Olympiad Notes: Geometrical Shapes and Solids | Math Olympiad for Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What are Shapes? |

|
| Types of Shapes |

|
| Difference Between 2D and 3D Shapes |

|
| What is Area? |

|
| Units of Measurement |

|
Introduction
Imagine this: You are building with toy blocks—some are flat, like squares, and some are solid, like cubes. What if you could understand how these shapes work and how they fit together? That’s exactly what geometry teaches us! Let’s explore shapes and solids that make up the world around us.
What are Shapes?
Shapes are figures that describe the outline of objects. Some shapes are flat and have two dimensions, while others are solid and have three. Learning about these shapes helps us recognize, measure, and understand the structure of things around us.
- 2D Shapes are flat and only have length and breadth. These shapes lie on a surface and do not occupy space.
- 3D Shapes (Solids) have length, breadth, and height and take up space in the real world.

Types of Shapes
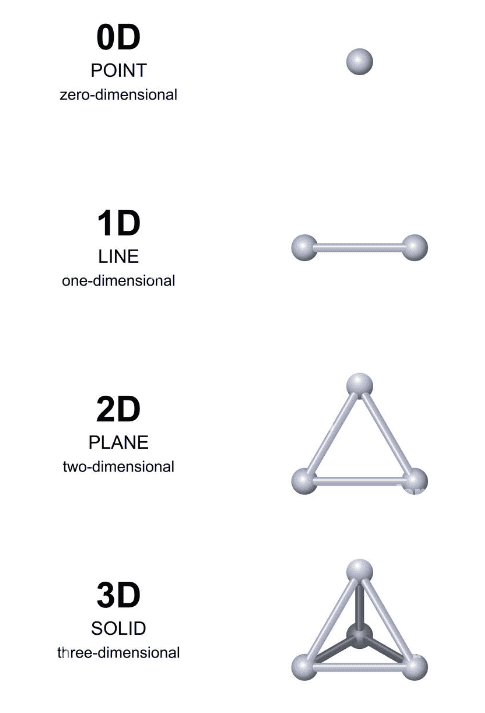
Zero-Dimensional Shape (Point)
A point represents a position in space. It has no size, length, or width—just a spot or marker.One-Dimensional Shape (Line)
A line has only one dimension—length. You can think of it as a path that extends endlessly in two directions.
Two-Dimensional Shapes (2D)
These shapes are flat and have two dimensions—length and breadth.- Square: Four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides equal and four right angles.
- Circle: Round with no corners, where every point on the curve is equally far from the center.
- Triangle: Three sides and three angles.
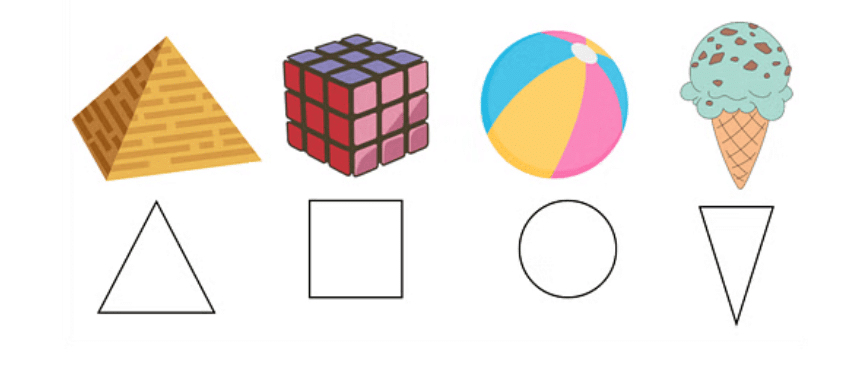
Three-Dimensional Shapes (3D Solids)
These shapes take up space and have three dimensions—length, breadth, and height.- Cube: Six equal square faces, twelve edges, and eight corners (vertices).
- Cuboid: Similar to a cube but with rectangular faces.
- Sphere: A perfectly round object, like a ball, with no edges or corners.
- Cylinder: Two flat circular surfaces and one curved surface.
- Pyramid: A polygon base and triangular sides that meet at a single point.
Difference Between 2D and 3D Shapes
- 2D Shapes are flat and do not occupy space, while 3D shapes (solids)have volume and occupy space.
- A square is a 2D shape, but a cube is a 3D version of it.
- Circles are 2D, while spheres are their 3D counterpart.

What is Area?
The area is how much space a flat shape takes up.
- It's like counting how many small squares fit inside a shape.
- We measure area using square units like cm² or m².
- Shapes like circles, triangles, squares, and rectangles all have areas.
- Area is the space inside the lines that make up a shape.
Area of Rectangle and Square
Area of a Rectangle
- The area of a rectangle is how much space it takes up inside.
- You find the area by multiplying the length and width of the rectangle.
- Formula: Area = length × width.
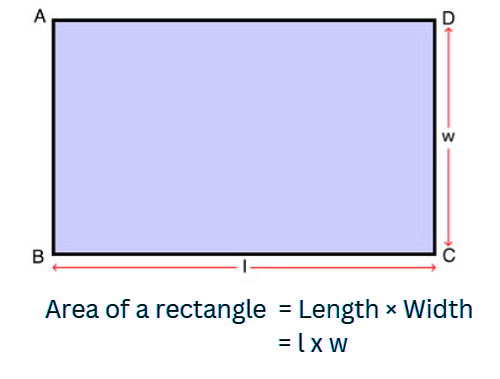
- It's like counting how many unit squares fit inside the rectangle.
- So, if a rectangle has a length of 'l' and a width of 'w', the area is 'l' times 'w'.
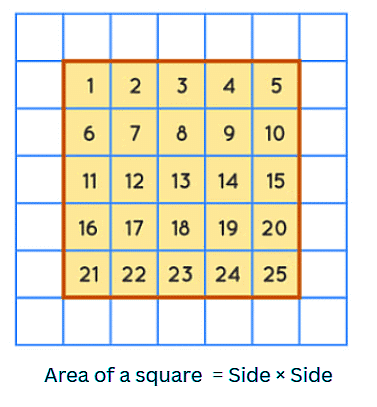
Area of a Square
- The area of a square is how much space it takes up inside.
- You find the area by multiplying the length of one side by itself.
- Formula: Area = side × side.

- The unit of area is given in square units.
- For example, if a square has a side length of 5 units, its area is 5 × 5 = 25 square units.
- This means if you count the squares inside, it tells you how much space the square covers.
Example 1: If the length of the board is 12 cm and the breadth is 10 cm and we want to cover the board with square sheets. The side of the square sheet is 2 cm. How many sheets are required to cover the board?
Sol:
Length of board = 12 cm
Breath of board = 10 cm
Step 1: Calculate the area of the board
Area of board = length x breadth
⇒ Area of board = (10 x 12) cm²
⇒ Area of board = 120 cm²
Step 2: Calculate the area of one square sheetSide of sheet = 2 cm
Area of sheet = side × side
⇒ Area of sheet = (2 × 2) cm²
⇒ Area of sheet = 4 cm²
Step 3: Calculate the number of sheets required
Number of sheets required = Area of board / Area of sheet
⇒ Number of sheets required = 120 / 4
⇒ Number of sheets required = 30
Example 2: Calculate the length and breadth of the rectangle whose area is 512 cm² and the length is twice the breadth.
Sol:
Let the breadth of the rectangle be x, and then the length will be 2x.
Area of rectangle = x × 2x = 512
⇒ 2x² = 512
⇒ x² = 512/2 = 256
⇒ x² = 256
⇒ x = 16
Thus, the breadth is 16 cm, and the length is 32 cm.
Example 3: If the area of a square is 289 cm², then find the measure of its side.
Sol:
Let a be the side of a square.
We know that the area of a square with side “a” = a²
So, a² = 289 cm² (given)
⇒ a = 17 cm
Hence, the measure of the side of the square is 17 cm.
Perimeter of Rectangle and Square
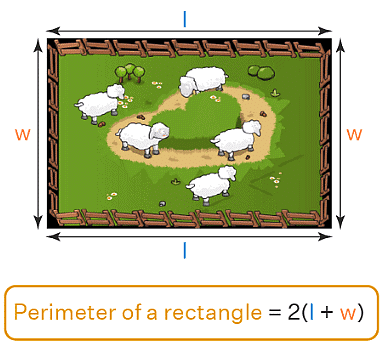
Perimeter of a Rectangle
- The perimeter of a rectangle is how long the boundary is all around.
- We can find the perimeter by adding up the lengths of all four sides.
- Formula: Perimeter = 2 × (length + width).
- Imagine walking around the edges of a farm – you're measuring the perimeter.
- If the length of the farm is 'l' and the width is 'w', the perimeter is 2 times the sum of 'l' and 'w'.
Perimeter of a Square
- The perimeter of a square is how long the whole edge is all around.
- You find the perimeter by adding up the lengths of all four sides.
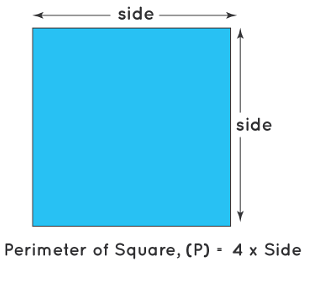
- Formula: Perimeter = 4 times the length of one side.
- It's like adding up how much all the sides of the square measure altogether.
Example 1: It is known that the area of a square is 81 cm². Find the perimeter of the square.
Sol:
Area = 81 cm²
Area = side × side
⇒ 81 = (a)²
⇒ (9)² = (a)²
⇒ 9 cm = a
Perimeter = 4 × side
⇒ Perimeter = 4 × 9
⇒ Perimeter = 36 cm
Example 2: A bedsheet has a length of 120 inches and a breadth of 95 inches. How much lace will be required to complete the border?
Sol:
The perimeter of the bedsheet will be determined using the perimeter of the rectangle formula to determine the amount of lace required for the bedsheet’s border.
Given,
Length, l = 120 inches
Breadth, b = 95 inches.
As we know, the perimeter of a rectangle = 2(l + b) units.
Substituting the values in the formula, we get
Perimeter = 2(120 + 95) = 2 × 215 = 430 inches.
Hence, we will need 430 inches of lace to complete the border.
Example 3: Find the length of the sides of the square park, whose perimeter is 232 m.
Sol:
Perimeter of square park = 4 × side = 232 m
⇒ side = 232/4
⇒ side = 58 m.
Therefore, the length of the sides of the square park is 58 m.
Units of Measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a quantity that is adopted by law and is used as a standard for measuring the same type of quantity.
- We measure the perimeter of any figure in mm, cm, m, or km.
- We measure the area of any figure in mm², cm², m², or km².
Measurement Abbreviations and their Comparisons
Millimeter (mm):
This is a tiny measurement, like the thickness of a paperclip wire.
Example: The width of a small button might be a few millimeters.Centimeter (cm):
A bit bigger than millimeters, like the width of your fingernail.
Example: The length of a small toy car could be a few centimeters.Meter (m):
This is bigger, like the height of a door or the length of a desk.
Example: The height of a basketball hoop is a few meters.Kilometer (km):
A very large measurement, like the distance between your home and school.
Example: The distance from one town to another might be a few kilometers.
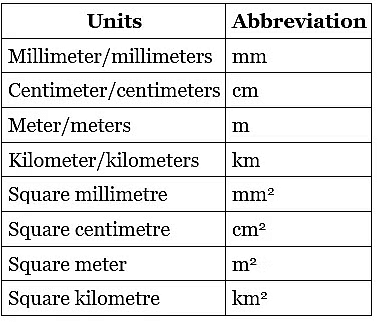
Area Measurements
Square Millimeter (mm²):
Imagine a tiny square made by connecting four dots, each one a millimeter apart on each side.
Example: The area of a small sticker might be measured in square millimeters.Square Centimeter (cm²):
A bit bigger than the square millimeter, like a small square on a piece of paper.
Example: The size of a postage stamp might be a few square centimeters.Square Meter (m²):
Larger than the square centimeter, like the floor space in a room.
Example: The area of a small kitchen might be a few square meters.Square Kilometer (km²):
This is very big, like the area of a city or a large park.
Example: The size of a big national park might be measured in square kilometers.
- Always remember:
1 mm < 1 cm < 1 m < 1 km.
Similarly, 1 mm² < 1 cm² < 1 m² < 1 km².
Scale of Drawing
A drawing of a real object reduced or enlarged by a certain amount (called the scale).
Example: A garden with a paved border is shown below. 1 cm on this garden is equal to 100 m on the ground.
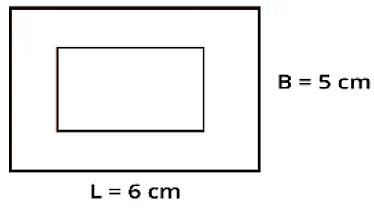
Rectangular Garden
Let’s find the length and breadth of the garden on the ground.
- Length will be 6 × 100 m = 600 m.
- Breadth will be 5 × 100 m = 500 m.
Relationship Between Area and Perimeter
Consider two rectangles A and B having the same perimeter as 18 units.
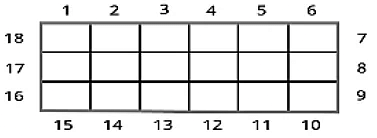
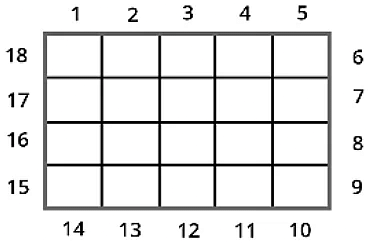
Observe that both of them have different areas:
- Area of Rectangle A = 18 square units.

- Area of Rectangle B = 20 square units.
Hence, we conclude that:
- Two shapes having the same perimeter can have different areas.
- Similarly, two shapes having the same areas can have different perimeters.
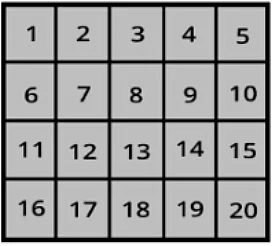
Area When We Cut the Image
If we cut any 2D figure, the area of that figure will be equal to the area of the pieces.
For example, if we cut a polygon into three pieces, the area of the polygon is equal to the sum of the areas of the three pieces.
Before Cutting
After Cutting
Example: Take a sheet of paper with a length of 14 cm and a breadth of 5 cm. Now cut this sheet into 5 equal rectangles. Find the area of each smaller rectangle.
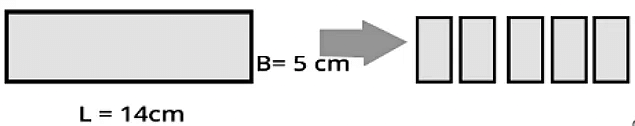
Area of a sheet of length 14 cm and breadth 5 cm = Sum of the area of five equal rectangles.
- Area of sheet = 14 × 5 = 70 cm².
- The area of each smaller rectangle = 14 cm².
|
32 videos|57 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Geometrical Shapes and Solids - Math Olympiad for Class 5
| 1. What are the main characteristics of 2D shapes? |  |
| 2. How can we differentiate between 2D and 3D shapes? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for calculating the area of common shapes? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding units of measurement important in geometry? |  |
| 5. What role do geometrical shapes play in everyday life? |  |