Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > English Grammar for Class 6 > Noun Genders
Noun Genders | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Gender in Nouns? |

|
| Types of Noun Genders |

|
| Ways to Form Feminine Genders |

|
| Examples of Masculine and Feminine Nouns |

|
What is Gender in Nouns?
In English grammar, gender is used to classify nouns based on their association with males, females, or neutral objects.
Types of Noun Genders
- Masculine Gender: Refers to male living beings.
Examples: Man, Boy, King, Lion, Father, Uncle - Feminine Gender: Refers to female living beings.
Examples: Woman, Girl, Queen, Lioness, Mother, Aunt - Common Gender: Refers to nouns that can be used for both males and females.
Examples: Teacher, Doctor, Student, Child, Friend - Neuter Gender: Refers to non-living things without life.
Examples: Table, Book, Pen, Chair, Water, Air
Ways to Form Feminine Genders
By Adding ‘-ess’ to Masculine Nouns
- Actor → Actress
- Lion → Lioness
- Poet → Poetess
By Using a Completely Different Word
- King → Queen
- Man → Woman
- Husband → Wife
By Adding a Prefix or Suffix
- Landlord → Landlady
- He-goat → She-goat
By Changing the Word Partially
- Hero → Heroine
- Emperor → Empress
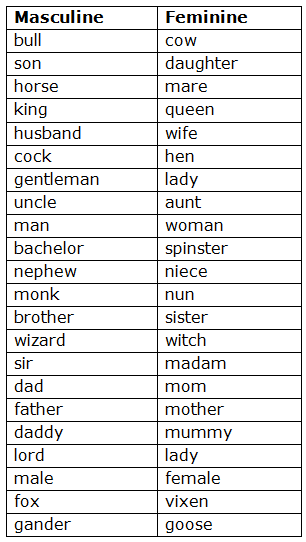
Examples of Masculine and Feminine Nouns
By making a change in the last part of the word: Some Feminine are formed by simply adding –ess to the Masculine.
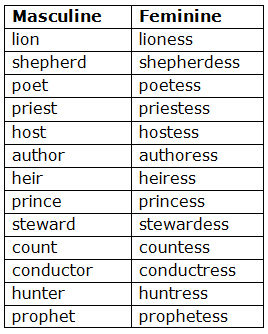
Sometimes the form is slightly changed before –ess is added.
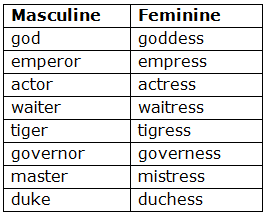
Note – Also note how the following Feminines are formed:
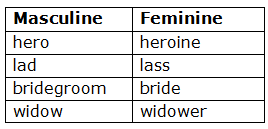
By adding a word after or before: The Feminine of a Compound Noun is formed by changing that part which shows the gender.
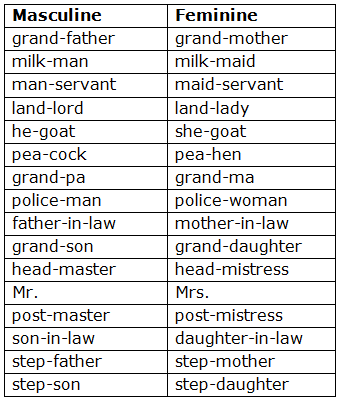
By changing the word: Many Nouns have different words for the Masculine and the Feminine.
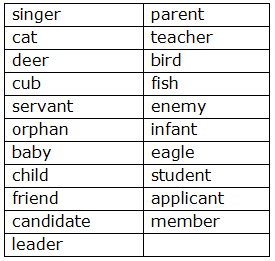
Common Gender:
Key Points to Remember
- Some nouns do not change their form (e.g., cousin, teacher, singer).
- Neuter nouns are usually objects or elements of nature.
- Common gender nouns can be used for both males and females.
The document Noun Genders | English Grammar for Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course English Grammar for Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
49 videos|500 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Noun Genders - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What are noun genders? |  |
Ans. Noun genders refer to the classification of nouns into masculine, feminine, and neuter genders based on their grammatical gender in a particular language.
| 2. How do noun genders affect grammar? |  |
Ans. Noun genders affect grammar by influencing the agreement of other words, such as adjectives and articles, with the noun in terms of gender, number, and case. This agreement is necessary for grammatical correctness and clarity in sentences.
| 3. Are there any rules to determine noun genders in languages? |  |
Ans. Yes, there are rules in certain languages that can help determine the gender of a noun. However, these rules can vary greatly between languages and may not always be predictable. In some cases, the gender of a noun may need to be memorized or learned through exposure to the language.
| 4. Can the gender of a noun change in different languages? |  |
Ans. Yes, the gender of a noun can change when comparing different languages. For example, a noun that is masculine in one language may be feminine in another. It is important to learn the gender of nouns in each specific language, as it cannot always be assumed to be the same as in one's native language.
| 5. What challenges do noun genders pose for language learners? |  |
Ans. Noun genders can pose challenges for language learners, particularly for those whose native language does not have grammatical gender. Remembering and correctly using the appropriate gender for nouns can be difficult, as it requires memorization and understanding of language-specific rules. Mistakes in noun gender agreement can lead to grammatically incorrect sentences.
Related Searches





















