206 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Noun Clause - Writing for Academic IELTS
| 1. What is the IELTS exam? |  |
| 2. How is the IELTS exam structured? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between the Academic and General Training modules in the IELTS exam? |  |
| 4. How is the IELTS exam scored? |  |
| 5. How can I prepare for the IELTS exam? |  |
















