Olympiad Notes: Symmetry | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Linear Symmetry |

|
| Line of Symmetry |

|
| Reflection or Mirror Symmetry |

|
| Three-dimensional shapes |

|
| Net of a Solid |

|
Introduction
Symmetry refers to the property of an object that allows it to be divided into two equal parts where one part perfectly aligns with the other.
Linear Symmetry
Linear symmetry is a specific type of symmetry involving the creation of a line through the centre of a figure. This line divides the figure into two identical parts, often referred to as mirror images or reflections of each other.In other words, one side of the figure corresponds exactly to the other side. The line responsible for this division is known as the line of symmetry or axis of symmetry.
A figure is considered asymmetrical when there is no line of symmetry which means it cannot be divided into two equal and matching halves.
Example of Linear Symmetry
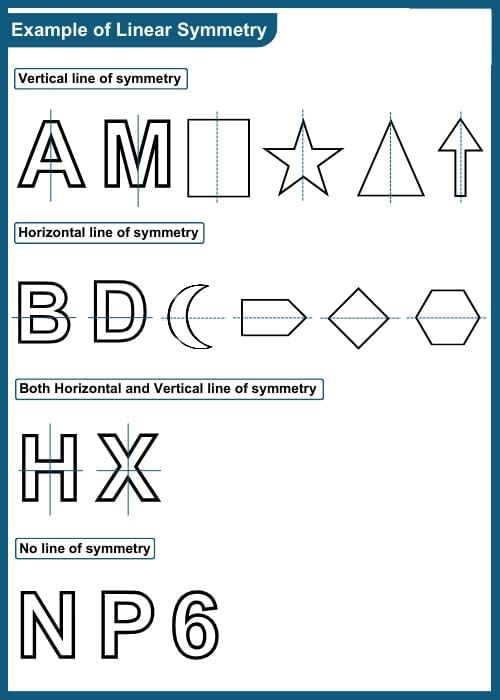
Line of Symmetry
The "line of symmetry" is referred to as the "axis of symmetry" or "symmetry line," which is an imaginary line that divides a figure into two equal and mirror-image halves.
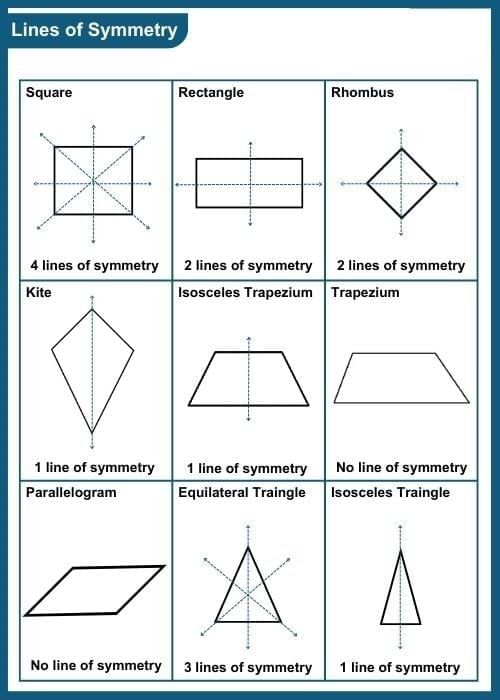
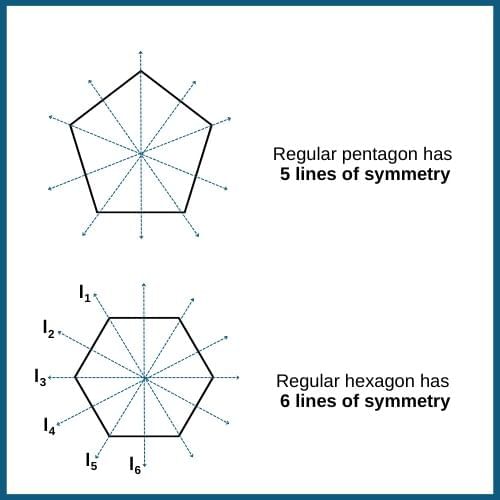
In regular polygons, the lines of symmetry correspond to the number of sides in the polygon.
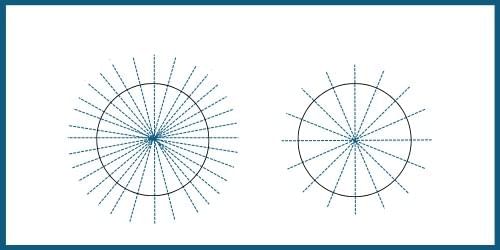
A circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
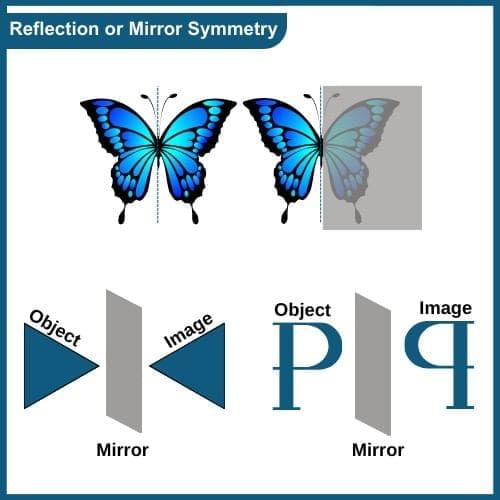
Reflection or Mirror Symmetry
Reflection or Mirror Symmetry is also known as mirror-image symmetry which occurs when a mirror is positioned along the central line of a figure. In this arrangement, the first half of the figure reflects through the mirror, creating an exact duplicate of the remaining half on the opposite side, equidistant from the mirror.
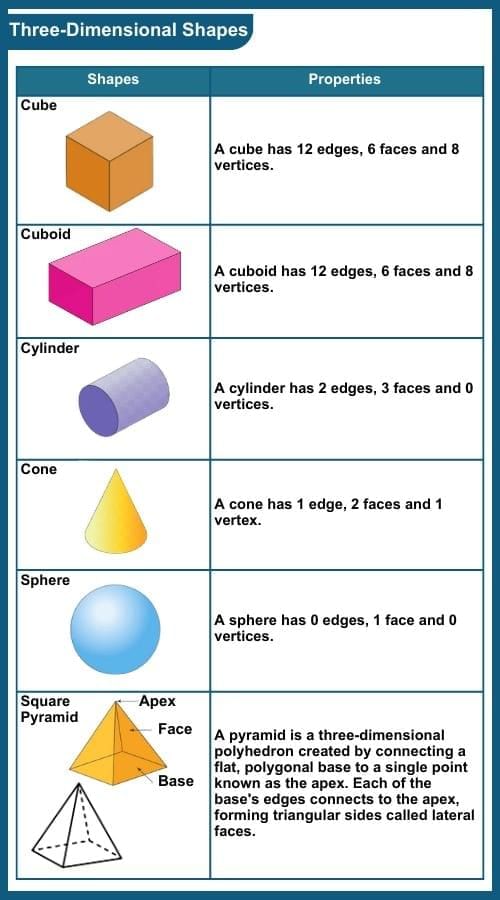
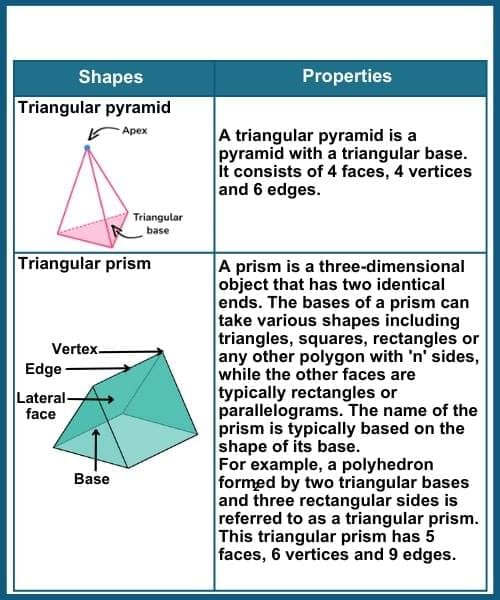
Three-dimensional shapes
Three-dimensional shapes (3-D shapes) are solid objects or figures characterized by having three dimensions: length, width and height. 3-D shapes include the cube, cuboid, cone, cylinder, sphere, prism and pyramid.
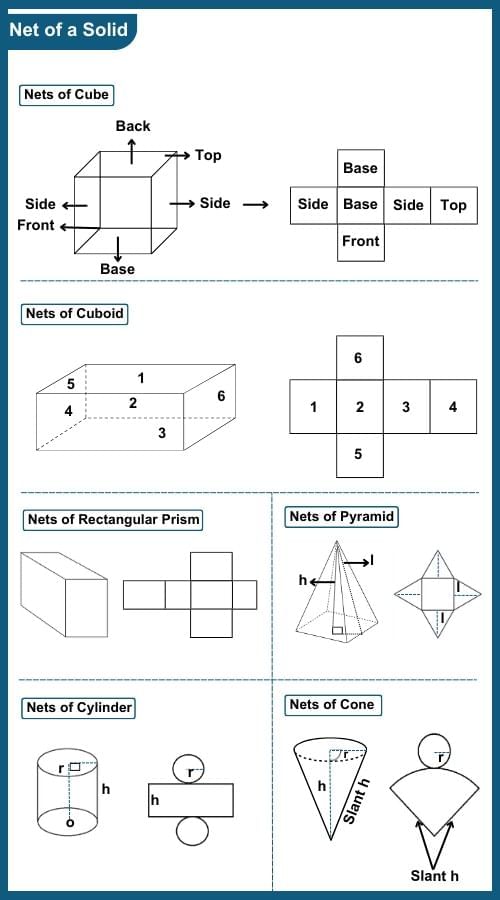
Net of a Solid
A geometry net is a two-dimensional shape that creates a three-dimensional solid when folded. To determine whether a given net can indeed form a solid, follow these steps:
Step 1: Start by ensuring that both the solid and the net have an identical number of faces. Additionally, make sure that the shapes of the solid's faces correspond to the shapes of the faces in the net.
Step 2: Proceed by mentally visualizing how the net should be folded to produce the solid. Confirm that all the sides of the net align and fit together correctly to create a solid shape.
Nets of Cube, Cuboid, Rectangular Prism, Pyramid, Cylinder and Cone are shown as:
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Symmetry - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What is linear symmetry and how is it observed in shapes? |  |
| 2. What is a line of symmetry and can you give examples of shapes that have multiple lines of symmetry? |  |
| 3. What is reflection or mirror symmetry, and how does it differ from other types of symmetry? |  |
| 4. How do three-dimensional shapes exhibit symmetry, and what are some examples? |  |
| 5. What is a net of a solid, and how does it relate to symmetry? |  |














