Nucleic Acids: Structure & Bonding | Biology for ACT PDF Download
Nucleic Acids
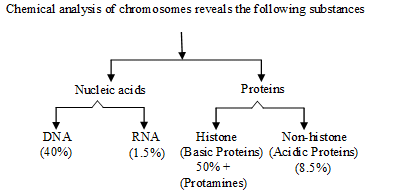
Chemical Composition
Chemical Composition
- Meischer discovered nucleic acids in nucleus of pus cell and called it ''nuclein''.
- The name nucleic acid proposed by ''Altman''.
Nucleic acids are polymer of nucleotides = nitrogen base + pentose + phosphate
A. Nitrogenous Base
On the basis of structure, nitrogen bases are broadly of two types :
1. Pyrimidines – Consist of one pyrimidine ring. Skeleton of ring composed of two nitrogen and four Carbon atoms e.g. Cytosine, Thymine and Uracil.
2. Purines – Consist of two rings i.e. one pyrimidine ring (2N + 4C) and one imidazole ring (2N + 3C) e.g. Adenine and Guanine.
B. Pentose Sugar
Nitrogen base forms bond with first carbon of pentose sugar to form a nucleoside. Nitrogen of first place (N1) forms bond with sugar in case of Pyrimidines while in purines nitrogen of ninth place (N9) forms bond with sugar.
C. Phosphate
Phosphate forms ester bond (covalent bond) with fifth carbon of sugar to form a complete nucleotide.
Types of Nucleosides and Nucleotides:
1. Adenine + Ribose = Adenosine
Adenosine + Phosphate = Adenylic acid
2. Adenine + Deoxyribose = Deoxy adenosine
Deoxy adenosine + P = Deoxy adenylic acid
3. Guanine + Ribose = Guanosine
Guanosine + P = Guanylic acid
4. Guanine + Deoxyribose = Deoxy guanosine
Deoxy guanosine + P = Deoxy guanylic acid
5. Cytosine + Ribose = Cytidine
Cytidine + P = Cytidylic acid
6. Cytosine + Deoxyribose = Deoxycytidine
Deoxycytidine + P = Deoxycytidylic acid
7. Uracil + Ribose = Uridine
Uridine + P = Uridylic acid
8. Thymine + Deoxyribose = Deoxy thymidine
Deoxythymidine + P = Deoxythymidylic acid
|
226 videos|247 docs|150 tests
|
FAQs on Nucleic Acids: Structure & Bonding - Biology for ACT
| 1. What are the chemical components of nucleic acids? |  |
| 2. How are nucleotides bonded to form nucleic acids? |  |
| 3. What is the structure of nucleic acids? |  |
| 4. What is the function of nucleic acids in living organisms? |  |
| 5. How do nucleic acids contribute to the diversity of life? |  |

















