Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > GK Olympiad for Class 5 > Notes: Science & Technology
Notes: Science & Technology | GK Olympiad for Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Light |

|
| Sound |

|
| Force |

|
| Computers |

|
| Scientific Inventions and Inventors |

|
| Scientific Instruments |

|
Introduction
- Science plays a big role in our daily lives, impacting us in many ways.
- Progress in science has led to significant improvements in technology.
- Many tools and devices we use every day are products of advanced technology, even if we don't always notice it.
What is Matter?
- Matter is anything with mass that takes up space.
- Almost everything around us on Earth is considered matter.
- All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms and molecules.
- These particles are too small to see with the naked eye and require a microscope to be seen.
Atoms and Molecules
- Atoms are the tiny building blocks of matter and are usually invisible to us.
- Molecules are formed when two or more atoms join together.
- Both atoms and molecules are extremely small and require a microscope to be seen.
Question for Notes: Science & TechnologyTry yourself: What are atoms and molecules?View Solution
States of Matter
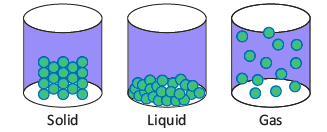
- There are three main states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases.
Solids
- Have fixed mass, volume, and shape.
- Molecules are closely packed with a strong attraction, making them hard to compress.
- Have a low temperature compared to other states.
Liquids
- Have fixed mass and volume but no fixed shape; they take the shape of their container.
- Molecules are less tightly packed than in solids, allowing slight compression.
- Have a moderate temperature.
Gases
- Have no fixed mass, volume, or shape.
- Molecules are far apart with little attraction, making them easy to compress.
- Have the highest temperature among the three states.
Light
- Light is necessary for seeing objects; without it, we cannot see anything.
Light Components
- Visible light (white light) is made of seven colors: Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red (VIBGYOR).
- Invisible parts of light include ultraviolet rays, X-rays, infrared rays, radio waves, alpha rays, gamma rays, and more.
Sources of Light
- The Sun is Earth’s main source of light.
- The Moon reflects sunlight and doesn’t produce its own light.
Types of Objects
- Luminous objects produce their own light, like the sun, stars, fireflies, bulbs, candles, and torches.
- Non-luminous objects don’t produce light; they are visible only when illuminated by luminous objects, such as mountains, rivers, buildings, and vehicles.
Did You Know?
- Light moves super fast, at about 3,00,000 kilometers per second. To help you understand how far light can go in just one minute, it travels around 1,80,00,000 kilometers in that time!
- Now, think about the distance between the Earth and the Sun. Light takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to travel from the Sun to the Earth. In that time, it covers a huge distance of about 15,00,00,000 kilometers between our planet and the Sun!
Sound
- Sound is a form of energy that creates the sensation of hearing.
- Sound is produced by vibrating objects.
- Vibrations cause particles in a medium (like air, water, or solids) to move, forming sound waves.
- Sound waves need a medium to travel through, so sound moves through solids, liquids, and gases.
- Sound travels fastest in solids because particles are closely packed.
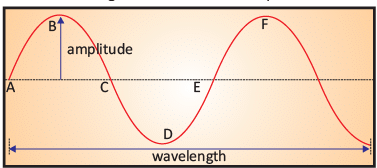
- An echo is heard when sound waves bounce back to our ears.
- Sound is represented as waves with points indicating particle positions:
1. Points A, C, and E are mean positions where particles are at rest.
2. Points B and D are the extreme positions, marking the highest and lowest points reached by the particle. - One complete vibration:
1. Involves the particle moving from mean position A to extreme B, back to mean C, then to extreme D, and returning to mean E.
2. Can also be measured from one extreme position back to the same extreme position.
Facts
- Tug of war is a game that involves using a lot of force.
- Glass is made from sand.
- The study of insects is called entomology.
Force
- Force is an invisible push or pull on an object that we can feel.
- Examples of using force: kicking a football, pulling a shopping trolley, or riding a bicycle.
- Applying force to an object can change:
1. Whether the object is at rest or moving
2. The speed of the object
3. The direction of the object’s movement
4. The shape of the object
Question for Notes: Science & TechnologyTry yourself: Which of the following states of matter has the highest temperature?View Solution
Simple Machines
- Simple machines are tools that make work easier by requiring less effort.
- They have few or no moving parts and help move, lift, or separate objects by changing the direction or amount of force.
- Common types of simple machines:
1. Lever: A rod that pivots on a point to lift or move objects.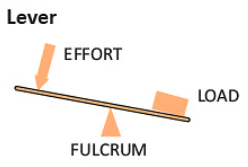 2. Wheel and Axle: A wheel attached to a rod that helps move things easily.
2. Wheel and Axle: A wheel attached to a rod that helps move things easily.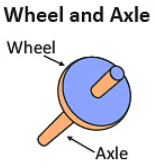 3. Pulley: A wheel with a rope to lift objects or change the direction of force.
3. Pulley: A wheel with a rope to lift objects or change the direction of force.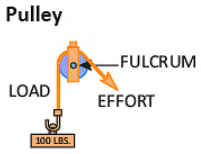 4. Inclined Plane: A sloped surface that helps raise or lower objects.
4. Inclined Plane: A sloped surface that helps raise or lower objects.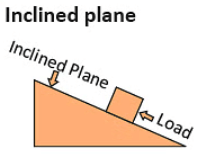 5. Wedge: A triangular tool used to split or lift objects.
5. Wedge: A triangular tool used to split or lift objects. 6. Screw: A twisted metal piece used to hold or lift things.
6. Screw: A twisted metal piece used to hold or lift things.
Computers
- Computers are important machines that help us with many tasks.
- The word "computer" comes from "compute," meaning to calculate.
- Initially, computers were only used for calculations, but now they do much more.
- Computers enable global connections through the Internet, a vast network linking devices on Earth, with satellites, and even in space.
- Today, we can control home devices like refrigerators, microwaves, and TVs with our phones, thanks to the Internet.
Some important people in the history of computers and the Internet are:
- Herman Hollerith: 'Father of Modern Machine Data Processing' for creating machines that process data automatically.
- Charles Babbage: 'Father of Computer' for designing the first mechanical computer.
- Vannevar Bush: 'Father of Information Science' for his work on managing and finding information.
- Vint Cerf: 'Father of Internet' for inventing protocols that make the Internet work.
- Tim Berners Lee: 'Father of the World Wide Web (WWW)' for creating the system to access information on the Internet.
- Alan Turing: 'Father of Computer Science' and 'Father of Artificial Intelligence' for his pioneering work in these fields.
- Ed Roberts: 'Father of Personal Computer' for making computers small and affordable for personal use.
- Ralph Baer: 'Father of Video Games' for creating early video games and consoles.
Scientific Inventions and Inventors
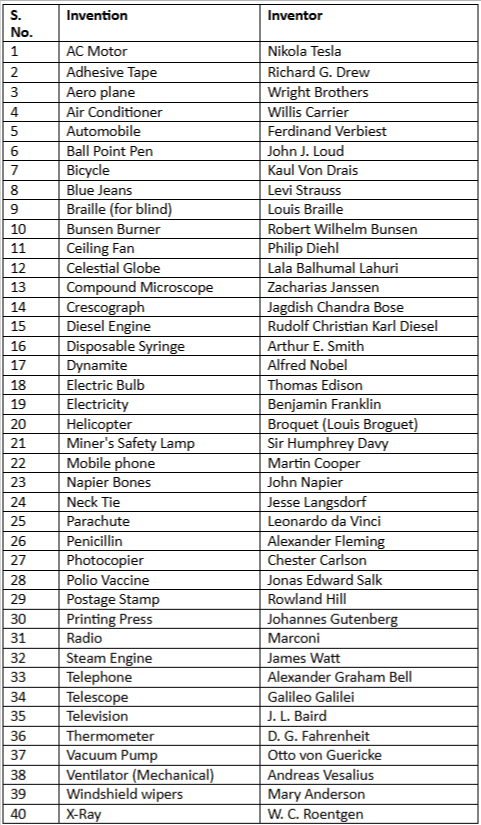
Scientific Instruments
- Altimeter: Measures an object's height from a specific level, like ground or sea level.
- Ammeter: Measures the electric current in a circuit.

- Barometer: Measures atmospheric pressure, useful for weather prediction.

- Computer: A versatile machine for tasks like typing, designing, presenting, and internet use.

- Crescograph: Measures plant growth over time.
- Hygrometer: Measures air moisture (humidity), important for weather and environment.

- Microscope: Allows us to see tiny objects like cells or germs.
- Modem: Converts digital data for internet transmission and reception.

- Odometer: Measures the distance traveled by a vehicle.

- Periscope: Allows viewing above water from underwater, used in submarines.

- Sphygmomanometer: Measures blood pressure in blood vessels.

- Telescope: Used to observe distant objects, especially in the sky.

- Thermometer: Measures temperature, such as body temperature.
The document Notes: Science & Technology | GK Olympiad for Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course GK Olympiad for Class 5.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
8 videos|19 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Science & Technology - GK Olympiad for Class 5
| 1. What are the main properties of light? |  |
Ans.Light has several key properties, including reflection, refraction, dispersion, and absorption. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface. Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another. Dispersion is the separation of light into its component colors, such as when light passes through a prism. Absorption happens when materials take in light energy.
| 2. How does sound travel and what are its properties? |  |
Ans.Sound travels in waves through different media, such as air, water, and solids. Its key properties include pitch, loudness, and timbre. Pitch is determined by the frequency of the sound waves, loudness relates to the amplitude of the waves, and timbre is the quality or color of the sound that distinguishes it from others.
| 3. What is force and how does it affect motion? |  |
Ans.Force is a push or pull that can change the motion of an object. It can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction. The effect of a force on an object depends on its size, direction, and the mass of the object. According to Newton's laws of motion, an unbalanced force is required to change an object's state of motion.
| 4. What are the different types of computers and their uses? |  |
Ans.Computers can be categorized into several types, including personal computers (PCs), laptops, tablets, and servers. PCs are commonly used for personal tasks, while laptops offer portability for work and school. Tablets provide touch-screen functionality for various applications, and servers manage resources for networks and provide services to other computers.
| 5. Who are some famous inventors and what are their contributions to science? |  |
Ans.Some famous inventors include Thomas Edison, who invented the electric light bulb; Alexander Graham Bell, known for inventing the telephone; and Marie Curie, who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. Their inventions and discoveries have significantly impacted how we live and interact with the world, advancing technology and science.
Related Searches















