Notes: Volume | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Volume |

|
| Measuring Volume |

|
| Volume of a Cuboid |

|
| Volume of a Cube |

|
| Capacity |

|
Volume is a fundamental concept in mathematics and physics that measures the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object. It's a crucial topic for the CTET and other educational exams. Here's a brief overview:
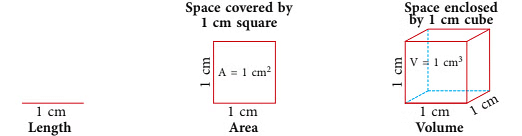
Volume is the measure of how much space occupies a three-dimensional object. It is typically measured in cubic units (e.g., cubic meters, cubic centimeters).
Units of Volume:
Common units of volume include cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), liters (L), milliliters (mL), and gallons (gal), among others.
Volume
Volume is like the inside space of something, such as a box or a ball. We measure it in cubic units because it's three-dimensional. Flat things, like book pages or a blackboard, don't have volume; instead, we measure their size using area.
Look at the following solid shapes:

Thus, we observe that solids have three dimensions—length, breadth and height.
For example:-
(i) Glass has space to fill water in it,
(ii) The box has space to fill objects or items in it.
(iii) The balloon has space to fill the air in it.
(iv) The space inside the solid is known as the volume of a solid.
The volume of a solid is the amount of space enclosed by it or the amount of space it takes up.
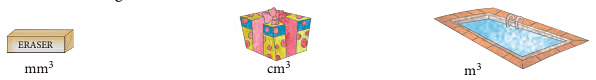
The other units used for measuring volume are cubic millimetres (mm3) and cubic metre (m3). The unit used for measuring volume depends on the size of the solid being measured.
Measuring Volume
- We say that a 1 cm cube is a unit cube and has a volume of 1 cubic centimetre (1 cu cm).
- We also write it as 1 cm3.
- To measure the volume of a solid region, we find out the number of unit cubes that make up the solid or fill the solid.
Let us study the following example.
Example 1: Find the volume of these solids by counting the number of cubes in
each solid. The volume of each small cube is 1 cm3.
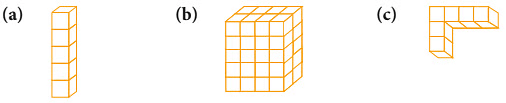
Sol: (a) There are 5 cubes in the given solid, so, volume = 5 cm3.
(b) 1st row = 8 cubes; 2nd row = 8 cubes; 3rd row = 8 cubes; 4th row = 8 cubes; 5th row = 8 cubes
∴ Volume = 8 cm3 + 8 cm3 + 8 cm3 + 8 cm3 + 8 cm3 = 40 cm3.
We can also say that there are 5 layers of cubes and each layer consists of 8 cubes. So, Volume = Number of layers × Number of cubes in each layer
V = (5 × 8) cm3 = 40 cm3.
(c) Cubes in horizontal row = 4 cubes Cubes in vertical row = 2 cubes
Volume = 4 cm3 + 2 cm3 = 6 cm3.
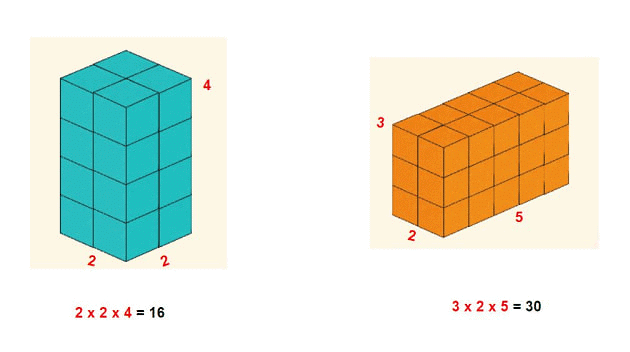
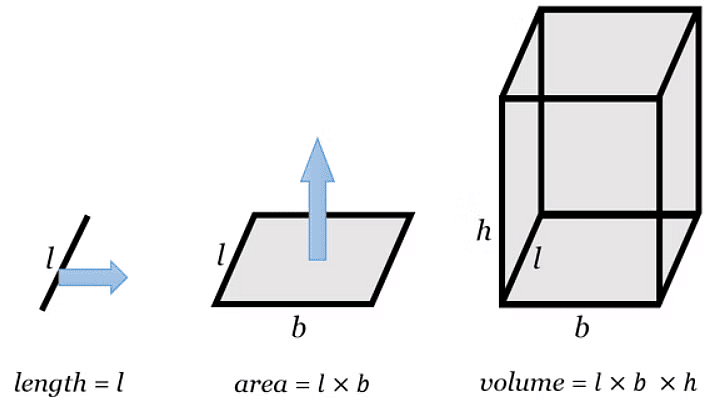
Volume of a Cuboid
- A cuboid is a shape made by stacking rectangular sheets.
- It has length, width, and height.
- The volume of a cuboid is the amount of space it takes up inside.
- Volume is measured in cubic units, like cubic meters or cubic centimetres.
- A cuboid has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 corners (vertices).
- If you change the length, width, or height, you change the volume of the cuboid.
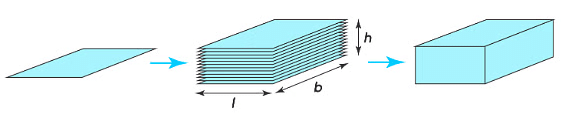
Formula for Volume of Cuboid
- To find the volume of a cuboid, we multiply the area of its base by its height.
- The area of the base is the length multiplied by the width.
- So, Volume = Length × Width × Height, which can be written as V = l × b × h.
- This means the volume of the cuboid is found by multiplying its length, width, and height together.
 Volume of Cuboid
Volume of Cuboid
Solved Examples for Volume of Cuboid
Example 1: See how a cuboid is built from 1-centimetre cubes and how we can find its volume.
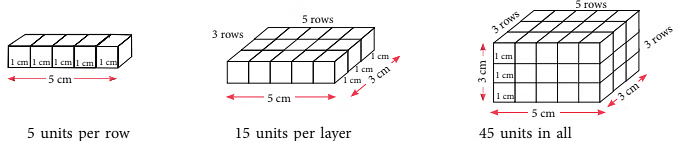
Sol:

Example 2: The given cuboids are built from 1-centimetre cubes. Find the volume of each solid.
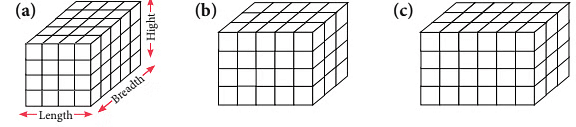
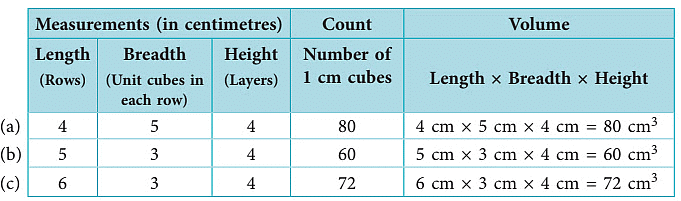
Sol: Let us study the table given below using these cuboids as shown.
Example 3: Find the volume of a cuboid whose length, breadth and height are 15 cm, 11 cm and 6 cm, respectively.
Sol: Length of the cuboid = 15 cm
Breadth of the cuboid = 11 cm
Height of the cuboid = 6 cm
Volume of the cuboid = length × breadth × height
= (15 × 11 × 6) cu cm = 990 cu cm.
Volume of a Cube
- The volume of a cube is the total space inside it.
- A cube is a solid object with six square faces.
- All sides of a cube are the same length.
- A cube is also called a regular hexahedron.
 Cube
Cube - It's one of the five Platonic solid shapes.
- Volume is measured in cubic units like cubic meters or cubic inches.
- The SI unit for volume is cubic meters (m³), based on a cube with each side measuring 1 meter.
- The USCS units for volume include inches cubed and yards cubed.
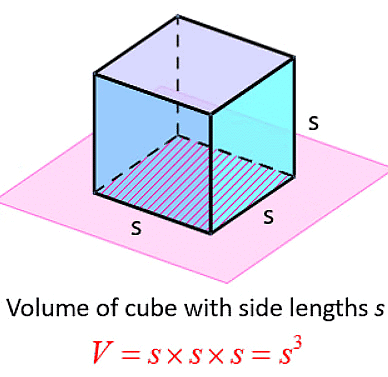
Formula for Volume of Cube
- To find the volume of a cube, you multiply the length of one side by itself three times.
- This means you "cube" the length of the side.
- So, if the length of one side of a cube is 4, you find the volume by doing 4 x 4 x 4, which is written as 4³.
- The formula for the volume of a cube is: Volume = side length × side length × side length, or simply V = s³.
- Here, 's' represents the length of one side of the cube.
Solved Examples for Volume of Cube
Example 1: Find the volume of a cube whose one edge measures 2 cm.
Sol: Length of each side of the cube = 2 cm.
Volume of the cube = side × side × side
= (2 × 2 × 2) cu cm = 8 cu cm.
Example 2: A box is 20 cm by 18 cm and 40 mm thick. How many cubic centimetres of space will the books keep in it occupy?
Sol: Length = 20 cm
Breadth = 18 cm
Height = 40 mm = (40 ÷ 10) cm = 4 cm
∴ Volume of the box = (20 × 18 × 4) cu cm = 1440 cu cm.
Hence, the books will occupy 1440 cu cm of space.
Capacity
- The volume is the amount of space a solid takes up or encloses.
For example, the amount of space in a swimming pool (in m3).
1. The capacity is the amount of liquid that a given solid can hold. Thus, the capacity of the swimming pool is the amount of water needed to fill the swimming pool. 2. The capacity of a gas cylinder is the amount of gas it can hold.3. The capacity of a fuel tank in a vehicle is the amount of petrol or diesel needed to fill it full.
2. The capacity of a gas cylinder is the amount of gas it can hold.3. The capacity of a fuel tank in a vehicle is the amount of petrol or diesel needed to fill it full. - The standard unit of capacity is litre (L). Liquids are often measured in litres or millilitres.
Edurev Tips:
- 1 litre = 1000 mL = 1000 cm3, 1 mL = 1 cm3
- 1 cm3 = 1 mL,
- 1 m3 = 100 cm × 100 cm × 100 cm
= 1000000 cm3
= 1000000 mL = 1000 L
Solved Examples for Capacity
Example 1: A rectangular tank measures 2.5 m by 3 m by 4 m and is full of water. What is its capacity in liters?
Sol: The tank measures 2.5 m by 3 m by 4 m, i.e., 250 cm by 300 cm by 400 cm.
Volume of the tank = (250 × 300 × 400) cm3
Since 1 litre = 1000 cm3,
so capacity in litres = 250 × 300 × 400/1000 L = 30000 L.
Example 2: A machine for making ice freezes 5.76 litres of water into ice bricks measuring 3 cm by 2 cm by 1 cm. How many ice bricks will be made?
Sol: Volume of 1 ice brick = (3 × 2 × 1) cm3 = 6 cm3
Volume of water = 5.76 litres = 5.76 × 1000 cm3 = 5760 cm3
∴ Number of ice bricks made = 5760 ÷ 6 = 5760/6 = 960.
Example 3: There are 1.75 litres of water in the rectangular container shown. How much more water is needed to fill the container completely?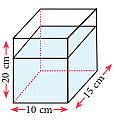
Sol: Capacity of the rectangular container = 15 cm × 10 cm × 20 cm
= 3000 cm3 = 3 L (Q 1000 cm3 = 1 L)
Volume of water in the container = 1.75 L
∴ Volume of water needed to fill the container
= 3 L – 1.75 L = 1.25 L
= (1.25 × 1000) mL = 1250 mL.
|
41 videos|151 docs|72 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Volume - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. How do you calculate the volume of a cuboid? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between volume and capacity? |  |
| 3. How do you calculate the volume of a cube? |  |
| 4. How can you measure the volume of an irregular object? |  |
| 5. Can the volume of an object change? |  |

 2. The capacity of a gas cylinder is the amount of gas it can hold.3. The capacity of a fuel tank in a vehicle is the amount of petrol or diesel needed to fill it full.
2. The capacity of a gas cylinder is the amount of gas it can hold.3. The capacity of a fuel tank in a vehicle is the amount of petrol or diesel needed to fill it full.



















