Types of Number Series | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
Number series is a form of sequence, where some numbers are mistakenly put into the series of numbers and some number is missing in that series, we need to observe first and then find the accurate number to that series.
A sequence is the list of numbers written in the specific order.
Example: 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36……..
Questions on number series are common in most of MBA entrance examinations. The questions on this topic are based on the numerical sequence that follows a logical pattern. These patterns are based on basic mathematical concepts.
The different types of series and their examples are listed below:
(a) Prime Number Series
A series based on prime numbers in a specific order and generally one number is missing or wrongly placed.
Example 1: Find the next term of the series 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, ……...
Solution:
► In the above series, all numbers are odd, but we don’t have 9 after 7.
► Therefore, we need to look for some other pattern.
► We observe all numbers are prime; hence it’s a prime number series; hence the next term will be 17.
Example 2: Find the term in place of question mark 8, 10, 13, 18, 25, ?
Solution:
Here the difference between consecutive terms :
- 10 – 8 = 2
- 13 – 10 = 3
- 18 – 13 = 5
- 25 – 18 = 7.
Hence the differences 2, 3, 5 , 7 form a prime number series.
Hence the next difference should be the next prime number after 7, which is 11.
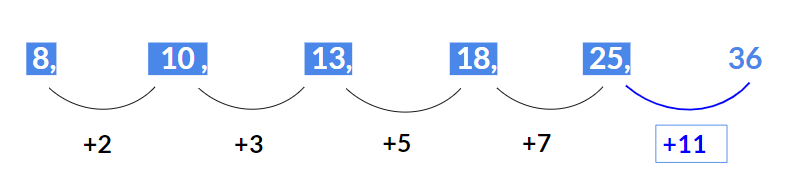
Therefore, the next missing term will be 25 + 11 = 36.
Example 3: 5 , 24 , 122 , 340, ?
Solution:
In the above series, the pattern that is being followed is as given below:
- First term 5 = 23 – 3
- Second term 24 = 33 – 3
- Third term 122 = 53 – 3
- Fourth term 340 = 73 – 3
We observe that the series is [(prime)3 – 3].
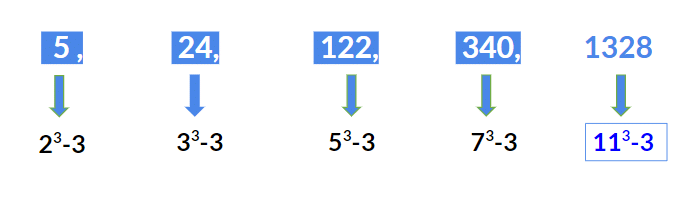 Hence the next term should be 113 – 3 = 1331 - 3 = 1328.
Hence the next term should be 113 – 3 = 1331 - 3 = 1328.
(b) Perfect Square Series
A series based on Perfect squares in a specific order and generally one number is missing or wrongly placed.
Example 1: Find the next term of the given series 25, 49, 81, 121, ……
Solution:
The above series is a perfect squares series of consecutive odd numbers starting from 5 i.e.
- 25 = 52
- 49 = 72
- 81 = 92
- 121 = 112
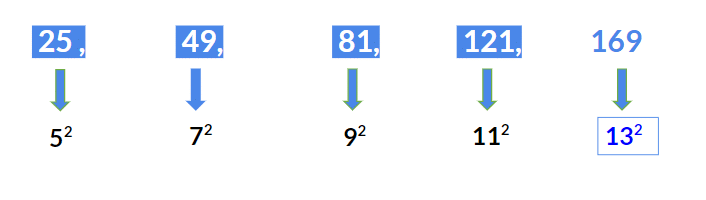 Hence next term will be 132 = 169.
Hence next term will be 132 = 169.
Example 2: Find the next term in the given series 1, 2, 6, 15, 31……….
Solution:
Here the difference between consecutive terms are:
- 2 – 1 = 1
- 6 – 2 = 4
- 15 – 6 = 9
- 31 – 15 = 16
We observe the differences 1, 4, 9, 16 are perfect squares.
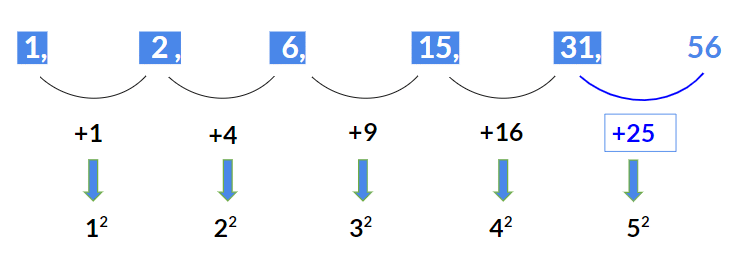
Hence the next term should be 31 + 25 = 31 + 52 = 56.
Example 3: 0, 5, 8, 17, 24, ?
Solution:
In the above series, the pattern that is being followed is as given below:
► First term 0 = 12 – 1
► Second term 5 = 22 + 1
► Third term 8 = 32 – 1
► Fourth term 17 = 42 + 1
► Fifth term 24 = 52 – 1
We observe that the series is alternately [(prime)2 – 1] and [(prime)2 + 1]
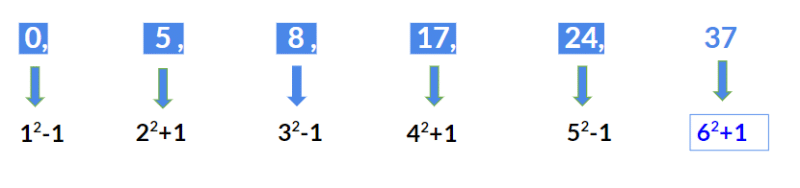
Hence the next term should be 62 + 1 = 37.
(c) Perfect Cube Series
A series based on Perfect cubes in a specific order and generally one number is missing or wrongly placed.
Example 1: Find the next term 512, 729, 1000, 1331, ?
Solution:
The above series is a perfect cube series:
- First term 512 = 83
- Second term 729 = 93
- Third term 1000 = 103
- Fourth term 1331 = 113
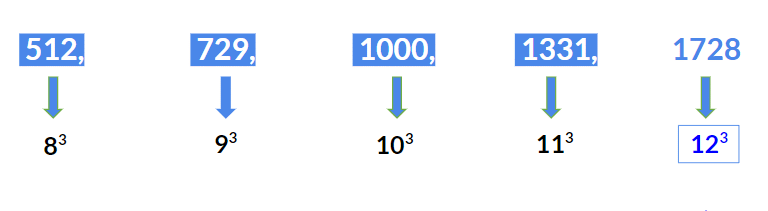 Hence the next term will be 123 = 1728.
Hence the next term will be 123 = 1728.
Example 2: Find the next term 63, 124, 215, 342, 511, ?
Solution:
Here the series is formed following the given rule:
- 63 = (43 - 1)
- 124 = (53 - 1)
- 215 = (63 - 1)
- 342 = (73 - 1)
- 511 = (83 - 1)
Hence next term should be (93 - 1) = 728
(d) Arithmetic Series
A series in which the next term is obtained by adding or subtracting a constant number to its previous term.
Example 1: Find the next term 7, 12, 17, 22, 27, ?
Solution:
The above series is an Arithmetic series where 5 is added to each term to get the next term i.e.
- 12 = 7 + 5
- 17 = 12 + 5
- 22 = 17 + 5
- 27 = 22 + 5
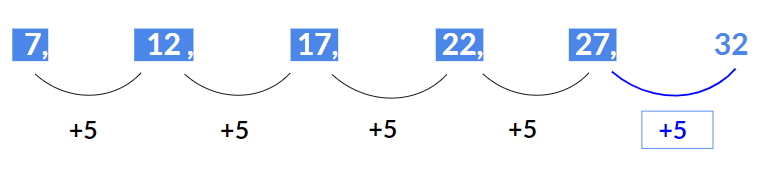 Hence next term will be 27 + 5 = 32.
Hence next term will be 27 + 5 = 32.
Example 2: Write the missing term 29, 23, 17, 11, ?
Solution:
The above series is an Arithmetic series where 6 is subtracted from each term to get the next term i.e.
- 29 – 6 = 23
- 23 – 6 = 17
- 17 – 6 = 11
Hence next term will be 11 - 6 = 5.
(e) Geometric Series
A series where each successive number is obtained by either multiplying or dividing the previous number by a specific number.
Example 1: Find the missing term 3, 12, 48, 192, ?
Solution:
Here each number is multiplied by 4 to get the next number i.e.
- 12 = 3 x 4
- 48 = 12 x 4
- 192 = 48 x 4
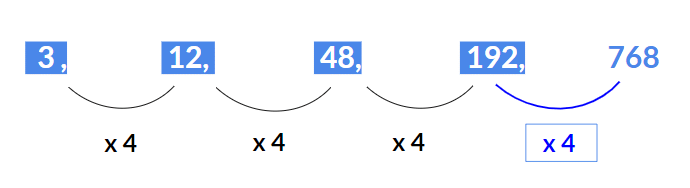 Hence next term will be 192 x 4 = 768.
Hence next term will be 192 x 4 = 768.
Example 2: Find the next term 729, 243, 81, 27, ?
Solution.
Here each number is divided by 3 to get the next number.
- 729/3 = 243
- 243/3 = 81
- 81/3 = 27
Hence next term will be 27/3 = 9.
(f) Mixed Series
A series where more than one pattern is arranged in a single series.Example 1: Find the missing term 2, 8, 26, 80, 242, ?
Solution:
Here the pattern is (x 3 + 2).
- 2 x 3 + 2 = 8
- 8 x 3 + 2 = 26
- 26 x 3 + 2 = 80
- 80 x 3 + 2 = 242
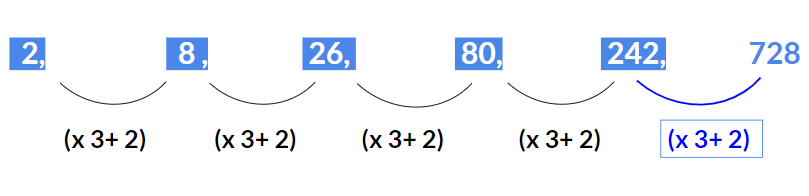 Hence missing term will be242 x 3 + 2 = 728
Hence missing term will be242 x 3 + 2 = 728
Example 2: Find the next term 5, 12, 27, 59, ?
Solution:
Here each term is multiplied by 2 and consecutive prime numbers are added.
- 5 x 2 + 2 = 12
- 12 x 2 + 3 = 27
- 27 x 2 + 5 = 59
Hence next term will be 59 x 2 + 7 = 125
(g) Arithmetic – Geometric Series
A series which is a combination of Arithmetic and Geometric series.
Example: Find the next term 3, 5, 10, 12, 24, 26, ?
Solution:
Here the pattern is (+ 2, x 2, + 2, x 2 …..)
- 3 + 2 = 5
- 5 x 2 = 10
- 10 + 2 = 12
- 12 x 2 = 24
- 24 + 2 = 26
Hence the next term will be 26 x 2 = 52
(h) Alternate Series
A series where two series is combined into a single series.
Example 1: Find the next term 2, 3, 5, 8, 8, 13, 11, ?
Solution:
► Here alternate terms starting with 2 forms an Arithmetic series with a common difference as 3. (2, 5, 8, 11)
► Also, alternate terms starting with 3 forms another Arithmetic series with a common difference as 5. ( 3, 8, 13,..)
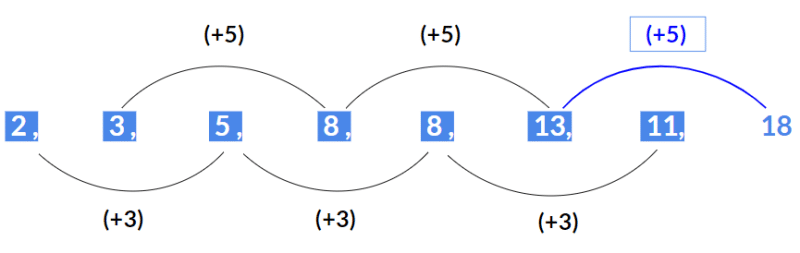 Hence next term will be 18.
Hence next term will be 18.
Example 2: Find the next term 3, 5, 7, 10, 11, 15, 15, ?
Solution:
Here alternate terms starting with 3 forms an Arithmetic series with a common difference as 4. (3, 7, 11, 15)
Also, alternate terms starting with 5 forms a Geometric series with a common ratio as 2. (5, 10, 15)
Hence next term will be 20.
In any MBA entrance examinations, questions on Number series can be categorized as three types which are discussed below:
➢ Type 1
A numerical series in which a specific number is missing. Hence, we need to find the missing term or the next term.Example 1: Find the next term 4, 6, 9, 13, 18, ?
Solution:
Here the pattern being followed is (+ 2, + 3, + 4, + 5 and so on)
- 4 + 2 = 6
- 6 + 3 = 9
- 9 + 4 = 13
- 13 + 5 = 18
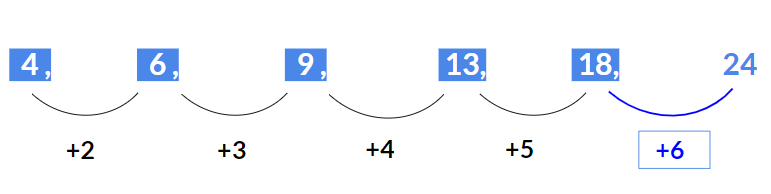 Hence next term will be 18 + 6 = 24
Hence next term will be 18 + 6 = 24
Example 2: Find the missing term 8, 24, 12, ?, 18, 54
Solution:
Here the pattern is (x 3 ; ÷ 2, x 3, ÷ 2 and so on)
- 8 x 3 = 24
- 24 ÷ 2 = 12
- 12 x 3 = 36
- 36 ÷ 2 = 18
- 18 x 3 = 54
Hence missing term will be 12 x 3 = 36
➢ Type 2
A numerical series in which a number is wrongly placed.
Example 1: Find the wrong term 100, 121, 143, 169, 196, 225.
Solution:
The above series is a perfect square series starting with 10.
- 102= 100
- 112= 121
- 122 = 144
- 132 = 169
- 142= 196
- 152 = 225
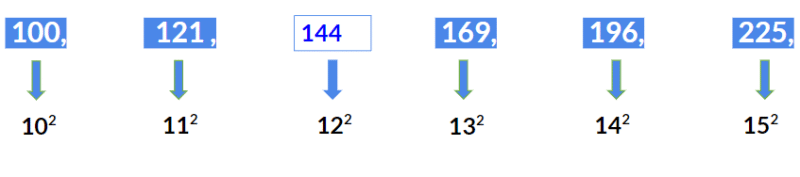 Hence 143 is wrongly placed. Instead it should be 122= 144.
Hence 143 is wrongly placed. Instead it should be 122= 144.
Example 2: Find the wrong term 2, 2, 4, 12, 50, 240
Solution:
The pattern that is being followed in the above series is
(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5).
- 2 x 1 = 2
- 2 x 2 = 4
- 4 x 3 = 12
- 12 x 4 = 48
- 48 x 5 = 240
Hence the wrongly placed number is 50. Instead it should be 12 x 4 = 48.
➢
Type 3
A complete numerical series is given followed by an incomplete numerical series.
Example 1: [67, 84, 95] : [?, 133, 144]
Solution:
In the first set of numbers [67, 84, 95] :
84 – 67 =17
95 – 11 = 11
Hence the same difference needs to be maintained in the second set of numbers as well.
116 – 133 = 17
144 – 133 = 11
 Hence missing number should be 116.
Hence missing number should be 116.
Example 2: [3, 6, 12] : [4, ?, 16]
Solution:
As in first set numbers are obtained by doubling the previous number:
3 x 2 = 6
6 x 2 = 12
Hence the same pattern needs to be followed in the second set as well.
4 x 2 = 8
8 x 2 = 16
Hence missing number will be 4 x 2 = 8.
|
164 videos|626 docs|1131 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Number Series - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is a prime number series? |  |
| 2. How is a perfect square series defined? |  |
| 3. What is an arithmetic series? |  |
| 4. How is a geometric series characterized? |  |
| 5. What is a mixed series in number theory? |  |






















