NEET Exam > NEET Notes > ORBITAL STRUCTURE OF ETHYNE
ORBITAL STRUCTURE OF ETHYNE - NEET PDF Download
Electronic structure of the ethyne?
Ref: https://edurev.in/question/683086/Electronic-structure-of-the-ethyne-
| ORBITAL STRUCTURE OF ETHYNE | |
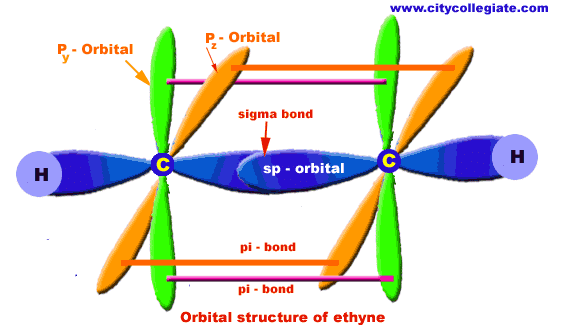
| COMPOSITION OF ETHYNE MOLECULE: Ethyne molecule consists of two C-atoms and two H-atoms (C2H2). NATURE OF HYBRIDIZATION: In ethyne molecule, each carbon atom is Sp-hybridized. Due to Sp-hybridization each carbon atom generates two Sp-hybrid orbitals. In this way there exists four Sp-orbital in ethyne. These Sp-orbital are arranged in linear geometry and 180o apart. Remaining py and pz unhybrid orbitals of each carbon atom lie perpendicular to the plane of Sp-orbitals. SIGMA BOND FORMATION: One Sp-hybrid orbital of each carbon atom overlaps to produce one sigma bond between two C-atoms.The remaining one Sp-orbital of each C-atom overlaps with one H-atom to produce sigma bond. Pi-BOND FORMATION: Py and Pz orbital of two carbon atoms are un-hybrid and make parallel overlapping to produce pi-bond. BOND LENGTH: The C--H bond is 1.09A and C-C is 1.2A.o. BOND ANGLE: HCC bond angle is 180o. | |
 | |
FAQs on ORBITAL STRUCTURE OF ETHYNE - NEET
| 1. What is the orbital structure of ethyne? |  |
| 2. How many sigma and pi bonds are there in ethyne? |  |
Ans. In ethyne, there are two sigma bonds and two pi bonds. The two sigma bonds are formed by the overlapping of hybridized sp orbitals on each carbon atom, while the two pi bonds are formed by the overlapping of unhybridized p orbitals.
| 3. What is the significance of the orbital structure in ethyne? |  |
Ans. The orbital structure of ethyne is significant because it determines its chemical reactivity and physical properties. The presence of two pi bonds in ethyne makes it highly reactive, allowing it to undergo addition reactions with electrophiles. The sp hybridization of carbon atoms also gives ethyne a linear shape, which affects its bond angles and molecular geometry.
| 4. How does the orbital structure of ethyne affect its bond length and strength? |  |
Ans. The orbital structure of ethyne influences its bond length and strength. The presence of two pi bonds in ethyne results in shorter bond lengths compared to a single bond. The sp hybridization of carbon atoms also leads to stronger sigma bonds due to the greater overlap of orbitals. However, the pi bonds in ethyne are weaker than the sigma bonds due to the sideways overlap of p orbitals.
| 5. How does the orbital structure of ethyne contribute to its triple bond character? |  |
Ans. The orbital structure of ethyne contributes to its triple bond character. The presence of two pi bonds, formed by the overlap of unhybridized p orbitals, results in a higher electron density between the carbon atoms, giving rise to a stronger bond. This triple bond character is responsible for the unique properties and reactivity of ethyne.
Download as PDF
Related Searches















