Operating System | Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Functions of an Operating System |

|
| Types of Operating Systems |

|
| User Interface |

|
| Some Important Operating Systems |

|
| MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System) |

|
| Mobile Operating Systems |

|
An Operating System (OS) is a program that serves as an intermediary between the user and the computer hardware, enabling efficient utilization of hardware resources. It is an organized collection or integrated set of specialized programs that oversee the overall operations of a computer and is essential for proper booting.
Functions of an Operating System
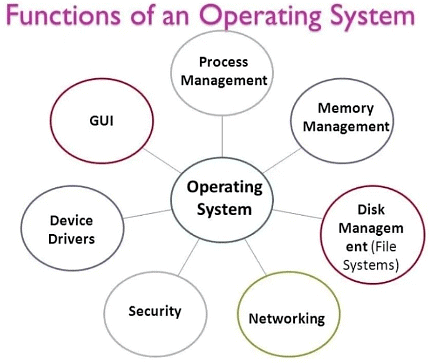
Process Management: A process is the fundamental unit of execution in an OS. Process management involves the OS controlling the planning, monitoring, and performance of the CPU.
- Memory Management: This involves controlling and coordinating computer memory, ensuring all processes can access their required memory.
- File Management: The OS manages all data files within a computer system. During program execution, it also handles copying files from secondary to primary memory.
- Device Management: This function involves managing the operation and maintenance of input/output devices and facilitating the interface between all connected devices.
Types of Operating Systems
- Batch Processing Operating System
- This OS processes a group of jobs together, scheduling them based on priority and resource requirements (e.g., Unix).
- Single User Operating System
Designed for one user at a time, this OS manages one task at a time, common in personal computers (e.g., MS-DOS, Windows 9X). - Multi-User Operating System
- Allows multiple users to access a computer system concurrently, used in networks where the same data and applications are accessed simultaneously (e.g., VMS).
- Multi-Tasking Operating System
Executes more than one process concurrently and allows users to switch between running applications (e.g., Linux, Unix, Windows 95).
This OS is further divided into:- Preemptive Multitasking OS: Allows programs to share OS and hardware resources.
- Cooperative Multitasking OS: Each program controls the CPU as long as needed.
- Time Sharing Operating System
- Allows multiple programs to share computer resources simultaneously (e.g., Mac OS).
- Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)
Designed to respond to events within a pre-determined time, increasing system availability and reliability, often used in critical applications like flight reservation systems and military applications (e.g., Linux). RTOS is classified into:- Hard Real-Time OS: All tasks must be completed within specified time limits.
- Soft Real-Time OS: Not all tasks are required to be completed within specified time limits.
User Interface
The user interface facilitates interaction between the user and the computer, allowing easy access and communication with applications and hardware. There are mainly two types of interfaces:
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Enables communication through symbols, visual metaphors, and pointing devices, prominently used in Apple products.
- The first GUI was developed by Xerox Corporation in the 1970s and can be found in handheld devices like MP3 players, portable media players, and gaming devices.
Character User Interface (CUI)
- Also known as Command Line Interface (CLI), this interface involves typing commands to perform specific tasks, used in systems like MS-DOS.
Booting
 Booting is the process of starting up a computer until it is ready for use, initiated either by hardware (Start button) or software command.
Booting is the process of starting up a computer until it is ready for use, initiated either by hardware (Start button) or software command.
There are two types of booting:
- Cold Booting: Turning on a computer after it has been completely shut down.
- Warm Booting: Restarting a computer using a combination of keys (Ctrl + Alt + Del) or the Restart button.
Some Important Operating Systems
UNIX:
- Developed in 1969 by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie, UNIX is primarily used on servers rather than workstations and is complex enough that it should only be used by those familiar with the system.
Apple Macintosh (Mac OS):
- Introduced by Steve Jobs in January 1984, initially called "System Software" and later renamed Mac OS.
- Versions include Yosemite, Mavericks, Mountain Lion, Tiger, Panther, and Jaguar.
Linux:
- Objective: The first Linux kernel was released by Linus Torvalds in September 1991.
- An open-source software, Linux operates similarly to UNIX but can be challenging for beginners.
- The kernel is the core of the operating system, facilitating communication between processes and peripheral devices.
Microsoft Windows:
- A GUI-based operating system developed by Microsoft, first introduced in November 1985.
MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System)
- Developed by Microsoft in 1980 for microcomputers, MS-DOS was the first operating system to run on IBM PCs, introduced in 1981. It is a single-user OS that can be loaded into main memory using just a single disk.
Structure of MS-DOS:
- Boot Record: Responsible for loading the operating system into main memory, it is the primary program of MS-DOS.
- Basic Input/Output System (BIOS.sys): Acts as an interface between the hardware and software.
- MS-DOS.sys: Contains program routines and data tables for high-level programs.
- Command.com: Provides a standard set of commands for file management, configuration, and various functions.
Configuration of MS-DOS:
- Config.sys: Adjusts system settings according to commands.
- Autoexec.bat: Executes commands automatically when the system is powered on.

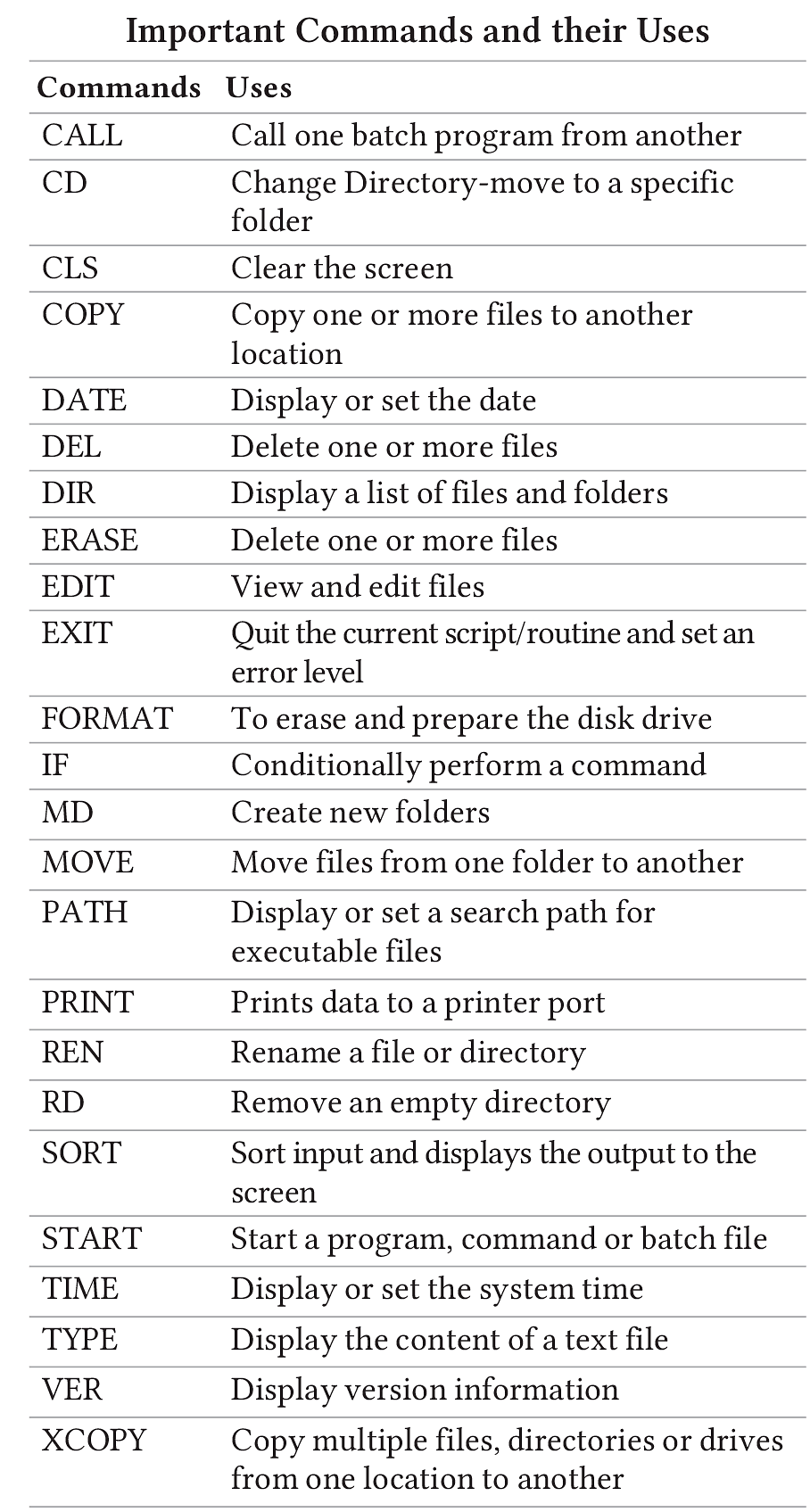
Types of MS-DOS Commands
MS-DOS commands fall into two categories:
Internal Commands
- These commands are loaded into the computer's main memory automatically during the boot process. Examples include DATE, TIME, VER, VOL, DIR, COPY, and CLS.
External Commands
- These commands require external files to be loaded to run. Examples include disk checking, disk comparison, and formatting commands.
Mobile Operating Systems
 Mobile operating systems are designed for smartphones, tablets, and other digital mobile devices. They manage the operation of mobile devices, support wireless communication, and handle various mobile applications with built-in support for multimedia formats.
Mobile operating systems are designed for smartphones, tablets, and other digital mobile devices. They manage the operation of mobile devices, support wireless communication, and handle various mobile applications with built-in support for multimedia formats.
Popular Mobile Operating Systems
Android
- Developed by Google and based on Linux, Android is designed for touch screen devices such as smartphones and tablets.
- It is currently the most widely used mobile OS.
- The latest version is Android 11, released on September 8, 2020.
Symbian
- Developed and sold by Symbian Ltd., Symbian is an open-source mobile OS for smartphones.
- It has been used by major manufacturers like Motorola, Nokia, Samsung, and Sony.
- The latest version, Nokia Belle, was released on October 2, 2012.
iOS
- Developed by Apple Inc., iOS is used in Apple devices like the iPhone, iPod Touch, and iPad.
- The latest version is iOS 14.3, released on December 14, 2020.
BlackBerry
- Known for its high security, BlackBerry OS is used in BlackBerry smartphones and supports WAP 1.2.
- The latest version is BlackBerry OS 7.1.0, released in 2013.
Windows Phone
- Developed by Microsoft and introduced in 2010, Windows Phone is a commercial proprietary OS for smartphones.
- The latest version is Windows Phone 8.1, released on June 2, 2015.
|
48 videos|44 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Operating System - Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL
| 1. What are some functions of an Operating System? |  |
| 2. What are some types of Operating Systems? |  |
| 3. What is the User Interface in an Operating System? |  |
| 4. What are some important Operating Systems? |  |
| 5. What is MS-DOS and what is its significance? |  |




















