Our Constitution and Government | Social Science Olympiad Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is a Constitution? |

|
| Equality and Secularism |

|
| Levels of Government |

|
| Local Government |

|
| Types of Local Government |

|
Introduction
On August 15, 1947, India became independent from British rule after years of struggle. This day is celebrated as Independence Day every year. However, when India became free, it was divided into two countries:
- India and Pakistan.
- Pakistan was made from parts of India in the northwest and east.

Challenges after Independence
- Migration
- Many Hindus who lived in parts of what became Pakistan had to leave their homes and move to India. This is called migration.
- They had left behind their houses, lands, and belongings. The Indian government had the difficult task of helping them find new homes and jobs in India.
- New Rules for Free India
- After gaining freedom, India needed its own set of rules or laws. These laws would guide how the country should be run.
- The responsibility of writing these rules was given to the Constituent Assembly, a group of elected people.
Creating the Constitution of India
The Constituent Assembly worked for about three years to write the rules for the new country. The person in charge of writing these rules was Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, who was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee.
The Constitution (the set of rules) was ready and approved on November 26, 1949. It was put into action from January 26, 1950, and that’s why we celebrate Republic Day on this date every year.
 Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
What is a Constitution?
Every country has a set of rules that guides how the government runs the country. This set of rules is called a Constitution.
India also has its own Constitution, which is the longest-written Constitution in the world. It became active on 26 January 1950, and since then, India became a republic. That's why we celebrate Republic Day on this date every year.
What is a Democratic Government?
- Democracy means that the people of the country choose their leaders through voting.
- In India, all citizens above 18 years old have the right to vote and elect representatives. These representatives make the laws and rules for the country.

No Kings or Queens in India
- India is a Democratic country, which means there are no kings or queens ruling the country. In the past, some countries had kings and queens, and the title would pass from parent to child.
- In India, people have the power to choose who will govern the country. The government is made by the people and works for the welfare of everyone.
[Question: 1739212]
Equality and Secularism
India is a secular country, meaning people from all religions are treated equally.
The government does not favor any one religion and works for the welfare of all citizens, no matter their faith.
In some countries, like Pakistan, only a Muslim can become the President. This is not the case in India, where people of all religions have the same rights.
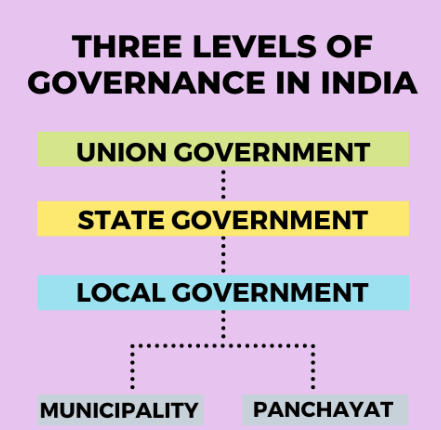
Levels of Government
The government works at three different levels:
- Central (National)
- State (Regional), and
- Local (In our Area).
(i) Central Government:
- The central government is based in New Delhi.
- It is responsible for matters that affect the entire country or multiple states, including defense, foreign affairs, currency, telecommunications, and interstate commerce.

- It consists of the President, the Parliament (comprising the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha), and the Prime Minister, who heads the executive branch.
(ii) State Government:
- India is divided into 28 states and 8 Union territories, each with its own elected government.
- State governments have jurisdiction over matters not exclusively reserved for the central government. This includes police, healthcare, education, agriculture, local infrastructure, and more.
- Each state has its own legislative assembly, headed by a Chief Minister, who is the head of the state government.
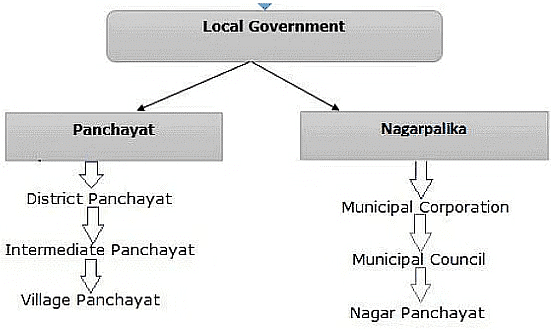
(iii) Local Government:
- Local governments are referred to as Panchayats in rural areas and Municipalities or Municipal Corporations in urban areas.
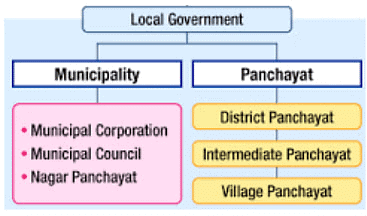
- They are responsible for local governance, including urban planning, local infrastructure development, waste management, water supply, and other essential services.
- Local bodies have elected representatives who serve on local councils. These representatives are elected by the people residing in the respective areas.
Local Government
The government that takes care of our area is chosen by the people living there. In villages, it's called the gram panchayat. In towns and cities, it's either the municipal committee or municipal corporation.
In India, local government means that people who live in a place choose leaders to take care of their area. These leaders manage things like water, roads, and other important services in villages, towns, and cities. They make sure everyone has what they need to live comfortably.
Types of Local Government
Municipal Committees
These are local governing bodies responsible for smaller cities or urban areas.- They handle the administration of various civic amenities and services within their jurisdiction.
- Municipal committees typically oversee functions such as sanitation, water supply, street lighting, public health, and maintenance of roads and parks.
Municipal Corporations
Municipal corporations are governing bodies for larger cities with significant populations, typically exceeding 1 million inhabitants.
- They have broader responsibilities compared to municipal committees due to the larger scale of urban infrastructure and services required.
- Municipal corporations handle a wide range of functions including urban planning, public transportation, education, healthcare, waste management, and more
Election Process
- Members of the municipal committee or corporation are elected by the residents of the city through periodic elections, typically held every five years.
- These elections are conducted democratically, with eligible voters casting their votes to choose their representatives.
- Each geographical area within the city, known as a ward, elects one or more members to represent their interests in the local government body.
|
26 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Our Constitution and Government - Social Science Olympiad Class 4
| 1. What is the significance of a Constitution in a country? |  |
| 2. How does the principle of equality manifest in a Constitution? |  |
| 3. What are the different levels of government established by the Constitution? |  |
| 4. What role does local government play in a democracy? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of local government systems? |  |




















