Nucleotide Structure | Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT PDF Download
What is Nucleotide?
A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities. ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) acts as the energy currency of cells. Nucleotides form various coenzymes and cofactors, such as NAD, NADP, FAD, coenzyme A, etc. and are essential for many metabolic processes.
Nucleotide Structure – What does a nucleotide look like?
A nucleotide consists of three units, which are covalently linked. They are:
- Nitrogenous bases – Purine and Pyrimidine
- Pentose Sugar – Ribose and Deoxyribose
- Phosphate – monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate
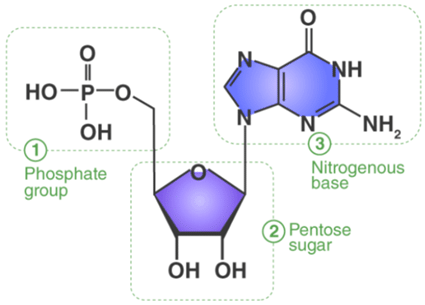
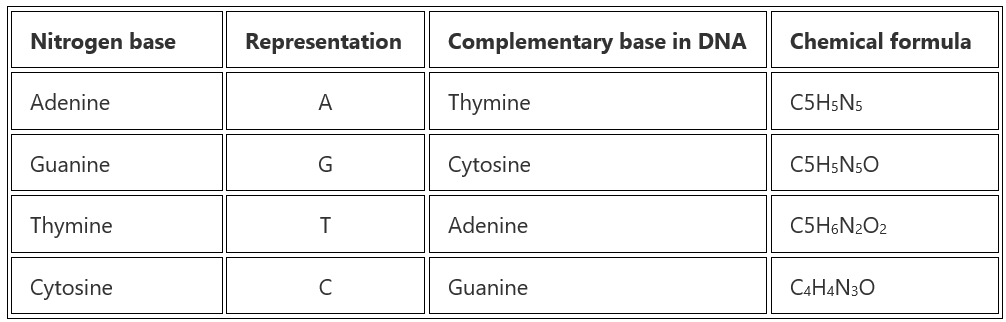
1. Nitrogenous Base: They comprise pyrimidine or purine base. DNA contains adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T) whereas RNA contains adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil (U).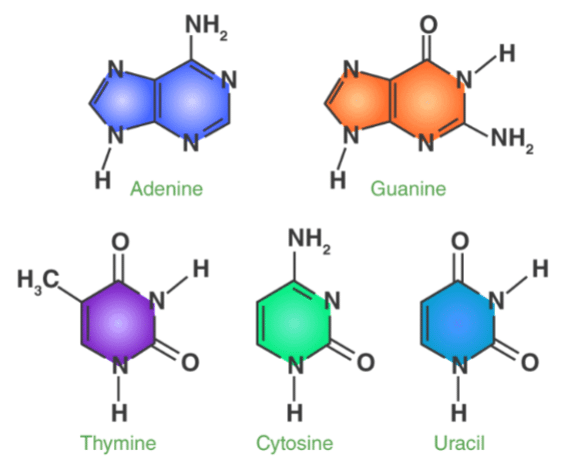
2. Sugar: A nucleotide comprises a pentose sugar. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) contains deoxyribose sugar and RNA (Ribonucleic acid) contains a ribose sugar.
A Nitrogenous base attached with the sugar is called “Nucleoside”.
3. Phosphate: Phosphate is associated with the sugar of nucleoside by an ester bond with the 5thC hydroxyl group. Nucleotides at least contain one phosphate group.
Phosphate of one nucleotide attaches to the 3rd C-OH group of the sugar of the 2nd nucleotide, thereby forming 5’ → 3’ linkage.
In DNA (double helix) there are two antiparallel strands of polynucleotides that are linked together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases. Purine pairs with pyrimidine base, A pairs with T and G pairs with C by two and three hydrogen bonds respectively.
In RNA instead of thymine (T), A pairs with U.
Phosphate group interlinks the sugar molecules of two nucleotides forming a chain. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides. Sugar phosphate chain forms the backbone of a polynucleotide chain. When the phosphate group attaches to the hydroxyl group of the same sugar, it forms cyclic nucleotide, they are present as a single monomer, e.g. cAMP, cGMP used in intracellular signal transduction processes.
How do Nucleotides and Nucleosides Differ?
Nucleoside = Nitrogenous base + Sugar
Nucleosides are named as Adenosine, Guanosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Uridine
Nucleotide = Nucleoside + Phosphate
Nucleotides are named as Adenylic acid, Guanylic acid, Thymidylic acid, Cytidylic acid and Uridylic acid.
Nucleotides are also named as nucleoside mono, di or triphosphate, based on the number of phosphate groups attached to it, e.g. Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
DNA and RNA only contain nucleotides.
Other than polynucleotide chain of DNA and RNA, nucleotides are present in the body in various forms and are essential for life, e.g. ATP, cAMP, NAD+, NADP+, FAD, coenzyme A, etc.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP): ATP is the energy currency of the cell. The energy required for metabolic processes is derived from ATP. It also acts as a coenzyme and is a precursor of DNA and RNA synthesis.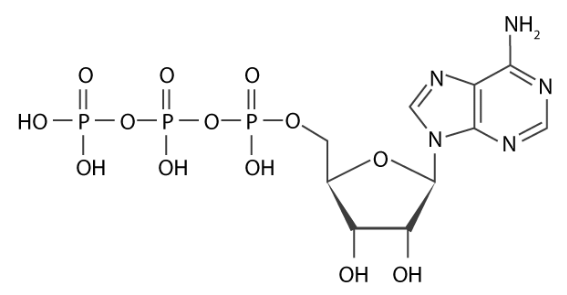
ATP Structure (Adenosine triphosphate)
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP): cAMP acts as a secondary messenger and used in signal transduction. It plays an important role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.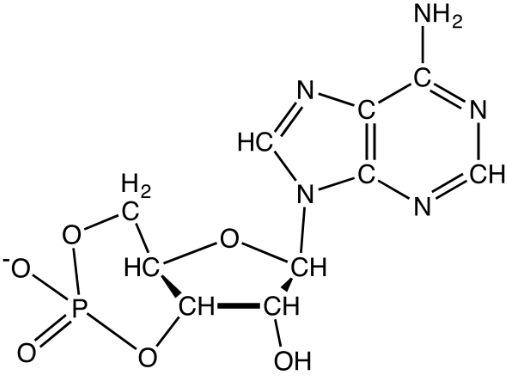
cAMP (3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD): NAD is a dinucleotide. It contains two nucleotides joined by phosphate groups. One of the nucleotides contains adenine base and the other nucleotide has nicotinamide. They play an important role in metabolic processes and act as an electron carrier. They exist in two forms, oxidised NAD+ and reduced NADH.
Similarly, NADP+ (NADPH) is also a cofactor used in the Calvin cycle and other anabolic processes.
The FAD is an adenine dinucleotide, which acts as a coenzyme and plays a key role in many enzymatic reactions.
Nitrogenous Bases – Structure of Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil
There are five nitrogenous bases, namely Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine and Uracil. They are nitrogen containing compounds that form an important part of the genetic code. The structures and description of the five nitrogenous bases are jotted below.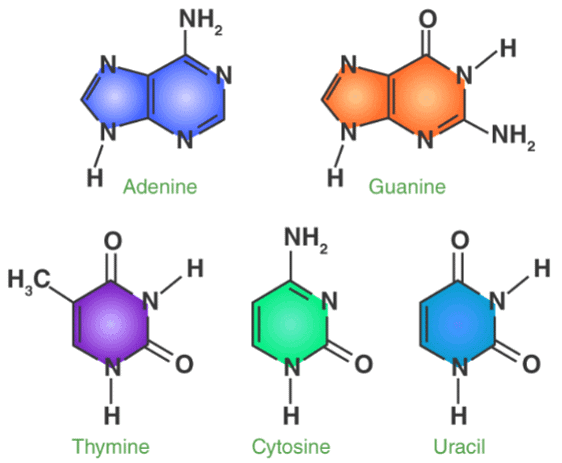
- Adenine Structure: Adenine is a purine derivative that is made up of two nitrogen containing rings. It forms a double bond with thymine in the nucleotide structure.
- Guanine Structure: Guanine is again, a purine derivative that is made up of two nitrogen containing rings. It forms a triple bond with cytosine in the nucleotide structure.
- Thymine Structure: Thymine is a pyrimidine derivative that is made up of a single ring containing nitrogen. It is also known as 5-methyluracil.
- Cytosine Structure: Cytosine, like thymine, is a pyrimidine derivative that is made up of an aromatic ring attached with an amino and keto group.
- Uracil Structure: Uracil is also a pyrimidine derivative that can also be thought of as a demethylated form of thymine.
Nucleotide Function
- Nucleotides are the building block of DNA and RNA. They contain genetic information
- Nucleotides act as coenzymes, which are required to catalyse many biochemical reactions by enzymes
- Energy is stored in our body as ATP. When there is a need for the energy they get converted to ADP or AMP. ATP also acts as a coenzyme
- NAD, NADP has an essential role to play in many redox reactions, they act as an electron carrier
- cAMP helps in transporting chemical signals and metabolic regulation
Biological importance of Nucleotides
- Forms the constituents of DNA and RNA – They serve as building blocks of nucleic acids and are the carriers of activated metabolites for the process of biosynthesis
- Involved in storing chemical energy
- Required for DNA replication and RNA transcription in stages that rapidly divide
- Provides cellular energy sources and other metabolic functions
- Required for chemical associations in the response of cells to the hormones and other extracellular stimuli
- Serve as structural components of enzyme cofactors and other metabolic intermediates
|
129 videos|60 docs|24 tests
|





















