Olympiad Notes: Sun the source of Energy | Science Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
The Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all life on Earth. It provides light and heat, without which life cannot exist. Plants, animals, and humans directly or indirectly depend on solar energy. The Sun not only sustains life but also controls Earth’s weather, climate, and temperature.
How the Sun’s Energy Reaches Earth
Energy from the Sun travels through empty space to reach us. Since there is no air in space, energy cannot come by conduction (through solids) or by convection (through liquids and gases). Instead, the Sun’s energy reaches Earth by a process called radiation.
Radiation means that energy travels in the form of waves (light and heat waves). These waves do not need any medium to travel. That is why the warmth of the Sun can reach Earth, even though space is a vacuum.
Example: When we feel the warmth of sunlight on our skin, it is due to solar radiation.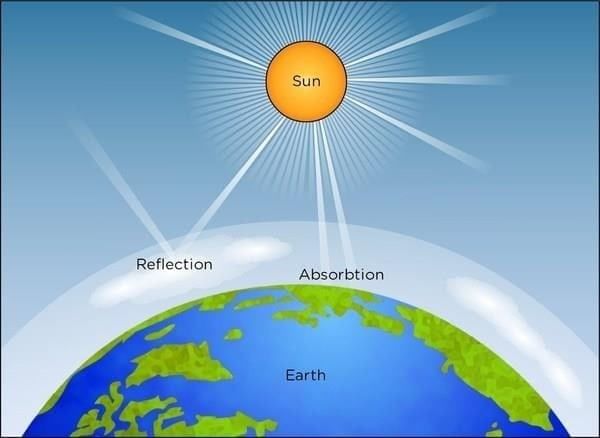
The Role of the Sun in Plants: Photosynthesis
Plants use the Sun’s energy directly in the process of photosynthesis. Their leaves, containing the green pigment chlorophyll, absorb sunlight. Using this energy, plants prepare food from carbon dioxide and water.
Since plants form the base of the food chain, the Sun indirectly provides food and energy to all animals and humans. Without the Sun, plants could not make food, and life on Earth would come to an end.
Example: Grass makes food using sunlight. A goat eats the grass, and a human eats the goat’s milk or meat. Thus, the energy flow starts from the Sun.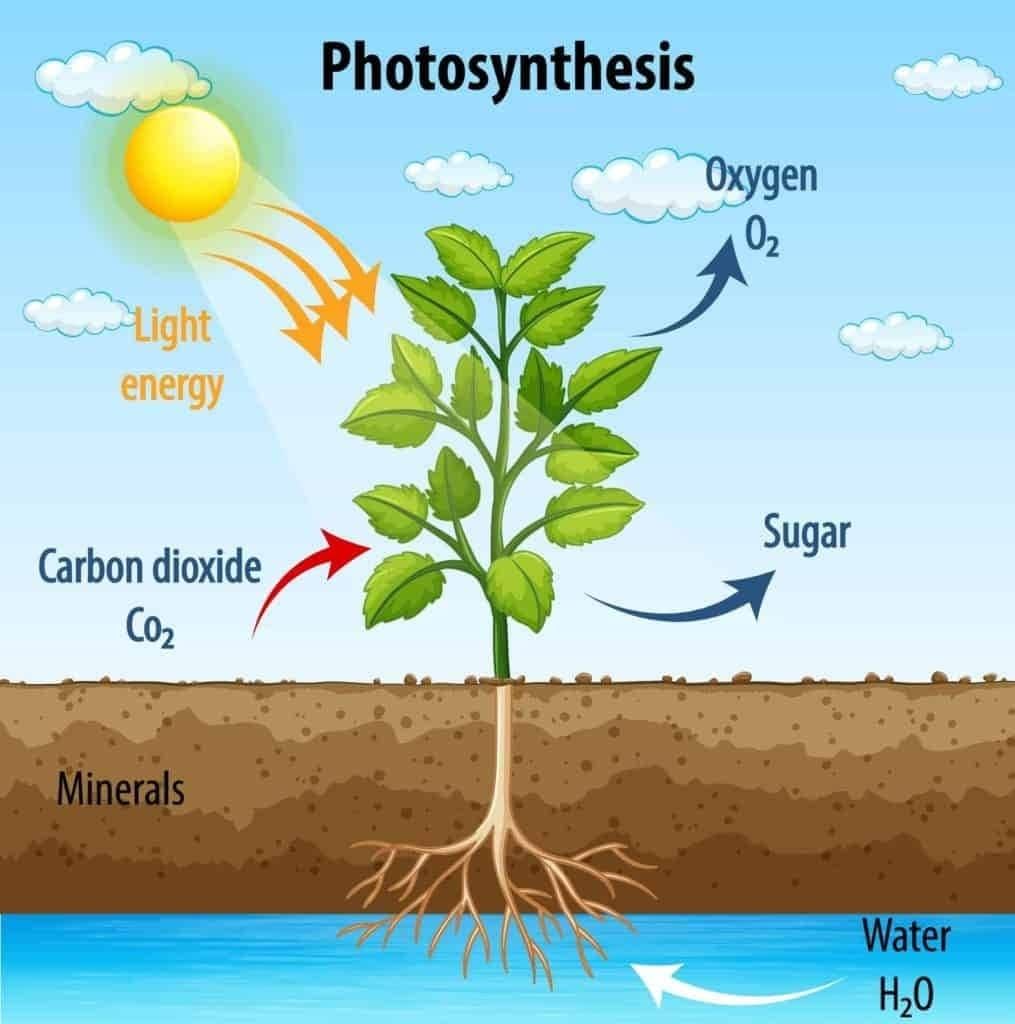
The Sun and Weather/Climate
The Sun plays a crucial role in controlling weather and climate on Earth.
- The Sun heats Earth’s surface unevenly. Some parts (like land) heat up faster, while others (like water bodies) heat slowly.
- This uneven heating creates differences in air pressure, which causes winds.
- Solar heat also causes evaporation of water, leading to cloud formation and rainfall.
- Solar energy maintains Earth’s temperature balance, keeping it suitable for life.
Direct and Indirect Uses of Solar Energy
Solar energy is used in both direct and indirect ways.
(a) Direct Uses
- Solar cookers: Use sunlight to cook food.
- Solar heaters: Heat water for domestic use.
- Solar panels (photovoltaic cells): Convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Example: Solar street lights and rooftop solar panels in homes.
(b) Indirect Uses
- Wind energy: Winds are generated due to uneven heating of Earth by the Sun.
- Hydroelectric energy: The Sun drives the water cycle. Evaporation → Clouds → Rain → Flowing water, which runs turbines to produce electricity.
- Biomass and fossil fuels: Plants store solar energy as food. Over millions of years, dead plants and animals formed coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are all stored solar energy.
Example: Coal used in thermal power plants is stored solar energy from ancient forests.
Sources of Energy Not Related to the Sun
Although most energy sources are related to the Sun, a few are independent of it. Geothermal energy is produced by the heat from inside the Earth, not from the Sun.
Example: Hot springs and geysers release geothermal energy.
Advantages and Limitations of Solar Energy
Advantages
- Renewable: Sunlight is unlimited and cannot be exhausted.
- Non-polluting: It does not produce smoke, ash, or harmful gases like fossil fuels.
- Free of cost: Sunlight is freely available in nature.
- Sustainable: Reduces dependence on coal, petrol, and other fossil fuels.
Example: Solar cookers provide clean cooking without air pollution.
Limitations
- Solar energy is not available at night or during cloudy days.
- Devices like solar cookers and panels cannot work without sunlight.
- Initial installation of solar panels can be costly, though long-term use saves money.

The Sun as a Star
The Sun is actually a star. It appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closest to the Earth. In reality, the Sun is an average-sized star compared to the billions of stars in the universe. However, due to its proximity, it provides us with almost all the energy we need.
Example: At night, stars look tiny and faint, but the Sun appears very large and bright because it is only about 150 million kilometers away from Earth.
Conclusion
The Sun is truly the source of all energy on Earth. Directly, it provides heat and light for daily life. Indirectly, it drives winds, rainfall, hydroelectric power, and even stores energy in fossil fuels and biomass. Only a few energy sources like geothermal energy are independent of the Sun.
The Sun not only sustains life through photosynthesis but also regulates Earth’s climate, weather, and temperature. It is the most important source of energy for our planet, and that is why it is rightly called the ultimate source of energy.
|
69 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Sun the source of Energy - Science Olympiad Class 6
| 1. How does the Sun’s energy reach Earth? |  |
| 2. What role does the Sun play in photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. How does the Sun influence weather and climate? |  |
| 4. What are the direct and indirect uses of solar energy? |  |
| 5. What are some advantages and limitations of solar energy? |  |




















