ICAI Notes- Number Series, Coding and Decoding and Odd Man Out - CA Foundation PDF Download
SERIES
Series Classified into
A. Number Series
B. Alphabet Series
A. NUMBER SERIES
Case 1: Missing terms of the series
In this type the questions we have to identify the missing term of the series real according to a specific pattern of the series rule to form its code. The students are required to detect the missing number of the series and answer the questions accordingly.
Example 1: Find the missing term of the series 2, 7, 16, ______ , 46, 67, 92
Explanation: Here the terms of the series are +5, +9, +13, +17, +21 , +25…
Thus, 2 + 5 = 6; and 7 + 9 = 16 …
So missing term = 16 + 13 = 29
Example 2: Find the wrong terms of the series 9, 29, 65, 126, 217, 344
Explanation: 23+1 , 33 + 1, 43 +1,…….
Here 29 is wrong term of series
Example 3: Find the missing term of the series 1,9, 25, 49, 81, 121, .............
Solution: The given terms of the series are consists square of consecutive odd number 12, 32, 52, 72, ....
So missing value = 132 = 169
B. ALPHABET SERIES
Alphabet series consists of letters of the alphabet placed in a specific pattern. For example, the series are in the following order of the numbers.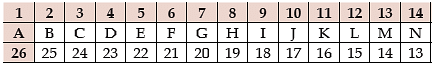
Example 4: Find the next term of the series BKS, DJT, FIU, HHV?
Explanation: In each term, the first letter is moved two steps forward, the second letter one step backward and third letter one step forward to obtain the corresponding letter of the next term. So the missing term is JGW.
C. LETTER SERIES:
This type of question usually consist of a series of small letters which follow a certain pattern.
However some letters are missing from the series. These missing letters are then given in a proper sequence as one of the alternatives.
Example 5: aab, ____, aaa, bba, ____
(a) baa (b) abb (c) bab (d) aab
1) The first blank space should be filled in by ‘b’ so that we have two a’s by two b’s.
2) The second blank place should be either `a’, so that we have three a’s followed by three b’s.
3) The last space must be filled in by ‘a’.
4) Thus we have two possible answers – ‘baa’and ‘bba’.
5) But only ‘baa’appers in the alternatives.
So the answer (a) is correct.
CODING AND DECODING
Before transmitting, the data is encoded and at receiver side encode data is decoded in order to obtain original data by determining common key in encoded data.
The Coding and Decoding is classified into, they are type.
Type 1: Letter Coding
Type 2: Number Coding
Type 1: Letter Coding
In this type the real alphabets in a word are replaced by certain other alphabets according to a specific rule to form its code. The candidate is required to detect the common rule and answer the questions accordingly.
Case1: To form the code for another word
Example 6: If in a certain language MYSTIFY is coded as NZTUJGZ, how is MENESIS coded in that language?
Explanation: Clearly, each letter in the word MYSTIFY is moved one step forward to obtain the corresponding letter of the code.
So, in MENESIS, N will be coded as O, E as F, M as N and so on. Thus, the code becomes NFOFTJT.
Example 7: If TAP is coded as SZO, then how is FRIEND coded?
Explanation: Clearly each letter in the word TAP is moved one step backward to obtain the corresponding letter of the code.
Thus, in FRIEND, F will be coded as E, R as Q , I as G, E as D, N as M and D as C. So, the code becomes EQGDMC.
Example 8: In a certain code, MENTION is written as LNEITNO. How is PRESENT written in that code?
Explanation: Clearly, to obtain the code, the first letter of the word MENTION is moved one step backward and the remaining letters are.
Reversed in order, taking two at a time. So, in PRESENT, P will be coded as O, and the sequence of the remaining letter in the code would be ERESTN. Thus the code becomes OERESTN. Hence, The answer is OERESTN.
Case 2: To find the word by analysing the given code (DECODING)
Example 9: If in a certain language CARROM is coded as BZQQNL, which word will be coded as HORSE?
Explanation: each letter of the word is one step ahead of the corresponding letter of the code
So, H is coded as I, O as P, R as S, S as T and E as F. HORSE is coded a IPSTF.
Type 2: Number Coding
In these questions, either numerical code values are assigned to a word or alphabetical code letters are assigned to the numbers. The candidate is required to analyse the code as per the directions.
Case 1: When a numerical code values are assigned to words.
Example 10: If in a certain language A is coded as 1, B is coded as 2, and so on, how is AICCI is coded in that code?
Explanation: As given the letters are coded as
So in AICCI, A is coded as 1, I as 9,and C as 3. Thus, AICCI is coded as 19339.
Example 11: If PAINT is coded as 74128 and EXCEL is coded as 93596, then how would you encode ANCIENT ?
Explanation: Clearly, in the given code, the alphabets are coded as follows: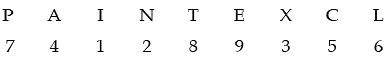
So, in ANCIENT, A is coded as 4, N is coded as 2, C as 5, I is coded as 3, E as 9, and T as 8. Hence, the correct code is 4251928.
Case 2: Number to letter coding.
Example 12: In a certain code, 2 is coded as P, 3 as N, 9 as Q, 5 as R, 4 as A and 6 as B. How is 423599 coded in that code?
Explanation: Clearly as given, 4 as A, 2 as P, 3 as N and 5 is coded as R, 9 as Q. So, 423599 is coded as APNRQQ.
ODD MAN OUT
Classification means ‘to assort the items’ of a given group on the basis of a certain common quality they possess and then spot the stranger or ‘odd one out’. These questions are based on words, letters and numerals. In these types of problems, we consider the defining quality of particular things. In these questions, four or have elements are given,out of which one does not belong to the group. You are required to find the ’odd one’.
Example 13: January, May, July, November
(a) January (b) May (c) July (d) November
Explanation: All the months above are 31 days , whereas , November 30 days
Answer: (d)
Example 14: 10, 14, 16, 18, 23, 24 and 26
(a) 26 (b) 17 (c) 23 (d) 9
Explanation: Each of the above series are even number, except 23.
Answer: (c)
Example 15: 6, 9, 15, 21, 24, 26, 30
(a) 9 (b) 26 (c) 24 (d) 30
Explanation: All are multiples of 3, except 26, answer (b)
Answer: (b)
Example 16: 1, 5, 14, 30, 51, 55, 91
(a) 5 (b) 55 (c) 51 (d) 91
Explanation: Each pattern is 12, 12 + 22, 12 + 22 + 32, 12 + 22 + 32 + 42, 12 + 22 + 32 + 42+ 52, 12 + 22 + 32 + 42 + 52 + 62
But 51, is not of the form.
Answer: (c)
Example 17: 16, 25, 36, 62, 144, 196, 225
(a) 36 (b) 62 (c) 196 (d) 144
Explanation:
Each of the number except 62, is a perfect square.
Answer: (b)
FAQs on ICAI Notes- Number Series, Coding and Decoding and Odd Man Out - CA Foundation
| 1. What are number series in the context of the CA Foundation exam? |  |
| 2. How can I improve my skills in solving number series questions for the CA Foundation exam? |  |
| 3. What is coding and decoding in the CA Foundation exam? |  |
| 4. How can I prepare for coding and decoding questions in the CA Foundation exam? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the 'Odd Man Out' concept in the CA Foundation exam? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|


















