Olympiad Notes: Numerals | Mathematics Olympiad for Class 1 PDF Download
What are Numerals?
A numeral is a symbol that represents a number. It is how we write numbers to show how many things we have.
 NumeralsFor example:
NumeralsFor example:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 are all numerals.
We use numerals to count things, like counting toys, books, or pencils. When we write down the number of things we have, we use numerals.
Example:
- Rahul has 3 apples.

- Timon has 5 balls.

Here, 3 and 5 are numerals.
Zero: The Smallest Number
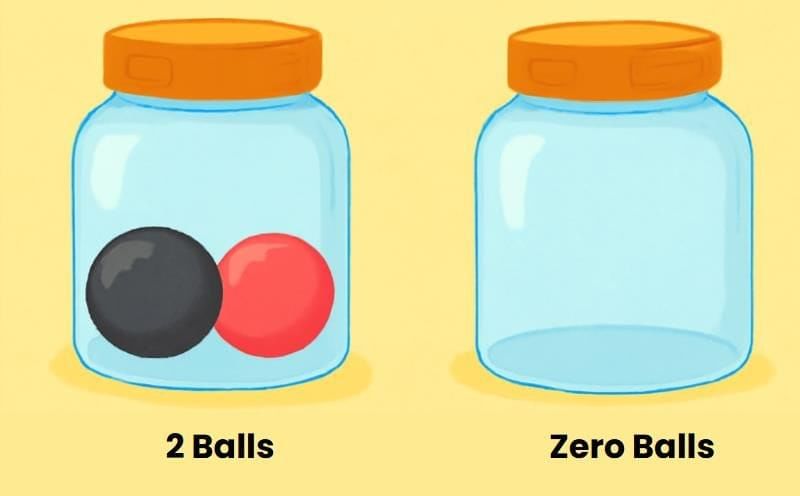
- Zero is the smallest counting number. It is written as 0.
- The image below shows a jar with two balls – black and red.
- Now if you remove the two balls, the jar contains 0 balls.

One-Digit Numbers
Numbers from 0 to 9 are one-digit numbers. 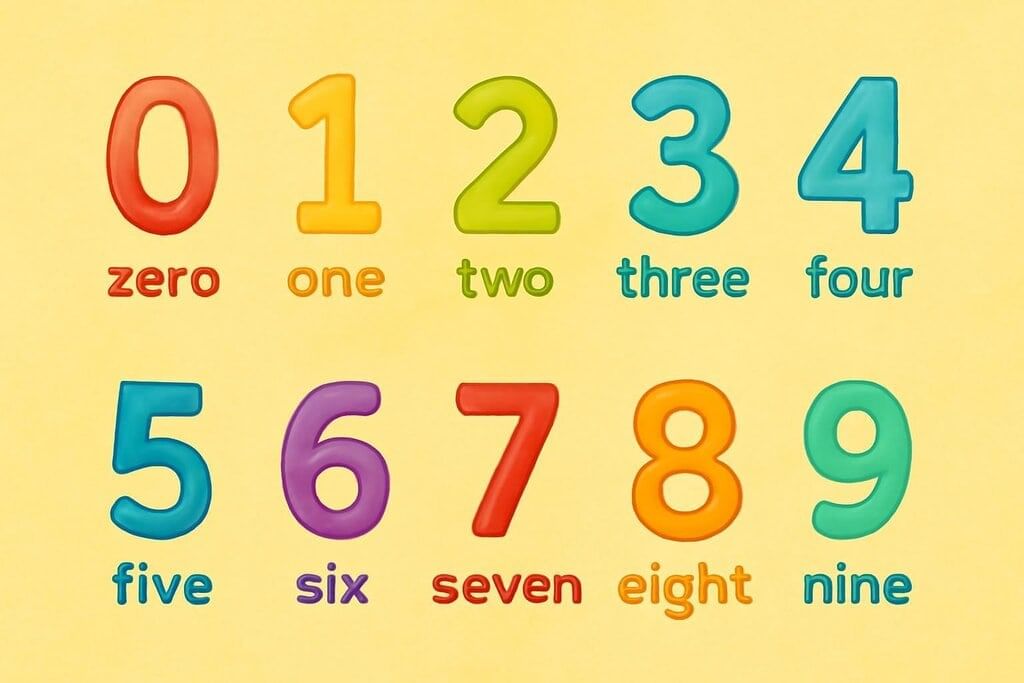
Number Line
A number line can be defined as a straight line with numbers placed at equal distance along its length.
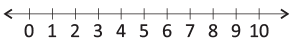
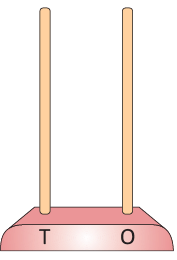
Place value
- The value of each digit in a number is known as the place value.
- Starting from right, the first place is units or ones (O) and the second place is tens (T).
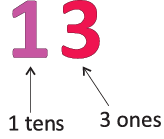
Example: The place value of the two-digit number 13 will be as follows:
Two-digit numbers
- Numbers from 10 to 99 are two-digit numbers.
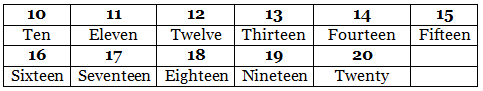
- Here are some examples for two-digit numbers.
- How to get the number 18?

- What number do you get when 3 tens is added to 4 ones?

- What number do you get when 5 tens is added to 1 one?

- What number do you get when 7 tens is added to 2 ones?

- What number do you get when 8 tens is added to 6 ones?

- What number do you get when 9 tens is added to 8 ones?

- See the following examples.
Given that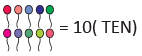
(a) 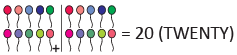
(b) 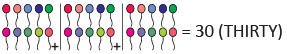
(c) 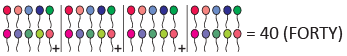
(d)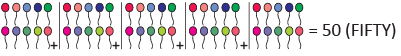
(e) 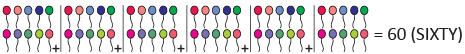
(f)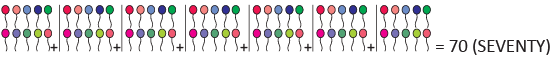
(g)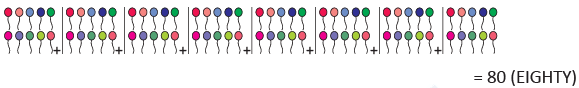
(h)
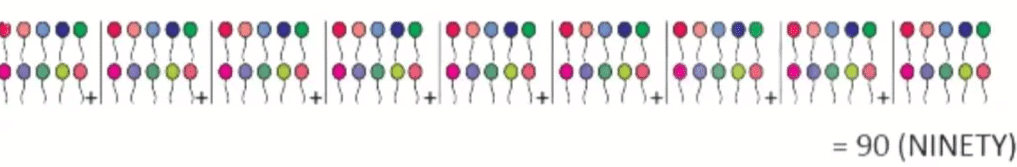
Comparing Numbers: Greater than, Less than and Equal to

Greater than
- Greater than Which number is greater: 7 or 10?
- We can identify the greater number using a number line.
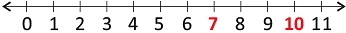
- 10 lies on the right side of 7, so 10 is greater than 7 and we write it as 10 > 7.
Less than
- Which number is smaller: 34 or 53?
- We compare the numbers using a number line.
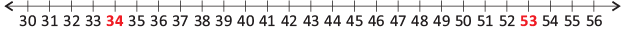
- 34 lies on the left side of 53, so 34 is smaller than 53 and we write it as 34 < 53.
Equal to
- If the two numbers given are same, we say that the numbers are equal.
- We can say that 7 is equal to 7 and write it as 7 = 7
Example: Are the numbers 19 and 91 equal?
The given numbers are 19 - Nineteen and 91 - Ninety-one. They are not same. So, 19 and 91 are not equal.
Writing Numbers in Reverse Order
9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0 is the backward order of one-digit numbers.
99, 98, 97, 96, 95, 94, 93, 92, 91, 90, 89, _______, 10 is the reverse order of two-digit numbers.
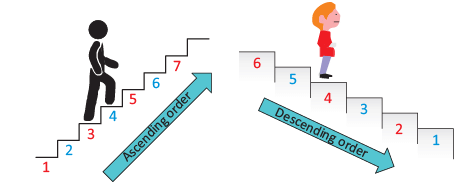
Ascending and descending orders
- Ascending order means an arrangement of numbers from small to big.
- Descending order means an arrangement of numbers from big to small.
Examples:
- Arrange the given numbers in ascending order: 54, 28, 47, 87, 18, 64
- Arrange the numbers from the smallest to the biggest or largest.
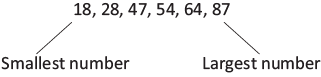 So, the order is 87, 64, 54, 47, 28, and 18.
So, the order is 87, 64, 54, 47, 28, and 18. - Arrange the numbers 45, 12, 56, 84 in descending order.
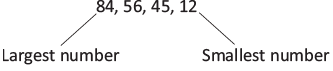
- Arrange the numbers from the biggest or largest to the smallest.
So, the order is 84, 56, 45, 12.
Just before, Just after, and In-between
- If the numbers are 13, 14, and 15,
- 13 comes just before 14.
- 15 comes just after 14.
- 14 lies in between 13 and 15.
Skip counting
- Skip counting means counting by skipping some numbers instead of counting one by one. It helps us count faster!
- Numbers are obtained by adding the same number.
How Does Skip Counting Work?
- Skip counting by 2s: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10... (We skip one number each time.)
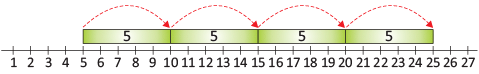
- Skip counting by 5s: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25... (We skip four numbers each time.)
- Skip counting by 10s: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50... (We skip nine numbers each time.)
Example: - 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 are the numbers we get by skip count of 2.
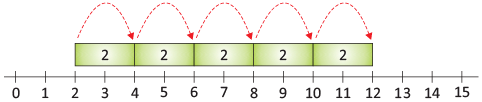
- 3,6,9,12,15 are the numbers we get by skip count of 3.
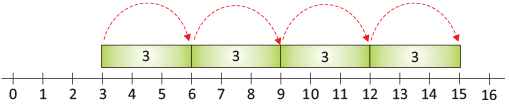
- 4, 8, 12, 16, 20 are the numbers we get by skip count of 4.
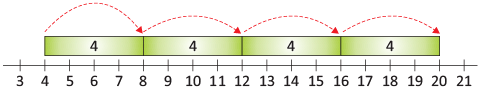
- 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 are the numbers we get by skip count of 5.
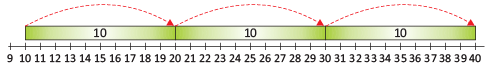
- 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 are the numbers we get by skip count of 10.
|
29 videos|109 docs|65 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Numerals - Mathematics Olympiad for Class 1
| 1. What is the definition of a prime number? |  |
| 2. How can I determine if a number is prime or composite? |  |
| 3. Can 1 be considered a prime number? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a prime number and a composite number? |  |
| 5. How can I find all the prime numbers within a given range? |  |

















