Olympiad Notes: Decimals | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
Introduction
- The numbers used to represent numbers smaller than unit 1 are called decimal numbers.
- The decimal point or the period plays a significant part in a Decimal Number.
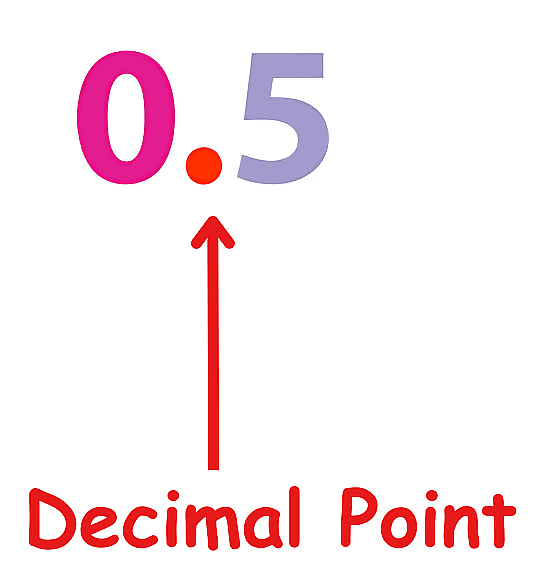
- This period separates the fractional part and whole number part in a decimal number.
- Place value of a digit can be defined as the value of a digit as per the place of that digit in a number.
Tenths
As we know that, 1 cm = 10 mm, so if we have to find the opposite then
1mm = 1/10 cm
or one-tenth cm or 0.1 cm.
Hence, the first number after the decimal represents the tenth part of the whole.
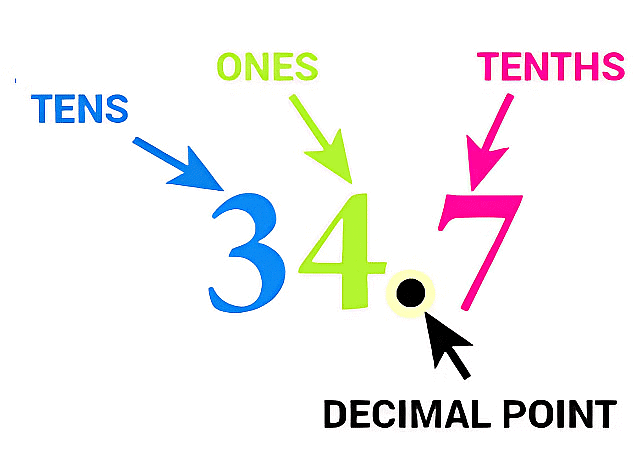 This reads as “thirty-four point seven”.
This reads as “thirty-four point seven”.
Representation of Decimals on Number Line
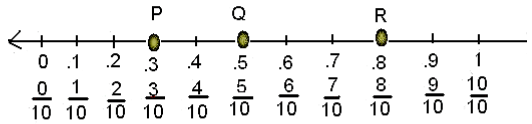
To represent decimals on the number line we have to divide the gap of each number into 10 equal parts as the decimal shows the tenth part of the number.Example: Show 0.3, 0.5 and 0.8 on the number line.
Sol: All the three numbers are greater than 0 and less than 1.so we have to make a number line with 0 and 1 and divide the gap into 10 equal parts.Then mark as shown below.
Fractions as Decimals
It is easy to write the fractions with 10 as the denominator in decimal form but if the denominator is not 10 then we have to find the equivalent fraction with denominator 10.Example: Convert 12/5 and 3/2 in decimal form.
Sol: 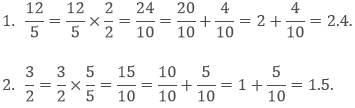
Decimals as Fractions
Example: Write 2.5 in a fraction.
Sol: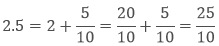
Hundredths
As we know that 1 m = 100 cm, so if we have to find the opposite then
1 cm = 1/100 m, or
one-hundredth m or 0.01 m.
Hence, the second numbers after the decimal represent the hundredth part of the whole.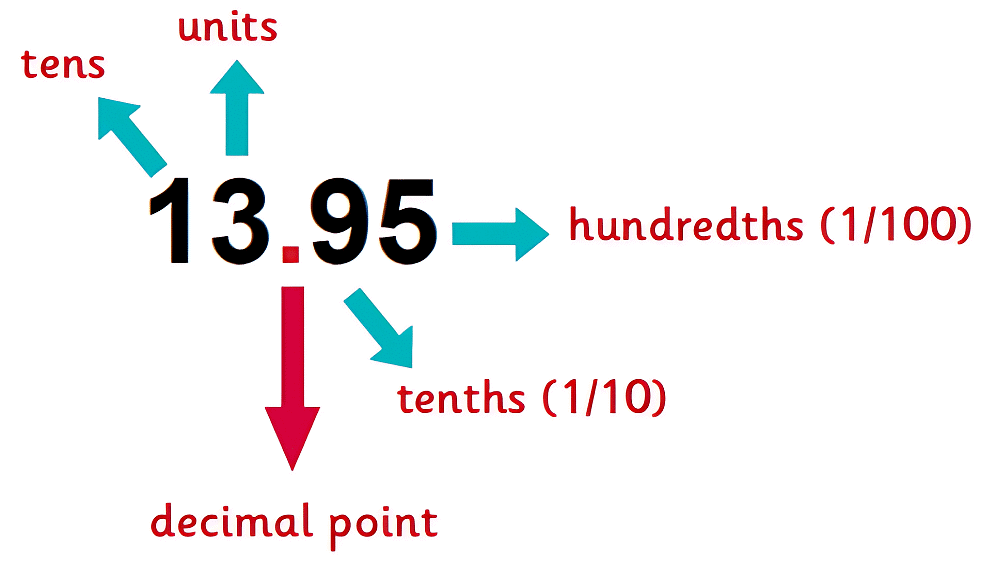
It reads as “thirteen point nine five”.
Decimal in the hundredth form shows that we have divided the number into hundred equal parts.
Example: If we say that 25 out of 100 squares are shaded then how will we write it in fraction and decimal form?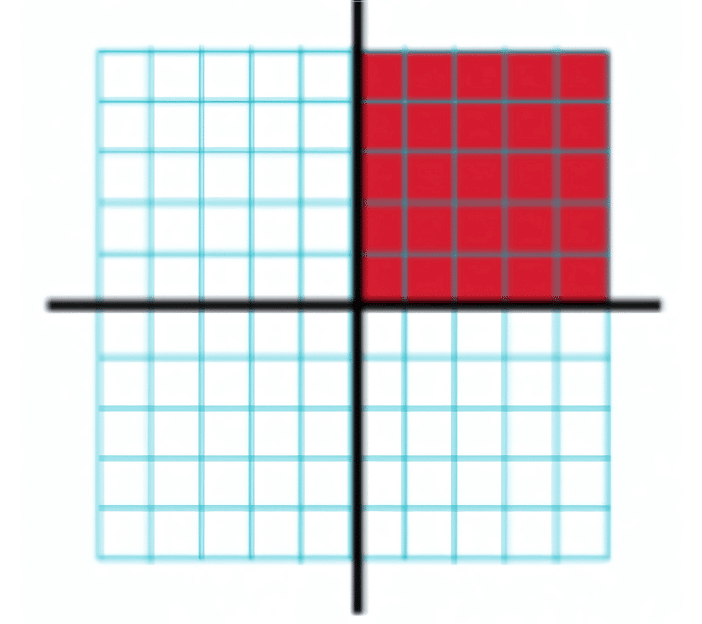
Sol: 25 is a part of 100, so the fraction will be 25/100.
In the decimal form we will write it as 0.25.
Place Value Chart
This is the place value chart which tells the place value of each digit in the decimal number. It makes it easy to write numbers in decimal form.
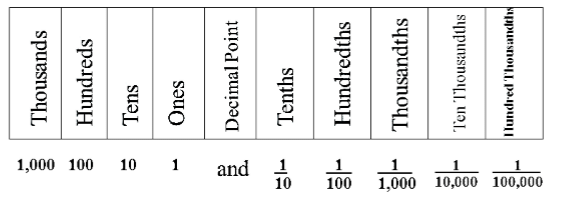
Example: With the given place value chart write the number in the decimal form.
| Hundreds (100) | Tens (10) | Ones (1) | Tenths (1/10) | Hundredths (1/100) |
| 4 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 5 |
Sol: According to the above table-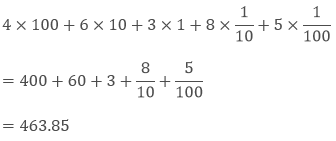
Recurring and Terminating Decimals
- A terminating decimal is a decimal number which has finite number of digits after the decimal.
Example: 0.35 - A recurring decimal is one where its decimal representation becomes periodic or same sequence of digits keeps repeating indefinitely.
Example: 31.213333…
Comparing Decimals
- Any two decimal numbers can be compared by comparing their whole part and decimal parts.
- If the whole parts are equal then the tenth parts can be compared and so on.
If the Whole Number is different
- If the whole numbers of the decimals are different then we can easily compare them.
- The number with the greater whole number will be greater than the other.
Example: Compare 532.48 and 682.26.
Sol: As the whole numbers are different, so we can easily find that the number with a greater whole number is greater.
Hence 682.26 > 532.48.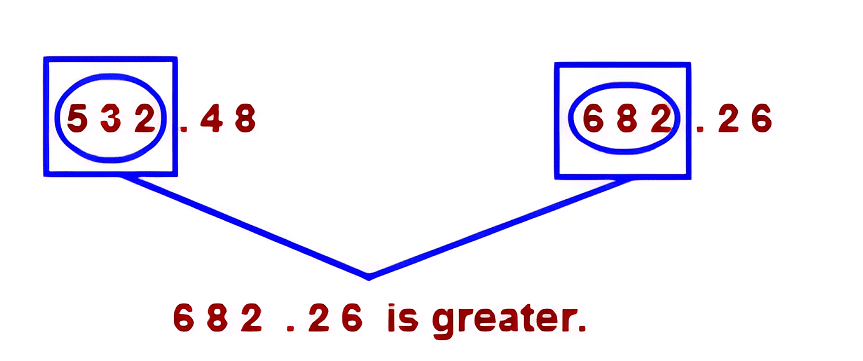
If the Whole Number is the Same
- If the whole numbers of the decimals are same, then we will compare the tenth and then the hundredth part if required.
- The number with the greater tenth number is greater than the other.
Example: Compare 42.36 and 42.68.
Sol: As the whole number is the same in both the numbers so we have to compare the tenth part.
Hence 42.68 > 42.36.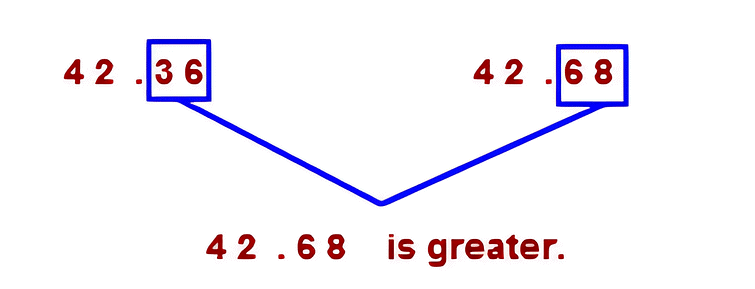
Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
Addition
For example: Add: 0.19 + 2.3
Decimal numbers, 0.19 and 2.3 have two digits and one digit respectively to the right of the decimal point. So, we add a zero to the right of 2.3.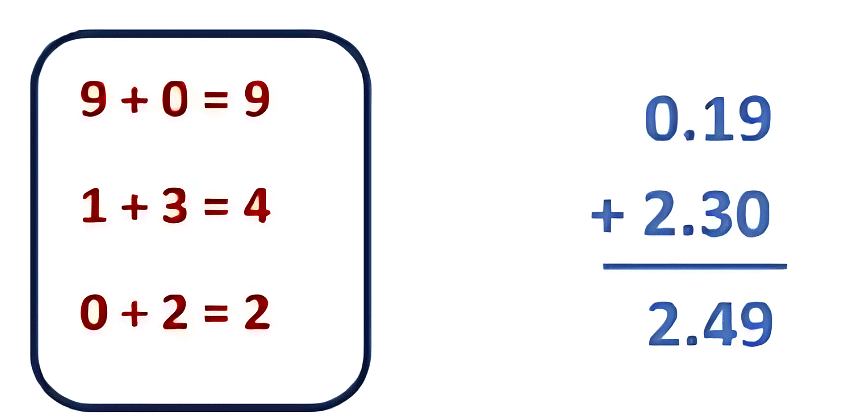
Subtraction
For example: Subtract: 39.87 - 21.98
Decimal numbers 39.87 and 21.98 have the same number of zeros after the decimal point.
Multiplication and Division of Decimals
Multiplication- 2.8 × 7 (There is only one digit to the right of the decimal point in 2.8)
- 28 × 7 (Ignoring the decimals)
- 28 × 7 = 196
- Now bring the decimal back after one digit from left and thus answer is 19.6
Division
- 3.4/2 = Quotient
- Ignore the decimal and divide the numerator by the denominator. Here, quotient = 34/2 = 17
- Since there is only one digit to the right of the decimal, put the decimal after one digit from left in the quotient. Therefore, quotient becomes 1.7
How to Use the Points
Point Shift Trick
Division: Point is shifted to the left by the number of zeroes in the denominator.
- 150/100 = 1.50 ( Shifting decimal by 2 points to the left)
- 1.5/1000 = 0.0015 ( Shifting decimal by 3 points to the left)
Decimals in Money
Example: Write 25 paise in decimals.Sol:
100 paise = 1 Rs.
1 paise = 1/100 Rs. = 0.01 Rs.
25 paise = 25/100 Rs. = 0.25 Rs.
Decimals in Length Measurement
- 1m = 100cm
- 1cm = 1/100m = 0.01m ( Move decimal to left by 2 units in the numerator as there are two zeroes in the denominator )
- 150cm = 150/100m = 1.5m
Example: If the height of Rani is 175 cm then what will be her height in meters?
Sol: 100 cm = 1 m
1 cm = 1/100 m = 0.01 m
175 cm = 175/100 m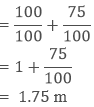 Hence, the height of Rani is 1.75 m.
Hence, the height of Rani is 1.75 m.
Decimals in Weight Measurement
- 1 kg = 1000 g
- 1 g = 1/1000 kg
- 298 g = 298/1000 kg = 0.298 kg ( Move the decimal to the left by 3 places in the numerator as there are 3 zeroes in the denominator )
Example: If the weight of a rice box is 4725 gram then what will be its weight in a kilogram?
Sol:
1000 gm = 1 kg
1 gm = 1/1000 kg = 0.001 kg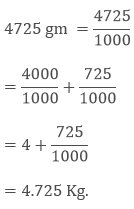
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Decimals - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. How can decimals be represented on a number line? |  |
| 2. How can fractions be converted into decimals? |  |
| 3. How can decimals be converted into fractions? |  |
| 4. How do you compare decimals? |  |
| 5. How do you add and subtract decimals? |  |





















